
This list is for ecoregions with high endemism. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the following ecoregions have the highest percentage of endemic plants.

This list is for ecoregions with high endemism. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the following ecoregions have the highest percentage of endemic plants.
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.

The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.
The Philippine archipelago is one of the world's great reservoirs of biodiversity and endemism. The archipelago includes over 7000 islands, and a total land area of 300,780 km².

The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica.

The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
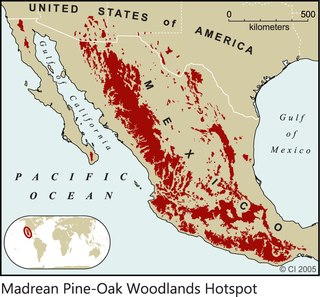
The Madrean pine–oak woodlands are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States. They are a biogeographic region of the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes, located in North America.

The Madrean Sky Islands are enclaves of Madrean pine–oak woodlands, found at higher elevations in a complex of small mountain ranges in southern and southeastern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and northwestern Mexico. The sky islands are surrounded at lower elevations by the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts. The northern west–east perimeter of the sky island region merges into the higher elevation eastern Mogollon Rim and the White Mountains of eastern Arizona.

The Sierra Madre Occidental pine–oak forests are a Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range from the southwest USA region to the western part of Mexico. They are home to a large number of endemic plants and important habitat for wildlife.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine–oak forests is a tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion in Southern Mexico.

The Petén–Veracruz moist forests is an ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest biome found in Belize, Guatemala, and Mexico.

The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt pine–oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt of central Mexico.

The Balsas dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion located in western and central Mexico.

The Luzon tropical pine forests are a tropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Philippines in the western Pacific Ocean. These pine forests are home to a large number of the island's endemic plants and animals.

The Sierra Madre del Sur pine–oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion in the Sierra Madre del Sur mountain range of southern Mexico.

The Luzon rain forest is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Luzon. Luzon is the largest island in the Philippines, and the Luzon rain forest is the most extensive rainforest ecoregion of the country. The ecoregion includes the lowlands of Luzon and neighboring islands below 1000 meters elevation. Very little of the original rainforest remains, and the status of this area is critical/endangered.

The Luzon montane rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The ecoregion is located on several volcanic and non-volcanic mountains of the island. Luzon is the largest and northernmost major island of the Philippines, located in the western Pacific Ocean.

The Southern Pacific dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico.

The Chimalapas montane forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico. It includes the montane tropical forests of the Chimalapas region on the boundary of Chiapas and Oaxaca.

The Sierra Madre de Chiapas moist forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico and southern Guatemala, extending into the northwestern corner of El Salvador.