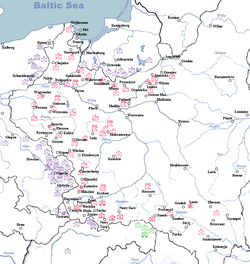
| | Karpaty Army (Armia Karpaty)
Kazimierz Fabrycy
2nd and 3rd Mountain Bdes, 11th Inf.Div, 24th Inf.Div, 38th Inf.Div |
| | Kraków Army (Armia Kraków)
Antoni Szylling
6th, 7th, 21st Mountain, 22nd Mountain, 23rd, 55th Infantry Divisions, 10th Mot., Kraków Cav.Bde., 1st Mountain |
| | Łódź Army (Armia Łódź)
Juliusz Rómmel, Wiktor Thommée
2nd Legions, 10th, 28th, 30th Infantry Divisions, Wołyńska and Kresowa Cavalry Brigades |
| | Modlin Army (Armia Modlin)
Emil Krukowicz-Przedrzymirski
8th and 20th Infantry Divisions, Mazowiecka and Nowogródzka Cavalry Brigades, Warsaw BON |
| | Pomorze Army (Armia Pomorze)
Władysław Bortnowski
4th, 9th, 15th, 16th and 27th Infantry Divisions, Pomorska Cavalry Brigade, Pomorze and Chełm National Defence Bdes, Wisła Independent Unit |
| | Poznań Army (Armia Poznań)
Tadeusz Kutrzeba
14th, 17th, 25th and 26th Inf.Div., Podolska and Wielkopolska Cav.Bdes, Poznań and Kalisz National Defence Bdes |
| | Prusy Army (Armia Prusy)
Stefan Dąb-Biernacki
3rd Legions, 12th, 13th, 19th, 29th and 36th Inf.Div, Wileńska Cavalry Brigade |
| | Lublin Army (Armia Lublin)
Tadeusz Piskor
39th Inf.Div., Motorised Bde, Sandomierz Group, Komorowski's Cavalry Group |
| | Małopolska Army (Armia Małopolska)
Kazimierz Fabrycy
See:Karpaty Army above |
| | Warszawa Army (Armia Warszawa)
Juliusz Rómmel, Walerian Czuma, Wiktor Thommée
|
| | Polish Army in France (Wojsko Polskie we Francji)
Władysław Sikorski
1st Grenadier, 2nd Rifle, 10th Armoured Brigade Bde |
| | I Corps (I Korpus Polski)
Stanisław Maczek
1st Armoured Division, 1st Para Brigade |
| | II Corps (II Korpus Polski)
Władysław Anders
3rd and 5th Infantry Divisions, 2nd Armoured Division |
| | First Army (1 Armia Wojska Polskiego)
Zygmunt Berling
1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 6th Infantry Divisions, Armoured Bde, Cavalry Bde |
| | Second Army (2 Armia Wojska Polskiego)
Karol Świerczewski
5th, 7th, 8th, 9th, 10th Inf. Divs, 16th Armoured Bde |