Related Research Articles

John Bardeen was an American physicist and electrical engineer. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the transistor; and again in 1972 with Leon N. Cooper and John Robert Schrieffer for a fundamental theory of conventional superconductivity known as the BCS theory.
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
The year 1957 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

Leon N. Cooper is an American physicist and Nobel Prize laureate who, with John Bardeen and John Robert Schrieffer, developed the BCS theory of superconductivity. His name is also associated with the Cooper pair and the BCM theory of synaptic plasticity.

Nick Holonyak Jr. was an American engineer and educator. He is noted particularly for his 1962 invention and first demonstration of a semiconductor laser diode that emitted visible light. This device was the forerunner of the first generation of commercial light-emitting diodes (LEDs). He was then working at a General Electric research laboratory near Syracuse, New York. He left General Electric in 1963 and returned to his alma mater, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, where he later became John Bardeen Endowed Chair in Electrical and Computer Engineering and Physics.

Fritz Wolfgang London was a German born physicist and professor at Duke University. His fundamental contributions to the theories of chemical bonding and of intermolecular forces are today considered classic and are discussed in standard textbooks of physical chemistry. With his brother Heinz London, he made a significant contribution to understanding electromagnetic properties of superconductors with the London equations and was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Chemistry on five separate occasions.
Chemical physics is a subdiscipline of chemistry and physics that investigates physicochemical phenomena using techniques from atomic and molecular physics and condensed matter physics; it is the branch of physics that studies chemical processes from the point of view of physics. While at the interface of physics and chemistry, chemical physics is distinct from physical chemistry in that it focuses more on the characteristic elements and theories of physics. Meanwhile, physical chemistry studies the physical nature of chemistry. Nonetheless, the distinction between the two fields is vague, and scientists often practice in both fields during the course of their research.

Anna Igorevna Krylov is the USC Associates Chair in Natural Sciences and Professor of Chemistry at the University of Southern California (USC). Working in the field of theoretical and computational quantum chemistry, she is the inventor of the spin-flip method. Krylov is the president of Q-Chem, Inc. and an elected member of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science, the Academia Europaea, and the American Academy of Sciences and Letters.

Arieh Warshel is an Israeli-American biochemist and biophysicist. He is a pioneer in computational studies on functional properties of biological molecules, Distinguished Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry, and holds the Dana and David Dornsife Chair in Chemistry at the University of Southern California. He received the 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, together with Michael Levitt and Martin Karplus for "the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems".

William Allan Bardeen is an American theoretical physicist who worked at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. He is renowned for his foundational work on the chiral anomaly, the Yang-Mills and gravitational anomalies, the development of quantum chromodynamics and the scheme frequently used in perturbative analysis of experimentally observable processes such as deep inelastic scattering, high energy collisions and flavor changing processes.
The timeline of quantum mechanics is a list of key events in the history of quantum mechanics, quantum field theories and quantum chemistry.

Piotr Piecuch is a Polish-born American physical chemist. He holds the title of university distinguished professor in the department of chemistry at Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, United States. He supervises a group, whose research focuses on theoretical and computational chemistry as well as theoretical and computational physics, particularly on the development and applications of many-body methods for accurate quantum calculations for molecular systems and atomic nuclei, including methods based on coupled cluster theory, mathematical methods of chemistry and physics, and theory of intermolecular forces. His group is also responsible for the development of the coupled-cluster computer codes incorporated in the widely used GAMESS (US) package.
The International Conference on Low Temperature Physics (LT) is an academic conference held every three years near the month of September attracting on average well over a thousand participants from all over the world. The LT conferences are endorsed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) via its Commission on Low Temperature Physics (C5). The mandate of the LT conferences is to promote the exchange of information and views among the members of the international scientific community in the general field of Low Temperature Physics.

