
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for in silico analyses of biological queries using mathematical and statistical techniques.
Computer science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. One well known subject classification system for computer science is the ACM Computing Classification System devised by the Association for Computing Machinery.
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017.

Molecular mechanics uses classical mechanics to model molecular systems. The Born–Oppenheimer approximation is assumed valid and the potential energy of all systems is calculated as a function of the nuclear coordinates using force fields. Molecular mechanics can be used to study molecule systems ranging in size and complexity from small to large biological systems or material assemblies with many thousands to millions of atoms.
Molecular modelling encompasses all methods, theoretical and computational, used to model or mimic the behaviour of molecules. The methods are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science to study molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and material assemblies. The simplest calculations can be performed by hand, but inevitably computers are required to perform molecular modelling of any reasonably sized system. The common feature of molecular modelling methods is the atomistic level description of the molecular systems. This may include treating atoms as the smallest individual unit, or explicitly modelling protons and neutrons with its quarks, anti-quarks and gluons and electrons with its photons.
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the NIH, and Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated.
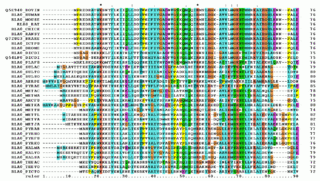
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a linkage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino acids or nucleotides.
InterPro is a database of protein families, domains and functional sites in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences in order to functionally characterise them.
BALL is a C++ class framework and set of algorithms and data structures for molecular modelling and computational structural bioinformatics, a Python interface to this library, and a graphical user interface to BALL, the molecule viewer BALLView.

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein. Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.
Biskit is an open source software package that facilitates research in structural bioinformatics and molecular modelling. Written in Python, it consists of:
WHAT IF is a computer program used in a wide variety of computational macromolecular structure research fields. The software provides a flexible environment to display, manipulate, and analyze small and large molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, and their interactions.
The PDBREPORT database is a database of anomalies and errors found in structures of biological molecules in the Protein Data Bank.
Discovery Studio is a suite of software for simulating small molecule and macromolecule systems. It is developed and distributed by Dassault Systemes BIOVIA.
Scigress, stylized SCiGRESS, is a software suite for molecular modelling, computational chemistry, drug design, and materials science, a successor to Computer Aided Chemistry (CAChe) software.

Macromolecular structure validation is the process of evaluating reliability for 3-dimensional atomic models of large biological molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. These models, which provide 3D coordinates for each atom in the molecule, come from structural biology experiments such as x-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The validation has three aspects: 1) checking on the validity of the thousands to millions of measurements in the experiment; 2) checking how consistent the atomic model is with those experimental data; and 3) checking consistency of the model with known physical and chemical properties.
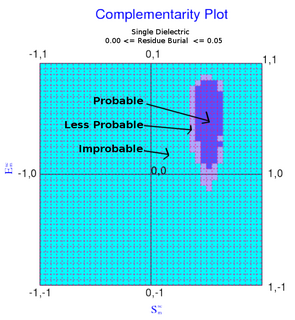
The complementarity plot (CP) is a graphical tool for structural validation of atomic models for both folded globular proteins and protein-protein interfaces. It is based on a probabilistic representation of preferred amino acid side-chain orientation, analogous to the preferred backbone orientation of Ramachandran plots). It can potentially serve to elucidate protein folding as well as binding. The upgraded versions of the software suite is available and maintained in github for both folded globular proteins as well as inter-protein complexes. The software is included in the bioinformatic tool suites OmicTools and Delphi tools.