
A floppy disk or floppy diskette is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device.
The gigabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The prefix giga means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte is GB.

A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk, is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box.
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperature. The SI unit of specific heat capacity is joule per kelvin per kilogram, J⋅kg−1⋅K−1. For example, the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 K is 4184 joules, so the specific heat capacity of water is 4184 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1.
The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as the environment's maximal load, which in population ecology corresponds to the population equilibrium, when the number of deaths in a population equals the number of births. The effect of carrying capacity on population dynamics is modelled with a logistic function. Carrying capacity is applied to the maximum population an environment can support in ecology, agriculture and fisheries. The term carrying capacity has been applied to a few different processes in the past before finally being applied to population limits in the 1950s. The notion of carrying capacity for humans is covered by the notion of sustainable population.

Light rail transit (LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit characterized by a combination of tram and rapid transit features. While its rolling stock is similar to a traditional tram, it operates at a higher capacity and speed, and often on an exclusive right-of-way. In many cities, light rail transit systems more closely resemble, and are therefore indistinguishable from, traditional underground or at-grade subways and heavy-rail metros.

The Isle of Man TT or Tourist Trophy races are an annual motorcycle racing event run on the Isle of Man in May/June of most years since its inaugural race in 1907. The event is often called one of the most dangerous racing events in the world as many competitors have died.

Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K).

Stadio Giuseppe Meazza, commonly known as San Siro, is a football stadium in the San Siro district of Milan, Italy, which is the home of A.C. Milan and Inter Milan. It has a seating capacity of 80,018, making it one of the largest stadiums in Europe, and the largest in Italy.

Molineux Stadium is a football stadium situated in Wolverhampton, West Midlands, England, has been the home ground of Premier League club Wolverhampton Wanderers since 1889. The first stadium built for use by a Football League club, it was one of the first British grounds to have floodlights installed and hosted some of the earliest European club games in the 1950s.

Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.

Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower. Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. However, when constructed in lowland rainforest areas, where part of the forest is inundated, substantial amounts of greenhouse gases may be emitted.

The City of Manchester Stadium in Manchester, England, is the home of Premier League club Manchester City F.C., with a domestic football capacity of 53,400, making it the 6th-largest football stadium in England and tenth-largest in the United Kingdom.

Legal capacity is a quality denoting either the legal aptitude of a person to have rights and liabilities, or altogether the personhood itself in regard to an entity other than a natural person.

Seating capacity is the number of people who can be seated in a specific space, in terms of both the physical space available, and limitations set by law. Seating capacity can be used in the description of anything ranging from an automobile that seats two to a stadium that seats hundreds of thousands of people. The largest sporting venue in the world, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, has a permanent seating capacity for more than 235,000 people and infield seating that raises capacity to an approximate 400,000.
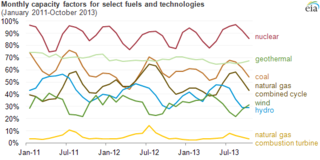
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

A battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell.
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity, maximum effect or Gross Capacity, is the intended full-load sustained output of a facility such as a power station, electric generator, a chemical plant, fuel plant, mine, metal refinery, and many others. Nameplate capacity is the theoretical output registered with authorities for classifying the unit. For intermittent power sources, such as wind and solar, nameplate power is the source's output under ideal conditions, such as maximum usable wind or high sun on a clear summer day.

NTPC Limited, formerly known as National Thermal Power Corporation, is an Indian central Public Sector Undertaking under the ownership of the Ministry of Power, Government of India which is engaged in generation of electricity and allied activities. The headquarters of the PSU are situated at New Delhi. NTPC's core function is the generation and distribution of electricity to State Electricity Boards in India. The body also undertakes consultancy and turnkey project contracts that involve engineering, project management, construction management, and operation and management of power plants.