
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than 2,175,000 miles (3,500,000 km) of pipeline in 120 countries of the world. The United States had 65%, Russia had 8%, and Canada had 3%, thus 75% of all pipeline were in these three countries.

TC Energy Corporation is a major North American energy company, based in the TC Energy Tower building in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, that develops and operates energy infrastructure in Canada, the United States, and Mexico. The company operates three core businesses: Natural Gas Pipelines, Liquids Pipelines and Energy.
Gas Transmission Northwest (GTN) is a 1353 mile long natural gas pipeline built in 1961 with a capacity of 2,900 million cubic feet per day. It brings gas from Alberta, Canada, beginning at Kingsgate, British Columbia and passing through Washington and terminates at Malin, Oregon then connecting to California, connecting to the Pacific Gas and Electric system. Prior to being purchased by TransCanada Corporation in 2004, it was named Pacific Gas Transmission. TransCanada subsequently sold 25 percent of its interest in GTN to TC PipeLines, LP, which connects via the Tuscarora Gas Pipeline. GTN's FERC code is 86.

Nord Stream is a set of offshore natural gas pipelines in Europe, running under the Baltic Sea from Russia to Germany. It includes the two Nord Stream 1 pipelines running from Vyborg in north-western Russia near Finland and the two Nord Stream 2 pipelines running from Ust-Luga in north-western Russia near Estonia. Both sets of pipelines run to Lubmin in the north-eastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.

The oil and gas industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream and downstream. The midstream sector involves the transportation, storage, and wholesale marketing of crude or refined petroleum products. Pipelines and other transport systems can be used to move crude oil from production sites to refineries and deliver the various refined products to downstream distributors. Natural gas pipeline networks aggregate gas from natural gas purification plants and deliver it to downstream customers, such as local utilities.
White Stream is a proposed pipeline project to transport natural gas from the Caspian region to Romania and Ukraine with further supplies to Central Europe.

The Russia–Belarus energy dispute began when Russian state-owned gas supplier Gazprom demanded an increase in gas prices paid by Belarus, a country which has been closely allied with Moscow and forms a loose union state with Russia. It escalated on 8 January 2007, when the Russian state-owned pipeline company Transneft stopped pumping oil into the Druzhba pipeline which runs through Belarus because Belarus was siphoning the oil off the pipe without mutual agreement. On 10 January, Transneft resumed oil exports through the pipeline after Belarus ended the tariff that sparked the shutdown, despite differing messages from the parties on the state of negotiations.

Russia's energy policy which is set out in the government's Energy Strategy document, first approved in 2000, which sets out the government's policy to 2020. The Energy Strategy outlines several key priorities: an increase in energy efficiency, reducing the impact on the environment, sustainable development, energy development and technological development, as well as improved effectiveness and competitiveness.

Türkiye Petrolleri Anonim Ortaklığı (TPAO) was founded in 1954 by Law No. 6327 with the responsibility of being involved in hydrocarbon exploration, drilling, production, refinery and marketing activities as Turkey's national company.

Russia supplies a significant volume of fossil fuels to other European countries. In 2021 it was the largest exporter of oil and natural gas to the European Union, and 40% of gas consumed in the EU came from Russia.
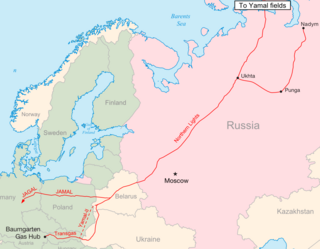
Northern Lights is a natural gas pipeline system in Russia and Belarus. It is one of the main pipelines supplying north-western Russia and is an important transit route for Russian gas to Europe.
Lithuania is a net energy importer. Primary energy use in Lithuania was 98 TWh, or 29 TWh per million people in 2009.

Gas Interconnection Poland–Lithuania (GIPL) is a gas pipeline between Poland and Lithuania. Natural gas will be able to flow in both directions. The project is being implemented by gas transmission system operators AB Amber Grid (Lithuania) and Gaz-System SA (Poland). The construction of the gas pipeline is due to start in October 2019. It is projected that the pipeline will be ready for operation in May 2022. The planned length of the pipeline is 508 km (316 mi). The pipeline will run from Jauniūnai Gas Compressor Station (GCS) in eastern Lithuania to the Hołowczyce GCS station in eastern Poland.
Jauniūnai is a village in the Širvintos District Municipality, Lithuania. It is near the A2 highway and European route E272. It had 185 residents at the time of the 2001 census.

AB Amber Grid is the main natural gas transmission operator in Lithuania. It was established in 2013 by spin-off of gas transmission operations from the gas company Lietuvos Dujos.
Jauniūnai natural gas compression station is a gas compressor station in Lithuania, located in Jauniūnai, Širvintos District Municipality. Capacity at the station is 34.5 MW.
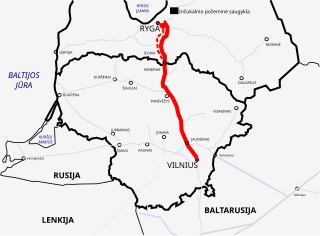
Lithuania–Latvia Interconnection is a natural gas pipeline which connects Lithuania and Latvia.

Minsk–Kaliningrad Interconnection is a natural gas pipeline interconnection between Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, Lithuania and Belarus. Currently it is the only pipeline supplying natural gas to Kaliningrad Oblast.













