Related Research Articles
Akan may refer to:

The Kwa languages, often specified as New Kwa, are a proposed but as-yet-undemonstrated family of languages spoken in the south-eastern part of Ivory Coast, across southern Ghana, and in central Togo. The Kwa family belongs to the Niger-Congo phylum. The name was introduced in 1895 by Gottlob Krause and derives from the word for 'people' (Kwa) in many of these languages, as illustrated by Akan names. This branch consists of around 50 different languages spoken by about 25 million people. Some of the largest Kwa languages are Ewe, Akan and Baule.
Asante, also known as Ashanti, Ashante, or Asante Twi, is one of the principal members of the Akan dialect continuum. It is one of the three mutually intelligible dialects of Akan which are collectively known as Twi, the others being Bono and Akuapem. There are over 3.8 million speakers of the Asante language, mainly concentrated in Ghana and southeastern Cote D'Ivoire, and especially in and around the Ashanti Region of Ghana.
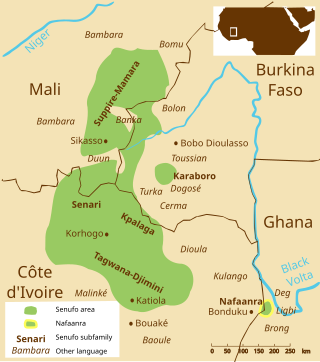
The Nafana are a Senufo people living in the central north-west of Ghana and the north-east of Côte d'Ivoire, in the area east of Bondoukou. They number about 45, 000 and they speak Nafaanra, a Senufo language. They are surrounded by Gur speakers to the north, the isolated Mande speaking Ligbi people to the east, and the Akan speaking Abron to the south.
Akan is a group of several closely related languages within the wider Central Tano languages. These languages are the principal native languages of the Akan people of Ghana, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana's population can speak an Akan language as a first or second language, and about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. There are populations of polyglots in Ghana who speak an Akan language as a third language. They are also spoken in parts of Côte d'Ivoire.
Sampa is a town in the Bono Region of Ghana, on the border with Côte d'Ivoire. It is the capital of Jaman North District, and was formerly the site of a slave market. It was also the capital of the Akan State of Gyaaman in the late 15th century. It is the largest border town in Ghana with a population of over 36,000. It is the principal town of the Nafana ethnic group. It is the leading producer of cashews in Ghana.
Bono State was a trading state created by the Bono people, located in what is now southern Ghana. Bonoman was a medieval Akan state that stretched across the modern Ghanaian regions of Bono, Bono East and Ahafo and the Eastern Ivory Coast. It is generally accepted as the origin of the subgroups of the Akan people who migrated out of the state at various times to create new Akan states in search of gold. The gold trade, which started to boom in Bonoman as early as the 14th century, led to the Akan War, as well as increased power and wealth in the region, beginning in the Middle Ages.
The Akan people of Ghana, Côte d'Ivoire and Togo frequently name their children after the day of the week they were born and the order in which they were born. These "day names" have further meanings concerning the soul and character of the person. Middle names have considerably more variety and can refer to their birth order, twin status, or an ancestor's middle name.

Gyaman was a medieval Akan state, located in what is now the Bono region of Ghana and Ivory Coast. According to oral tradition, Gyaman was founded by the Akwamu, Aduana clan, a branch of the Akan, in the late 17th century. The Gyamans then proceeded to conquer the Kulangos, Nafanas, Ligbis, and other ethnic groups of the area.

Bondoukou is a city in northeastern Ivory Coast, 420 km northeast of Abidjan. It is the seat of both Zanzan District and Gontougo Region. It is also a commune and the seat of and a sub-prefecture of Bondoukou Department.
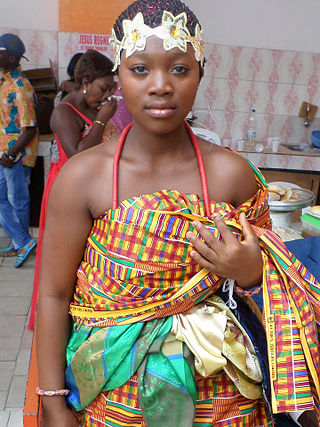
The Bono, also called the Brong and the Abron, are an Akan people of West Africa. Bonos are normally tagged Akan piesie or Akandifo of which Akan is a derivative name. Bono is the genesis and cradle of Akans. Bono is one of the largest ethnic group of Akan and are matrilineal people. Bono people speak the Bono Twi of Akan language. Twi language, thus the dialect of Bono is a derivative of a Bono King Nana Twi. In the late fifteenth century, the Bono people founded the Gyaaman kingdom as extension of Bono state in what is now Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire.

