Ghana is a country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea, just a few degrees north of the equator.

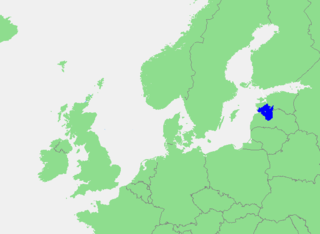
Latvia lies on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea on the level northwestern part of the rising East European platform, between Estonia and Lithuania. About 98% of the country lies under 200 m (656 ft) elevation. With the exception of the coastal plains, the ice age divided Latvia into three main regions: the morainic Western and Eastern uplands and the Middle lowlands. Latvia holds over 12,000 rivers, only 17 of which are longer than 100 km (60 mi), and over 3,000 small lakes, most of which are eutrophic. The major rivers include the Daugava, the Lielupe, the Gauja, the Venta and the Salaca. Woodlands cover around 52% of the country. Other than peat, dolomite, and limestone, natural resources are scarce. Latvia has 531 km (330 mi) of sandy coastline, and the ports of Liepāja and Ventspils provide important warm-water harbors for the Baltic coast.

Lithuania is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. The most populous of the Baltic states, Lithuania has 262 km (163 mi) of coastline consisting of the continental coast and the "Curonian Spit" coast. Lithuania's major warm-water port of Klaipėda (Memel) lies at the narrow mouth of Curonian Lagoon, a shallow lagoon extending south to Kaliningrad and separated from the Baltic sea by Curonian Spit, where Kuršių Nerija National Park was established for its remarkable sand dunes.

Courland, is one of the historical and cultural regions in western Latvia. The largest city is Liepāja, the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke.

The Neman, Nemunas, Nyoman, Niemen or Memel, is a major Eastern European river. It rises in Belarus and flows through Lithuania before draining into the Curonian Lagoon, and then into the Baltic Sea at Rusnė Island. It begins at the confluence of two smaller tributaries, about 15 kilometers (9 mi) southwest of the town of Uzda in central Belarus, and about 55 km (34 mi) southwest of Minsk. In its lower reaches it forms the border between Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast. It also, very briefly, forms part of the Belarus–Lithuania border. The largest river in Lithuania, and the third-largest in Belarus, the Neman is navigable for most of its 900 km (560 mi) length.
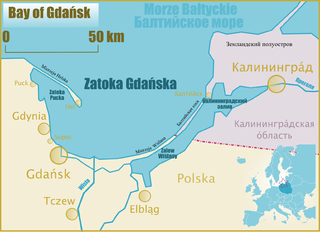
Gdansk Bay or the Bay of Gdansk Polish: Zatoka Gdańska; Kashubian: Gduńskô Hôwinga; Russian: Гданьская бухта, Gdan'skaja bukhta, and German: Danziger Bucht) is a southeastern bay of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the adjacent port city of Gdańsk in Poland and is sometimes referred to as the Gulf of Gdańsk.
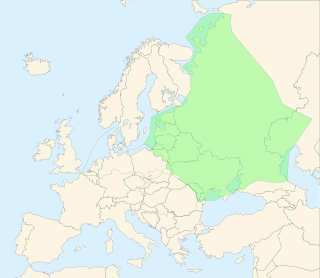
The East European Plain is a vast interior plain extending east of the North/Central European Plain, and comprising several plateaus stretching roughly from 25 degrees longitude eastward. It includes the westernmost Volhynian-Podolian Upland, the Central Russian Upland, and on the eastern border, encompasses the Volga Upland. The plain includes also a series of major river basins such as the Dnepr Basin, the Oka-Don Lowland, and the Volga Basin. Along the southernmost point of the East European Plain are the Caucasus and Crimean mountain ranges. Together with the North European Plain, and covering the Baltics, Moldova, south-eastern Romania, and its most southern expansion - the Danubian Plain in Northern Bulgaria,, it constitutes the majority of the Great European Plain, the greatest mountain-free part of the European landscape.

Semigallia, also spelled Semigalia, is a historical region of Latvia, sometimes also including a part of Lithuania. It lies in the middle of the southern part of Latvia.

Nemunėlis is a river in northern Lithuania and southern Latvia. It originates 6 km south of Rokiškis. It is 191 kilometres long before its confluence with the Mūša, near Bauska, forming the Lielupe.

Dubysa, at 131 km, is the 15th longest river solely in Lithuania. It originates just a few kilometers from Lake Rėkyva near Šiauliai city. At first it flows south, but at Lyduvėnai turns southeast and near Ariogala - southwest. Dubysa is a Samogitian river. The first few kilometres of Dybysa are also known as Genupis or Šventupis.

The Švėtė River flows through the Šiauliai and Joniškis districts in the northern part of Lithuania, and the southern part of Latvia. The source of the Švėtė is near Tulominai, about 16 km southeast of Kuršėnai, and the river flows north passing by Žagarė, near the Latvian border. It is a tributary of the Lielupe, joining it 8 km to the northwest of Jelgava. The Lielupe ultimately flows into the Baltic Sea.

The Curonian Lagoon is separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is 1,619 square kilometers (625 sq mi). The Neman River supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of about 100,450 square kilometres in Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast.
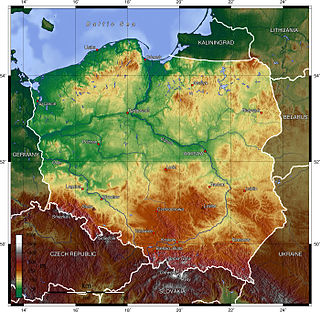
Poland is a country in East-Central Europe with an area of 312,679 square kilometres, and mostly temperate climate. Generally speaking, Poland is an almost unbroken plain reaching from the Baltic Sea in the north, to the Carpathian Mountains in the south. Within that plain, terrain variations run in bands east to west. The Baltic coast has two natural harbors, the larger one in the Gdańsk-Gdynia region, and a smaller one near Szczecin in the far northwest. The northeastern region, also known as the Masurian Lake District with more than 2,000 lakes, is densely wooded and sparsely populated. To the south of the lake district, and across central Poland a vast region of plains extends all the way to the Sudetes on the Czech and Slovak borders southwest, and to the Carpathians on the Czech, Slovak and Ukrainian borders southeast. The central lowlands had been formed by glacial erosion in the Pleistocene ice age. The neighboring countries are Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania and the Russian exclave of Kaliningrad to the northeast.