Emily A. Carter is the Gerhard R. Andlinger Professor in Energy and the Environment and a professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (MAE), the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment (ACEE), and Applied and Computational Mathematics at Princeton University. She is also a member of the executive management team at the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), serving as Senior Strategic Advisor and Associate Laboratory Director for Applied Materials and Sustainability Sciences.
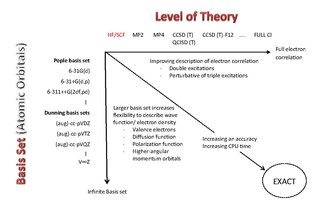
A Pople diagram or Pople's Diagram is a diagram which describes the relationship between various calculation methods in computational chemistry. It was initially introduced in January 1965 by Sir John Pople,, during the Symposium of Atomic and Molecular Quantum Theory in Florida. The Pople Diagram can be either 2-dimensional or 3-dimensional, with the axes representing ab initio methods, basis sets and treatment of relativity. The diagram attempts to balance calculations by giving all aspects of a computation equal weight.

Oleg V. Prezhdo is a Ukrainian–American physical chemist whose research focuses on non-adiabatic molecular dynamics and time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT). His research interests range from fundamental aspects of semi-classical and quantum-classical physics to excitation dynamics in condensed matter and biological systems. His research group focuses on the development of new theoretical models and computational tools aimed at understanding chemical reactivity and energy transfer at a molecular level in complex condensed phase environment. Since 2014, he is a professor of chemistry and of physics & astronomy at the University of Southern California.

Bidyendu Mohan Deb is an Indian theoretical chemist, chemical physicist and a professor at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata (IISER). he is known for his studies in theoretical chemistry and chemical physics. He is an elected fellow of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, The World Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy and the Indian Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1981, for his contributions to chemical sciences.
David Nathan Beratan is an American chemist and physicist, the R.J. Reynolds Professor of Chemistry at Duke University. He has secondary appointments in the departments of Physics and Biochemistry. He is the director of the Center for Synthesizing Quantum Coherence, a NSF Phase I Center for Chemical Innovation.
Samson Ally Jenekhe is the Boeing-Martin Professor of Chemical Engineering and Professor of Chemistry at the University of Washington. Jenekhe was previously a chemical engineer at the University of Rochester where his work focused on semiconducting polymers and quantum wires. He has authored over 300 research articles and 28 patents.
Valerii Vinokur is a condensed matter physicist who works on superconductivity, the physics of vortices, disordered media and glasses, nonequilibrium physics of dissipative systems, quantum phase transitions, quantum thermodynamics, and topological quantum matter. He is a senior scientist and Argonne Distinguished Fellow at Argonne National Laboratory and a senior scientist at the Consortium for Advanced Science and Engineering, Office of Research and National Laboratories, The University of Chicago. He is a Foreign Member of the National Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters and a Fellow of the American Physical Society.
References
- ↑ "Duke Physics". Phy.duke.edu. Archived from the original on 1 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "News & Events – Chemistry at Duke". Chem.duke.edu. 24 February 2003. Archived from the original on 12 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "Related Seminars – News & Events – Chemistry at Duke". Chem.duke.edu. Archived from the original on 12 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "News & Events – Chemistry at Duke". Chem.duke.edu. 7 April 2005. Archived from the original on 12 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "Duke Physics". Phy.duke.edu. 28 March 2006. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "News & Events – Chemistry at Duke". Chem.duke.edu. 27 February 2007. Archived from the original on 12 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "Duke Physics". Phy.duke.edu. 25 March 2008. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 June 2010. Retrieved 10 September 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Duke Physics". Phy.duke.edu. 6 April 2010. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "News & Events – Chemistry at Duke". Chem.duke.edu. 14 April 2011. Archived from the original on 12 March 2012. Retrieved 19 February 2012.
- ↑ "News & Events – Chemistry at Duke". Chem.duke.edu. 14 March 2012. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ↑ "Duke Events Calendar". calendar.duke.edu. 24 April 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ↑ "Duke Events Calendar". calendar.duke.edu. 16 April 2014. Retrieved 16 April 2014.