
Root beer is a sweet North American soft drink traditionally made using the root bark of the sassafras tree Sassafras albidum or the vine of Smilax ornata as the primary flavor. Root beer is typically, but not exclusively, non-alcoholic, caffeine-free, sweet, and carbonated. Like cola, it usually has a thick and foamy head. A common use is to add vanilla ice cream to make a root beer float.

Anise, also called aniseed or rarely anix, is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to the eastern Mediterranean region and Southwest Asia.

Fennel is a flowering plant species in the carrot family. It is a hardy, perennial herb with yellow flowers and feathery leaves. It is indigenous to the shores of the Mediterranean but has become widely naturalized in many parts of the world, especially on dry soils near the sea coast and on riverbanks.

Illicium verum is a medium-sized evergreen tree native to northeast Vietnam and South China. It is a spice that closely resembles anise in flavor and is obtained from the star-shaped pericarps of the fruit of I. verum which are harvested just before ripening. Star anise oil is a highly fragrant oil used in cooking, perfumery, soaps, toothpastes, mouthwashes, and skin creams. Until 2012, when they switched to using genetically modified E. coli, Roche Pharmaceuticals used up to 90% of the world's annual star anise crop to produce oseltamivir (Tamiflu) via shikimic acid.

Austrobaileyales is an order of flowering plants consisting of about 100 species of woody plants growing as trees, shrubs and lianas. The best-known species is Illicium verum, commonly known as star anise. The order belongs to the group of basal angiosperms, the ANA grade, which diverged earlier from the remaining flowering plants. Austrobaileyales is sister to all remaining extant angiosperms outside the ANA grade.

Pastis is an anise-flavoured spirit and apéritif traditionally from France, typically containing less than 100 g/L sugar and 40–45% ABV.
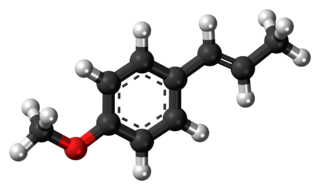
Anethole is an organic compound that is widely used as a flavoring substance. It is a derivative of the aromatic compound allylbenzene and occurs widely in the essential oils of plants. It is in the class of phenylpropanoid organic compounds. It contributes a large component of the odor and flavor of anise and fennel, anise myrtle (Myrtaceae), liquorice (Fabaceae), magnolia blossoms, and star anise (Schisandraceae). Closely related to anethole is its isomer estragole, which is abundant in tarragon (Asteraceae) and basil (Lamiaceae), and has a flavor reminiscent of anise. It is a colorless, fragrant, mildly volatile liquid. Anethole is only slightly soluble in water but exhibits high solubility in ethanol. This trait causes certain anise-flavored liqueurs to become opaque when diluted with water; this is called the ouzo effect.
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower shikimi, from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later.

Mama Juana is a spiced alcoholic beverage made by infusing a mixture of rum, red wine, and honey with tree bark and herbs. The taste is similar to port wine and the color is a deep red. It originates in the Dominican Republic.

Illicium anisatum, with common names Japanese star anise, Aniseed tree, and sacred Anise tree, known in Japanese as shikimi, is an evergreen shrub or small tree closely related to the Chinese star anise. Since it is highly toxic, the fruit is not edible; instead, the dried and powdered leaves are burned as incense in Japan. Its branches and evergreen leaves are considered highly sacred by Japanese Buddhists due to aversion from insects and their ability to remain fresh after pruning.

Illicium is a genus of flowering plants treated as part of the family Schisandraceae, or alternately as the sole genus of the Illiciaceae. It has a disjunct distribution, with most species native to eastern Asia and several in parts of North America, including the southeastern United States, Mexico, and the Caribbean. General common names include star anise and anisetree. The genus name comes from the Latin illicere.

Illiciaceae A.C.Sm. was a family of flowering plants recognized in a number of systems of plant taxonomy. The Illiciaceae is not recognized as a distinct family by the APG III system of plant taxonomy, the most well accepted system in use today.

Illicium floridanum is an evergreen shrub native to the Gulf Coast area of the Southern United States, from Florida to Louisiana.

Illicium parviflorum, commonly known as yellow anisetree, yellow-anise, swamp star-anise, and small anise tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Schisandraceae, or alternately, the Illiciaceae. It is native to Florida in the United States. It historically occurred in Georgia as well, but it has been extirpated from the state.

Merrilactone A is one of the four sesquiterpenes that were newly discovered from the fruit of Illicium merrillianum in 2000. Members of the genus Illicium include Chinese star anise, widely used as a spice for flavouring food and beverages, and also poisonous plants such as Japanese star anise. Chemical studies of Illicium have developed rapidly over the last 20 years, and merrilactone A has been shown to have neurotrophic activity in fetal rat cortical neuron cultures. This has led researchers to believe that Merrilactone A may hold therapeutic potential in the treatment of neuro-degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.

Brazilian tea culture has its origins in the infused beverages, or chás, made by the indigenous cultures of the Amazon and the Río de la Plata basins. It has evolved since the Portuguese colonial period to include imported varieties and tea-drinking customs.

Johan Fredrik Eykman or Johann Frederik Eijkman was a Dutch chemist.

Illicium henryi, also known by the common names Henry anise tree and Chinese anise tree is a species in the genus Illicium in the family Schisandraceae.
















