
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. According to 2023 estimates, the population of Kabul was 5 million people. In contemporary times, the city has served as Afghanistan's political, cultural, and economical center, and rapid urbanisation has made Kabul the 75th-largest city in the world and the country's primate city.

Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of 1,010 m (3,310 ft). It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the capital of Kandahar Province and the centre of the larger cultural region called Loy Kandahar. Kandahar is the founding city and spiritual center of the Taliban. Despite the capital of Afghanistan being Kabul, where the government administration is based, Kandahar is the seat of power in Afghanistan as the supreme leader and his spiritual advisers are based there. Kandahar has therefore been called the de facto capital of Afghanistan, though the Taliban maintain Kabul is the capital.

Kabul, situated in the east of the country, is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. The capital of the province is Kabul city, which is Afghanistan's capital and largest city. The population of the Kabul Province is over 5 million people as of 2020, of which over 85 percent live in urban areas. The current governor of the province is Qari Baryal.
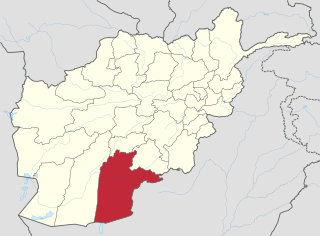
Kandahār is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the southern part of the country, sharing a border with Pakistan, to the south. It is surrounded by Helmand in the west, Uruzgan in the north and Zabul Province in the east. Its capital is the city of Kandahar, Afghanistan's second largest city, which is located on the Arghandab River. The greater region surrounding the province is called Loy Kandahar. The Emir of Afghanistan sends orders to Kabul from Kandahar making it the de facto capital of Afghanistan, although the main government body operates in Kabul. All meetings with the Emir take place in Kandahar, meetings excluding the Emir are in Kabul.
The Mohmand or Momand is a prominent tribe of Pashtun people. They are based primarily in the Mohmand territory, which is located in Nangarhar, Afghanistan and Mohmand Agency, Pakistan.
Dāwaṛ is a Karlani Pashtun tribe mostly inhabiting North Waziristan in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. The Dawaris inhabit the Tochi Valley and speak the Dawari dialect of Pashto.

The Northern Alliance, officially known as the United Islamic National Front for the Salvation of Afghanistan, was a military alliance of groups that operated between late 1996 to 2001 after the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (Taliban) took over Kabul. The United Front was originally assembled by key leaders of the Islamic State of Afghanistan, particularly president Burhanuddin Rabbani and former Defense Minister Ahmad Shah Massoud. Initially it included mostly Tajiks but by 2000, leaders of other ethnic groups had joined the Northern Alliance. This included Karim Khalili, Abdul Rashid Dostum, Abdullah Abdullah, Mohammad Mohaqiq, Abdul Qadir, Asif Mohseni, Amrullah Saleh and others.

Khalilullah Khalili was Afghanistan's foremost 20th century poet as well as a noted historian, university professor, diplomat and royal confidant. He was the last of the great classical Persian poets and among the first to introduce modern Persian poetry and Nimai style to Afghanistan. He had also expertise in Khorasani style and was a follower of Farrukhi Sistani. Almost alone among Afghanistan's poets, he enjoyed a following in Iran where his selected poems have been published. His works have been praised by renowned Iranian literary figures and intellectuals. Many see him as the greatest contemporary poet of the Persian language in Afghanistan. He is also known for his major work "Hero of Khorasan", a controversial biography of Habībullāh Kalakānī, Emir of Afghanistan in 1929.

Ghulam Haidar Khan High School is an all-boys school located in Khair Khana, Kabul, Afghanistan. The school is named after Afghan Prince Ghulam Haidar Khan, son of Emir Dost Mohammad Khan, who fought against the British forces in the July 1839 Battle of Ghazni during the First Anglo-Afghan War. It has about 10,000 students from seven to twelfth grade in four shifts.

Pashto literature refers to literature and poetry in Pashto language. The history of Pashto literature spreads over five thousands years having its roots in the oral tradition of Tappa. However, the first recorded period begins in 7th century with Amir Kror Suri. Later, Pir Roshan (1526–1574), who founded his own Sufi school of thoughts and began to preach his beliefs. He gave Pashto prose and poetry a new and powerful tone with a rich literary legacy. Khair-ul-Bayan, oft-quoted and bitterly criticized thesis, is most probably the first book on Sufism in Pashto literature. Among his disciples are some of the most distinguished poets, writers, scholars and sufis, like Arzani, Mukhlis, Mirza Khan Ansari, Daulat and Wasil, whose poetic works are well preserved. Akhund Darweza (1533–1615), a popular religious leader and scholar gave a powerful counterblast to Bayazid’s movement in the shape of Makhzanul Islam. He and his disciples have enriched the Pashto language and literature by writing several books of prose.

Ahmad Shah, Crown Prince of Afghanistan is the second son of Mohammad Zahir Shah, the former King of Afghanistan. He holds the title of Head of the House of Barakzai since his father's death in July 2007.

The Barakzai dynasty also known as the Muhmmadzai Dynasty ruled modern day Afghanistan from 1823 to 1978 when the monarchy ended de jure under Musahiban Mohammed Zahir Shah and de facto under his cousin Sardar Mohammed Daoud Khan. The Barakzai dynasty was established by Dost Mohammad Khan after the Durrani dynasty of Ahmad Shah Durrani was removed from power.
Akbarpura, or Akbarpūra is a village, which is located roughly 13 miles (21 km) northeast of Peshawar and is part of Pabbi Tehsil of Nowshera District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in Pakistan. Akbarpura is named after the Mughal Emperor Akbar, who camped there before going to Afghanistan. It was known originally as Sapalikhera. Akbarpura is noted for its Sufi shrines - Baba Saib and Nanga Baba.
Akora Khattak or Sarai Akora is a town in Jehangira tehsil of Nowshera District in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. It sits beside the Kabul River, which merges with the Indus River about 15 kilometres downstream. Neighbouring places are Nowshera Cantonment to the west and Jahangira town to the east.
The Centre d'Enseignement Français en Afghanistan (CEFA) consists of two Franco-Afghan schools in the center of Kabul, Afghanistan, together educating around 6,000 Afghan students.

Tourism in Afghanistan is regulated by the Ministry of Information and Culture. There are at least 350 tourism companies operating in Afghanistan. Tourism was at its peak before the 1978 Saur Revolution, which was followed by the decades of war. Between 2013 and 2016, Afghan embassies issued between 15,000 and 20,000 tourist visas annually.

Ustad Mohammad Ibraheem Khwakhuzhi son of Dur Mohammad Khan Baloch was born on 28 February 1920 in Malajat district of Kandahar province, Afghanistan.
His son Gharzai Khwakhuzhi is an active politician in Afghan government and his grandson Gharanai Khwakhuzhi is an Afghan Foreign Service Officer at Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Islamic Republic of Afghanistan.















