Related Research Articles
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by WWF, the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". So, for example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.
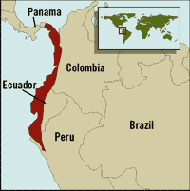
Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena is a biodiversity hotspot, which includes the tropical moist forests and tropical dry forests of the Pacific coast of South America and the Galapagos Islands. The region extends from easternmost Panama to the lower Magdalena Valley of Colombia, and along the Pacific coast of Colombia and Ecuador to the northwestern corner of Peru. Formerly called the Chocó-Darién-Western Ecuador Hotspot, it has been expanded to include several new areas, notably the Magdalena Valley in northern Colombia. It is bounded on the east by the Andes Mountains. The Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena Hotspot is 1,500 km long and encircles 274,597 km². Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena is near the Pacific Ocean. The factors that threaten Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena are farming encroachment, deforestation, illegal crops, and population growth. Whereas the Panamanian and Colombian portion of the hotspot are relatively intact, approximately 98% of native forest in coastal Ecuador has been cleared, rendering it the most threatened tropical forest in the world. The hotspot includes a wide variety of habitats, ranging from mangroves, beaches, rocky shorelines, and coastal wilderness to some of the world's wettest rain forests in the Colombian Chocó. The hotspot includes a number of ecoregions:

The Talamancan montane forests ecoregion, in the tropical moist broadleaf forest biome, are in montane Costa Rica and Panama in Central America.
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Costa Rica:

The Isthmian–Atlantic moist forests (NT0129) are a Central American tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion located on the lowland slopes on the caribbean sea side of Nicaragua and Costa Rica and the Gulf and Pacific Ocean sides of Panama. The forest species are a mix of North American and South American, as this region only became a land bridge in the past 3 million years.

The Chocó–Darién moist forests (NT0115) is an ecoregion in the west of Colombia and east of Panama. The region has extremely high rainfall, and the forests hold great biodiversity. The northern and southern parts of the ecoregion have been considerably modified for ranching and farming, and there are threats from logging for paper pulp, uncontrolled gold mining, coca growing and industrialisation, but the central part of the ecoregion is relatively intact.

The Eastern Panamanian montane forests (NT0122) is an ecoregion in the east of Panama and the extreme northwest of Colombia. It contains diverse flora and fauna, with considerable endemism. The ecoregion is largely intact due to its inaccessibility, although the opening of an extension of the Pan-American Highway has introduced threats from human activity.

The South American Pacific mangroves, or Panama Bight mangroves, is an ecoregion along the Pacific coast of Panama, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru.

The Isthmian–Pacific moist forests ecoregion covers the lowland tropical evergreen forests on the Pacific side of the central mountains of southern Costa Rica and western Panama. As the meeting zone between North and South American floral communities, the area is one of very high biodiversity. Much of the rainforest has, however, been cleared for subsistence agriculture and cattle grazing.

The Bocas del Toro-San Bastimentos Island-San Blas mangroves ecoregion covers the mangrove habitats along the Caribbean Sea coast of Costa Rica and across the northern coast of Panama. An offshore reef and barrier islands of the region help protect the mangroves from destructive waves. The ecoregion has a high number of endangered and threatened species, including the loggerhead sea turtle, green sea turtle, and hawk's bill sea turtle.

The Moist Pacific Coast mangroves ecoregion covers a series of disconnected mangrove sites along the Pacific Ocean coast of Costa Rica and Panama. These sites occur mostly on coastal flatlands around lagoons, particularly where rivers from the inland mountains reach the sea, bringing fresh water to the coastal forests. The area is in a transition zone from the drier coastline to the north; rainfall in this ecoregions is over 2,000 mm/year, and reaches over 3,600 mm/year at the southern end.
References
- ↑ "Chocó-Darién moist forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Eastern Panamanian montane forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Isthmian-Atlantic moist forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Isthmian-Pacific moist forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Talamancan montane forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Panamanian dry forests". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Bocas del Toro-San Bastimentos Island-San Blas mangroves". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Gulf of Panama mangroves". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Moist Pacific Coast mangroves". World Wildlife Fund. Retrieved 2013-09-24.
- ↑ "Chiriqui". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 2013-09-24.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Isthmus Caribbean". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 2013-09-24.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Santa Maria". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 2013-09-24.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Chagres". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 2013-09-24.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Rio Tuira". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 2013-09-24.[ permanent dead link ]
- 1 2 3 "Marine Ecoregions (Spalding 2007). [Map by] GEOMAR, University of Seville, Department of Human Geography". Marine ecoregions. marineplan.es. Archived from the original (jpg) on 2017-02-12. Retrieved 2013-09-26.