This is a list of scattering experiments.
Contents
- Specific experiments of historical significance
- Types of experiment
- Optical methods
- Neutron-based methods
- Particle accelerators
This is a list of scattering experiments.

Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics. The word crystallography is derived from the Ancient Greek word κρύσταλλος, with its meaning extending to all solids with some degree of transparency, and γράφειν. In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming that 2014 would be the International Year of Crystallography.

Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions and bosons. There are three generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction.

X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information.

SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a federally funded research and development center in Menlo Park, California, United States. Founded in 1962, the laboratory is now sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administrated by Stanford University. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV.

Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) is an experimental technique that uses elastic neutron scattering at small scattering angles to investigate the structure of various substances at a mesoscopic scale of about 1–100 nm.

Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of the structure of the material. The technique is similar to X-ray diffraction but due to their different scattering properties, neutrons and X-rays provide complementary information: X-Rays are suited for superficial analysis, strong x-rays from synchrotron radiation are suited for shallow depths or thin specimens, while neutrons having high penetration depth are suited for bulk samples.

A synchrotron light source is a source of electromagnetic radiation (EM) usually produced by a storage ring, for scientific and technical purposes. First observed in synchrotrons, synchrotron light is now produced by storage rings and other specialized particle accelerators, typically accelerating electrons. Once the high-energy electron beam has been generated, it is directed into auxiliary components such as bending magnets and insertion devices in storage rings and free electron lasers. These supply the strong magnetic fields perpendicular to the beam that are needed to stimulate the high energy electrons to emit photons.

In accelerator physics, a beamline refers to the trajectory of the beam of particles, including the overall construction of the path segment along a specific path of an accelerator facility. This part is either
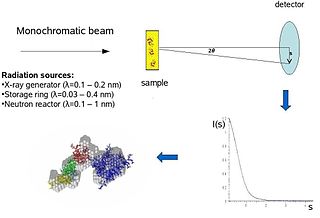
Biological small-angle scattering is a small-angle scattering method for structure analysis of biological materials. Small-angle scattering is used to study the structure of a variety of objects such as solutions of biological macromolecules, nanocomposites, alloys, and synthetic polymers. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) are the two complementary techniques known jointly as small-angle scattering (SAS). SAS is an analogous method to X-ray and neutron diffraction, wide angle X-ray scattering, as well as to static light scattering. In contrast to other X-ray and neutron scattering methods, SAS yields information on the sizes and shapes of both crystalline and non-crystalline particles. When used to study biological materials, which are very often in aqueous solution, the scattering pattern is orientation averaged.

The Spallation Neutron Source (SNS) is an accelerator-based neutron source facility in the U.S. that provides the most intense pulsed neutron beams in the world for scientific research and industrial development. Each year, this facility hosts hundreds of researchers from universities, national laboratories, and industry, who conduct basic and applied research and technology development using neutrons. SNS is part of Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which is managed by UT-Battelle for the United States Department of Energy (DOE). SNS is a DOE Office of Science user facility, and it is open to scientists and researchers from all over the world.
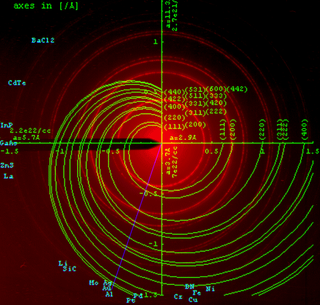
Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray, neutron, or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline samples for structural characterization of materials. An instrument dedicated to performing such powder measurements is called a powder diffractometer.

The Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, a division of SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy. SSRL is a National User Facility which provides synchrotron radiation, a name given to electromagnetic radiation in the x-ray, ultraviolet, visible and infrared realms produced by electrons circulating in a storage ring at nearly the speed of light. The extremely bright light that is produced can be used to investigate various forms of matter ranging from objects of atomic and molecular size to man-made materials with unusual properties. The obtained information and knowledge is of great value to society, with impact in areas such as the environment, future technologies, health, biology, basic research, and education.
High-energy X-rays or HEX-rays are very hard X-rays, with typical energies of 80–1000 keV (1 MeV), about one order of magnitude higher than conventional X-rays used for X-ray crystallography. They are produced at modern synchrotron radiation sources such as the beamlines ID15 and BM18 at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF). The main benefit is the deep penetration into matter which makes them a probe for thick samples in physics and materials science and permits an in-air sample environment and operation. Scattering angles are small and diffraction directed forward allows for simple detector setups.
Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation's Australian Synchrotron is a 3 GeV national synchrotron radiation facility located in Clayton, in the south-eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, which opened in 2007.

Fiber diffraction is a subarea of scattering, an area in which molecular structure is determined from scattering data. In fiber diffraction the scattering pattern does not change, as the sample is rotated about a unique axis. Such uniaxial symmetry is frequent with filaments or fibers consisting of biological or man-made macromolecules. In crystallography fiber symmetry is an aggravation regarding the determination of crystal structure, because reflexions are smeared and may overlap in the fiber diffraction pattern. Materials science considers fiber symmetry a simplification, because almost the complete obtainable structure information is in a single two-dimensional (2D) diffraction pattern exposed on photographic film or on a 2D detector. 2 instead of 3 co-ordinate directions suffice to describe fiber diffraction.

Neutron reflectometry is a neutron diffraction technique for measuring the structure of thin films, similar to the often complementary techniques of X-ray reflectivity and ellipsometry. The technique provides valuable information over a wide variety of scientific and technological applications including chemical aggregation, polymer and surfactant adsorption, structure of thin film magnetic systems, biological membranes, etc.
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a small-angle scattering technique by which nanoscale density differences in a sample can be quantified. This means that it can determine nanoparticle size distributions, resolve the size and shape of (monodisperse) macromolecules, determine pore sizes, characteristic distances of partially ordered materials, and much more. This is achieved by analyzing the elastic scattering behaviour of X-rays when travelling through the material, recording their scattering at small angles. It belongs to the family of small-angle scattering (SAS) techniques along with small-angle neutron scattering, and is typically done using hard X-rays with a wavelength of 0.07 – 0.2 nm. Depending on the angular range in which a clear scattering signal can be recorded, SAXS is capable of delivering structural information of dimensions between 1 and 100 nm, and of repeat distances in partially ordered systems of up to 150 nm. USAXS can resolve even larger dimensions, as the smaller the recorded angle, the larger the object dimensions that are probed.
J-PARC is a high intensity proton accelerator facility. It is a joint project between KEK and JAEA and is located at the Tokai campus of JAEA. J-PARC aims for the frontier in materials and life sciences, and nuclear and particle physics. J-PARC uses high intensity proton beams to create high intensity secondary beams of neutrons, hadrons, and neutrinos.
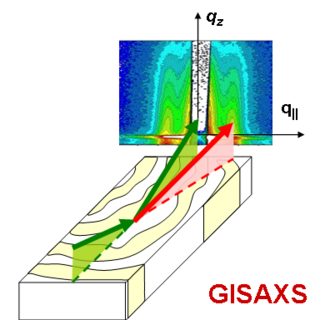
Grazing-incidence small-angle scattering (GISAS) is a scattering technique used to study nanostructured surfaces and thin films. The scattered probe is either photons or neutrons. GISAS combines the accessible length scales of small-angle scattering and the surface sensitivity of grazing incidence diffraction (GID).
Polymer scattering experiments are one of the main scientific methods used in chemistry, physics and other sciences to study the characteristics of polymeric systems: solutions, gels, compounds and more. As in most scattering experiments, it involves subjecting a polymeric sample to incident particles, and studying the characteristics of the scattered particles: angular distribution, intensity polarization and so on. This method is quite simple and straightforward, and does not require special manipulations of the samples which may alter their properties, and hence compromise exact results.