The following is a list of integrals (antiderivative functions) of irrational functions. For a complete list of integral functions, see lists of integrals. Throughout this article the constant of integration is omitted for brevity.
Assume x2 > a2 (for x2 < a2, see next section):
Assume (ax2 + bx + c) cannot be reduced to the following expression (px + q)2 for some p and q.

The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e, which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2.718281828459. The natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x, logex, or sometimes, if the base e is implicit, simply log x. Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity, giving ln(x), loge(x), or log(x). This is done particularly when the argument to the logarithm is not a single symbol, so as to prevent ambiguity.

In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate; the distance parameter could be any meaningful mono-dimensional measure of the process, such as time between production errors, or length along a roll of fabric in the weaving manufacturing process. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts.

In mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle. Just as the points (cos t, sin t) form a circle with a unit radius, the points (cosh t, sinh t) form the right half of the unit hyperbola. Also, similarly to how the derivatives of sin(t) and cos(t) are cos(t) and –sin(t) respectively, the derivatives of sinh(t) and cosh(t) are cosh(t) and +sinh(t) respectively.
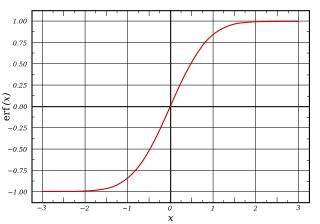
In mathematics, the error function, often denoted by erf, is a function defined as:
Integration is the basic operation in integral calculus. While differentiation has straightforward rules by which the derivative of a complicated function can be found by differentiating its simpler component functions, integration does not, so tables of known integrals are often useful. This page lists some of the most common antiderivatives.
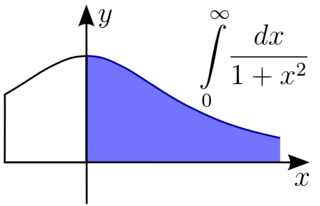
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is an extension of the notion of a definite integral to cases that violate the usual assumptions for that kind of integral. In the context of Riemann integrals, this typically involves unboundedness, either of the set over which the integral is taken or of the integrand, or both. It may also involve bounded but not closed sets or bounded but not continuous functions. While an improper integral is typically written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, it actually represents a limit of a definite integral or a sum of such limits; thus improper integrals are said to converge or diverge. If a regular definite integral is worked out as if it is improper, the same answer will result.

In mathematics, the inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions, under suitably restricted domains. Specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's trigonometric ratios. Inverse trigonometric functions are widely used in engineering, navigation, physics, and geometry.
In mathematics, a quadratic integral is an integral of the form

In mathematics, the inverse hyperbolic functions are inverses of the hyperbolic functions, analogous to the inverse circular functions. There are six in common use: inverse hyperbolic sine, inverse hyperbolic cosine, inverse hyperbolic tangent, inverse hyperbolic cosecant, inverse hyperbolic secant, and inverse hyperbolic cotangent. They are commonly denoted by the symbols for the hyperbolic functions, prefixed with arc- or ar-.

In mathematics, the natural logarithm of 2 is the unique real number argument such that the exponential function equals two. It appears regularly in various formulas and is also given by the alternating harmonic series. The decimal value of the natural logarithm of 2 truncated at 30 decimal places is given by:
Euler substitution is a method for evaluating integrals of the form
In geometry, the mean line segment length is the average length of a line segment connecting two points chosen uniformly at random in a given shape. In other words, it is the expected Euclidean distance between two random points, where each point in the shape is equally likely to be chosen.