Related Research Articles

Addis Ababa is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. In the 2007 census, the city's population was estimated to be 2,739,551 inhabitants. Addis Ababa is a highly developed and important cultural, artistic, financial and administrative center of Ethiopia. It is widely known as one of Africa's major capitals.

Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the East, Kenya to the South, South Sudan to the West, and Sudan to the Northwest. Ethiopia covers a land area of 1,104,300 square kilometres. As of 2024, it is home to around 132 million inhabitants, making it the 10th-most populous country in the world, the 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria, and the most populated landlocked country on Earth. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African and Somali tectonic plates.

The Cleveland Museum of Natural History is a natural history museum located approximately five miles (8 km) east of downtown Cleveland, Ohio in University Circle, a 550-acre concentration of educational, cultural and medical institutions. The museum was established in 1920 by Cyrus S. Eaton to perform research, education and development of collections in the fields of anthropology, archaeology, astronomy, botany, geology, paleontology, wildlife biology, and zoology. The museum traces its roots to the Ark, formed in 1836 on Cleveland's Public Square by William Case, the Academy of Natural Science formed by William Case and Jared Potter Kirtland, and the Kirtland Society of Natural History, founded in 1869 and reinvigorated in 1922 by the trustees of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History.

Wilfred Hudson Osgood was an American zoologist.

Michael Rogers Oldfield Thomas was a British zoologist.
Harold Oldroyd (24 December 1913 – 3 September 1978) was a British entomologist. He specialised in the biology of flies, and wrote many books, especially popular science that helped entomology to reach a broader public. His The Natural History of Flies is considered to be the "fly Bible". Although his speciality was the Diptera, he acknowledged that they are not a popular topic: "Breeding in dung, carrion, sewage and even living flesh, flies are a subject of disgust...not to be discussed in polite society". It was Oldroyd who proposed the idea of hyphenating the names of true flies (Diptera) to distinguish them from other insects with "fly" in their names. Thus, the "house-fly", "crane-fly" and "blow-fly" would be true flies, while the "dragonfly", "scorpion fly" and so on belong to other orders. He also debunked the calculation that a single pair of house-flies, if allowed to reproduce without inhibitions could, within nine months, number 5.6×1012 individuals, enough to cover the Earth to a thickness of 14.3 m (47 ft). Oldroyd calculated that such a layer would only cover Germany, but remarked "that is still a lot of flies".

Yohannes Haile-SelassieAmbaye is an Ethiopian paleoanthropologist. An authority on pre-Homo sapiens hominids, he particularly focuses his attention on the East African Rift and Middle Awash valleys. He was curator of Physical Anthropology at the Cleveland Museum of Natural History from 2002 until 2021, and now is serving as the director of the Arizona State University Institute of Human Origins. Since founding the institute in 1981, he has been the third director after Donald Johanson and William Kimbel.

AL 288-1, commonly known as Lucy or Dinkʼinesh, is a collection of several hundred pieces of fossilized bone comprising 40 percent of the skeleton of a female of the hominin species Australopithecus afarensis. It was discovered in 1974 in Ethiopia, at Hadar, a site in the Awash Valley of the Afar Triangle, by Donald Johanson, a paleoanthropologist of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History.
William Oscar Hall was the U.S. Ambassador to Ethiopia from 1967 to 1971, during the reign of Emperor Haile Selassie I.
The wildlife of Eritrea is composed of its flora and fauna. Eritrea has 96 species of mammals and a rich avifauna of 566 species of birds.

The richness and variety of the wildlife of Ethiopia is dictated by the great diversity of terrain with wide variations in climate, soils, natural vegetation and settlement patterns. Ethiopia contains a vast highland complex of mountains and dissected plateaus divided by the Great Rift Valley, which runs generally southwest to northeast and is surrounded by lowlands, steppes, or semi-desert.
The dwarf free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is found in Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, and Uganda. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.
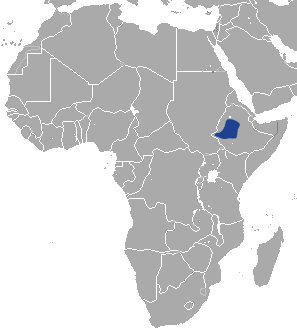
The Ethiopian hare is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It was first described in 1903, by the British mammalogist Oldfield Thomas. The dorsal pelage is brownish buff, and is finely grizzled with black. The ventral pelage is fluffy and white in colour. Endemic to Ethiopia, it is found in the Afromontane Biozone of Ethiopia, and in the borders of the Sudanian Savanna Biozone. It is rated as a least concern species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.

The Thyatirinae, or false owlet moths, are a subfamily of the moth family Drepanidae with about 200 species described. Until recently, most classifications treated this group as a separate family called Thyatiridae.

Alfred Marshall Bailey was an American ornithologist who was associated with the Denver Museum of Natural History in Colorado for most of his working life.
The International Year of Soils, 2015 was declared by the Sixty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly on December 20, 2013, after recognizing December 5 as World Soil Day.

Darrel Richmond Frost is an American herpetologist and systematist. He was previously head curator of herpetology at the American Museum of Natural History, as well as president of both the Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles (1998) and the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists (2006). Four taxa are named in his honor: the toad genus Frostius, the tree frog Dendropsophus frosti, Darrel's Chorus Frog Microhyla darreli, and Frost's arboreal alligator lizard Abronia frosti.

Udubidae is a family of araneomorph spiders, most of whose members were formerly placed in the family Zorocratidae, which is no longer accepted.
The Institute of Ethiopian Studies(IES) was officially established in 1963 to collect information on Ethiopian civilization, its history, cultures, and languages. The Institute includes a research and publication unit, a library, and a museum. It is located at Addis Ababa University, Sidist (6) Kilo campus, which was at the time of the IES's opening, named Haile Selassie I University after the last emperor of Abyssinia.
Rhinocolobus is an extinct genus of monkey closely related to modern colobus monkeys. It lived in eastern Africa during the Plio-Pleistocene, existing as recently as 1.5 million years ago.