Adinkra are symbols from Ghana that represent concepts or aphorisms. Adinkra are used extensively in fabrics, logos and pottery. They are incorporated into walls and other architectural features. Adinkra symbols appear on some traditional Akan goldweights. The symbols are also carved on stools for domestic and ritual use. Tourism has led to new departures in the use of symbols in items such as T-shirts and jewellery.

The Tchaman or Ébrié are an Akan people living in the Abidjan region of Côte d'Ivoire. Originally called the "Tchaman/Kyama/Gyama" or "Achan", the name Ébrié was given to them by the neighboring Abouré people. In the Abouré language, Ébrié means "bad" and was given to them after a military defeat. In turn, however, they refer to the Abouré as "Koroman," which means "dirty people" in the Tchaman, Kyaman, or Gyaman (Achan) language. The traditional lands of the Tchaman/Kyaman/Gyaman lie along the Ébrié Lagoon, which extends from Grand-Bassam to Assagni and includes the city of Abidjan and its environs. The Tchaman make up approximately 0.7% of the population of Côte d'Ivoire.
The Sasabonsam, or sometimes Asanbosam, is a vampire-like folkloric being from the Akan people. It belongs to the folklore of the Akan of southern Ghana, as well as Côte d'Ivoire, Togo and 18th century Jamaica from enslaved Akan. It is said to have iron teeth, pink skin, long red hair and iron hooks for feet and lives in trees, attacking from above. In the forests of West Africa, there were rules of renewal, and the Sasabonsam would enforce these rules. They take up territory in the trees in the forests, where they live and feed on people that wander into their home. It becomes a territorial aspect for them. While being humanoid, these creatures have bat-like features, including wings which can be nearly 20 feet wide. A good representation can be seen from The British Museum with the Sasabonsam figure they have in their collection. It is carved out of wood and estimated to have been made in 1935.

Ghana–Ivory Coast relations refers to the diplomatic relations between Ghana and Ivory Coast. Both nations are members of the United Nations.

Akan goldweights are weights made of brass used as a measuring system by the Akan people of West Africa, particularly for wei and fair-trade arrangements with one another. The status of a man increased significantly if he owned a complete set of weights. Complete small sets of weights were gifts to newly wedded men. This insured that he would be able to enter the merchant trade respectably and successfully.

Twi is a variety of the Akan language spoken in southern and central Ghana by several million people, mainly of the Akan people, the largest of the seventeen major ethnic groups in Ghana. Twi has about 4.4 million speakers.
Prostitution in Ivory Coast is legal, but associated activities, such as soliciting, pandering or running brothels, are illegal. Sex workers report law enforcement is sparse and corrupt. Police sometimes harass sex workers and demand bribes or sexual favours. Transgender prostitutes are often targeted by police and soldiers and subjected to violence. It was estimated in 2014 that there were 9,211 prostitutes in the country.

Adowa is a dance by the Akan people of Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire. It is a popular traditional dance in Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire and it is performed at cultural ceremonies like festivals, funerals, engagements, and celebrations. The Adowa dance is a sign of expression that allows performers to communicate their emotions and feelings through their hands and feet. There are different hand movements performed for each setting. People communicate positive emotions at weddings or engagements and negative emotions at funerals.
Osram ne nsoromma is one of the Bono Adinkra symbols, which is interpreted to mean "Osram" Moon "Ne" and "Nsoromma" Star. This symbol signifies love, bonding and faithfulness in marriage. The symbol is represented by a half moon with a star slightly hanging within the circumference of the moon. Adinkra are symbols that carry a message or a concept. They are very much used by the Bono people of the Bonoman and the Gyaman, an Akan people of Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire. Osram ne nsoromma symbols are incorporated into walls and other architectural features and quite recently has become common with tattoo designers. The most common ways through which the Adinkra messages are carried out or conveyed is having them printed extensively in fabrics and used in pottery.
References
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(January 2016) |
- ↑ Agyemang, Joseph Kwadwo (2013). "The people the boundary could not divide: The Gyaman of Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire in historical perspective". Journal of African Studies and Development. 5 (7): 177–189.