This is a list of Administrative Heads of Macquarie Island .
The following table outlines the legal status and administrative arrangements covering Macquarie Island.
| Legal status | Term start | Term end | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macquarie Island claimed by the United Kingdom, annexed to the Colony of New South Wales | 11 July 1810 | 2 December 1825 | Frederick Hasselborough discovered the uninhabited island | |
| Responsible self-government established in New South Wales | 1 January 1856 | |||
| Transferred to Tasmania | 17 June 1890 | ongoing | ||
| Leasehold estate | 1902 | 1920 | Government of Tasmania grants lease to Joseph Hatch. | [ citation needed ] |
| Base for the Australasian Antarctic Expedition | 1911 | 1914 | Established under the command of Douglas Mawson | |
| Declared a wildlife sanctuary | 17 May 1933 | [1] [2] | ||
| Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (ANARE) station | 25 March 1948 | |||
| Macquarie Island Nature Reserve | 1978 | |||
| Inscribed onto the UNESCO World Heritage List | 5 December 1997 | ongoing | A site of major geoconservation significance | [3] |
| Macquarie Island Marine Park declared | 27 October 1999 | 31 August 2007 | [1] | |
| Macquarie Island Commonwealth Marine Reserve declared | 31 August 2007 | ongoing |
The following officers were appointed to manage the Macquarie Island Meteorological Station under the Director of the Australian Bureau of Meteorology.
| No. | Name | Title | Term start | Term end | Time in office | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | George Ainsworth | 1911 | 1913 | 1–2 years | |||
| 2 | Harold Power | 1913 | 1914 | 0–1 years | |||
| 3 | Arthur Tulloch | 1914 | 1915 | 0–1 years | Closure of meteorological station |

The French Southern and Antarctic Lands is an Overseas Territory of France. It consists of:

Protected areas of Australia include Commonwealth and off-shore protected areas managed by the Australian government, as well as protected areas within each of the six states of Australia and two self-governing territories, the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory, which are managed by the eight state and territory governments.
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. It conducts and supports collaborative research programs with other Australian and international organisations, such as the Bureau of Meteorology and Geoscience Australia, as well as administering and maintaining a presence in Australian Antarctic and sub-Antarctic territories.

Casey Station, commonly called Casey, is one of three permanent stations and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Casey lies on the northern side of the Bailey Peninsula overlooking Vincennes Bay on the Budd Coast of Wilkes Land in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Casey is 3,880 kilometres (2,410 mi) due south of Perth, Western Australia.

The Mawson Station, commonly called Mawson, is one of three permanent bases and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Mawson lies in Holme Bay in Mac. Robertson Land, East Antarctica in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Established in 1954, Mawson is Australia's oldest Antarctic station and the oldest continuously inhabited Antarctic station south of the Antarctic Circle.

Macquarie Island is an island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, about halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica. Regionally part of Oceania and politically a part of Tasmania, Australia, since 1900, it became a Tasmanian State Reserve in 1978 and was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1997.
A dependent territory, dependent area, or dependency is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state, yet remains politically outside the controlling state's integral area.

The Australian Antarctic Territory (AAT) is a part of East Antarctica administered by the Australian Antarctic Division, an agency of the federal Department of Agriculture, Water, and the Environment. The territory's history dates to a claim on Enderby Land made by the United Kingdom in 1841, which was subsequently expanded and eventually transferred to Australia in 1933. It is the largest territory of Antarctica claimed by any nation by area. In 1961, the Antarctic Treaty came into force. Article 4 deals with territorial claims, and although it does not renounce or diminish any pre-existing claims to sovereignty, it also does not prejudice the position of Contracting Parties in their recognition or non-recognition of territorial sovereignty. As a result, only four other countries — New Zealand, the United Kingdom, France, and Norway recognise Australia's claim to sovereignty in Antarctica.
The Australian Department of the Environment was a department of the Government of Australia that existed between September 2013 and July 2016. The department was charged with responsibility for developing and implementing national policy, programs and legislation to protect and conserve Australia's environment and heritage.
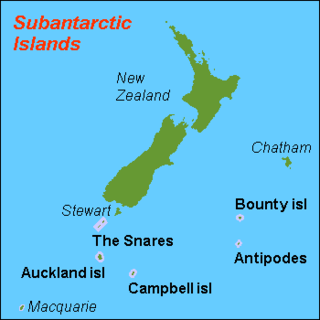
The New Zealand Subantarctic Islands comprise the five southernmost groups of the New Zealand outlying islands. They are collectively designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Mawson's Huts are the collection of buildings located at Cape Denison, Commonwealth Bay, in the far eastern sector of the Australian Antarctic Territory, some 3000 km south of Hobart. The buildings were erected and occupied by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (AAE) of 1911-1914, led by geologist and explorer Sir Douglas Mawson.
The Department of the Environment and Heritage was an Australian government department that existed between October 1998 and December 2007.
The Bishop and Clerk Islets are a 60-hectare (150-acre) group of islets, lying 33 kilometres (21 mi) south of Macquarie Island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. They are, with Macquarie Island, part of the Australian state of Tasmania. The group consists of Bishop Islet, 24 smaller islets, and various rocks and reefs. Bishop Islet has an area of 3 hectares and is mostly rock with some shallow patches of soil. Its highest elevation is 45 metres (148 ft).

The Macquarie Island Station is a permanent Australian subantarctic research base on Macquarie Island, commonly called Macca, situated in the Southern Ocean and located approximately halfway between mainland Australia and Antarctica, managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). The station lies at the base of Wireless Hill, between two bays on the isthmus at the northern end of the island.

The Judge and Clerk Islets are small islands, with a total land and reef area of no more than 20 hectares, lying 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) north of Macquarie Island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. They are, with Macquarie Island, part of Tasmania, Australia. They are in the Macquarie Island Nature Reserve and were inscribed in 1997 on the UNESCO World Heritage Area, and form a Special Management Area within the nature reserve. They are very infrequently visited and are free of introduced animals and plants.

Wireless Hill is a steep-sided hill with a summit plateau that takes up most of the North Head promontory at the northern end of Australia’s subantarctic Macquarie Island, lying in the Southern Ocean about halfway between Australia and Antarctica. Its highest point is about 100 m above sea level and it is joined to the main body of the island by a low and narrow isthmus that is occasionally wave-washed in heavy storms. Macquarie Island Station, operated by the Australian Antarctic Division and the only permanently populated place on the island, lies at the northern end of the isthmus at the foot of Wireless Hill. The hill is so named because it was the site of an early wireless telegraphy relay station, part of the first radio link to Antarctica.
The Department of the Environment and Energy (DEE) was an Australian government department in existence between 2016 and 2020.
The Macquarie Island Marine Park is an Australian marine park near Macquarie Island in the southwest Pacific. The marine park covers an area of 162,000 km2 (63,000 sq mi) and is assigned IUCN category IV. It is the largest of the 14 parks managed under the South-east Marine Parks Network.

The Australian Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE) is an Australian Government department which commenced operation on 1 February 2020. It represents Australia's national interests in agriculture, water and the environment.