The History of Slovakia, dates back to the findings of ancient human artifacts. This article shows the history of the country from prehistory to the present day.
The Slovaks are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
Gömör was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. In the 19th century, and in the beginning of the 20th century, it was united with the Kis-Hont County to form Gömör-Kishont County. Its territory is located in southern Slovakia and northern Hungary. Today names Gömör/Gemer are only an informal designation of the corresponding territory without administrative role.

Spiš is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland. Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one of the 21 official tourism regions of Slovakia. The region is not an administrative division in its own right, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary,.

Since 1949, Slovakia has been divided into a number of kraje. Their number, borders and functions have been changed several times. There are eight regions of Slovakia and they correspond to the EU's NUTS 3 level of local administrative units. Each kraj consists of okresy. There are 79 districts.
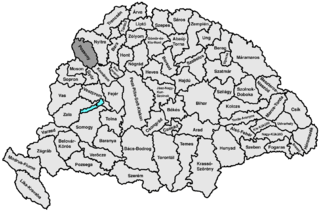
Pozsony county was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now mostly part of Slovakia, while a small area belongs to Hungary. In 1969, the three villages that remained in Hungary were combined to form Dunasziget.

Nyitra County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory lay in what is now western Slovakia.

Carpathian Germans are a group of ethnic Germans. The term was coined by the historian Raimund Friedrich Kaindl (1866–1930), originally generally referring to the German-speaking population of the area around the Carpathian Mountains: the Cisleithanian (Austrian) crown lands of Galicia and Bukovina, as well as the Hungarian half of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy, and the northwestern (Maramuresch) region of Romania. Since the First World War, only the Germans of Slovakia and those of Carpathian Ruthenia in Ukraine have commonly been called Carpathian Germans.
A county is the name of a type of administrative unit in Hungary.
Okres refers to administrative entities in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. It is similar to Landkreis in Germany or "okrug" in other Slavic-speaking countries.

Gömör-Kishont was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its capital was Rimaszombat. Most of its territory is now part of Slovakia, while a smaller part belongs to Hungary.

The Bratislava Region is one of the administrative regions of Slovakia. Its capital is Bratislava. The region was first established in 1923 and its present borders exist from 1996. It is the smallest of the eight regions of Slovakia as well as the most urbanized, most developed and most productive by GDP per capita.

Upper Hungary is the usual English translation of Felvidék, the Hungarian term for the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been called Felső-Magyarország.

Pećinci is a town and municipality located in the Srem District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The village has a population of 2,571 (2011), while Pećinci municipality has 19,675 inhabitants.

Transdanubia is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
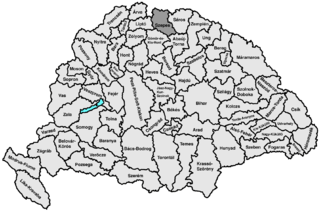
Szepes was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary, called Scepusium before the late 19th century. Its territory today lies in northeastern Slovakia, with a very small area in southeastern Poland. For the current region, see Spiš.
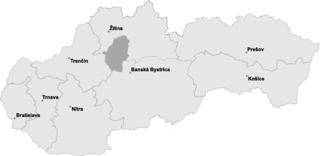
Turiec is a region in central Slovakia, one of the 21 official tourism regions. The region is not an administrative division today, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was the Turóc County in the Kingdom of Hungary.

Slovaks in Hungary are the fourth largest minority in Hungary, after Romas, Germans and Romanians. According to the Microcensus in 2016, 29,794 Slovaks live in the country. The number of people who can speak the Slovak language is 56,107, but this also includes ethnic Hungarians from Slovakia. According to the estimates of minority organisations, the number of people with Slovak ancestry might be as high as 100,000-110,000. Hence, the estimated population of Slovaks in Hungary ranges from 0.18% to 1.1% of the total population, depending on the criteria.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














