Related Research Articles

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia.

A disease is an abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders.

Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

An infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agents and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection.

Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer.

Chinchillas are either of two species of crepuscular rodents of the parvorder Caviomorpha. They are slightly larger and more robust than ground squirrels, and are native to the Andes mountains in South America. They live in colonies called "herds" at high elevations of up to 4,270 m (14,000 ft). Historically, chinchillas lived in an area that included parts of Bolivia, Peru, Argentina, and Chile, but today, colonies in the wild are known only in Chile. Along with their relatives, viscachas, they make up the family Chinchillidae. They are also related to the chinchilla rat.

Botrytis cinerea is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold".
A medical condition is a broad term that includes all diseases and disorders.
The Diseases Database is a free website that provides information about the relationships between medical conditions, symptoms, and medications. The database is run by Medical Object Oriented Software Enterprises Ltd, a company based in London.

Waterborne diseases are conditions caused by pathogenic micro-organisms that are transmitted in water. The study of pathogenic microbes is at the forefront of global focus as an urgent topic of research. These diseases can be spread while bathing, washing, drinking water, or by eating food exposed to contaminated water. They are a pressing issue in rural areas amongst developing countries all over the world. While diarrhea and vomiting are the most commonly reported symptoms of waterborne illness, other symptoms can include skin, ear, respiratory, or eye problems. Waterborne diseases are impacted by a country's economy and also impact the economy by being costly to deal with.
A notifiable disease is any disease that is required by law to be reported to government authorities. The collation of information allows the authorities to monitor the disease, and provides early warning of possible outbreaks. In the case of livestock diseases, there may also be the legal requirement to kill the infected livestock upon notification. Many governments have enacted regulations for reporting of both human and animal diseases.

An IUCN Red List Critically Endangered (CR) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of 2021, of the 120,372 species currently tracked by the IUCN, there are 8,404 species that are considered to be Critically Endangered.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to medicine:
Orphanet is a European website providing information about rare diseases as well as corresponding diagnosis, orphan drugs, clinical trials and expert networks

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.

Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.

An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. There are at least 80 types of autoimmune diseases. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms include low grade fever and feeling tired. Often symptoms come and go.
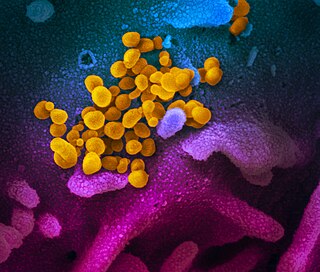
Disease X is a placeholder name that was adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in February 2018 on their shortlist of blueprint priority diseases to represent a hypothetical, unknown pathogen that could cause a future epidemic. The WHO adopted the placeholder name to ensure that their planning was sufficiently flexible to adapt to an unknown pathogen. Director of the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Anthony Fauci stated that the concept of Disease X would encourage WHO projects to focus their research efforts on entire classes of viruses, instead of just individual strains, thus improving WHO capability to respond to unforeseen strains. In 2020, it was speculated, including among some of the WHO's own expert advisors, that COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus strain, met the requirements to be the first Disease X.

Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease has since spread worldwide, leading to an ongoing pandemic.