Related Research Articles

HMS Grampus (N56) was the lead ship of her class of mine-laying submarine of the Royal Navy. She was built at Chatham Dockyard and launched on 25 February 1936. She served in World War II off China before moving to the Mediterranean Sea. She was sunk with all hands by the Regia Marina on 16 June 1940.

The Parthian-class submarine or P class was a class of six submarines built for the Royal Navy in the late 1920s. They were designed as long-range patrol submarines for the Far East. These boats were almost identical to the Odin class, the only difference being a different bow shape.

The Odin-class submarine was a class of nine submarines developed and built for the Royal Navy (RN) in the 1920s. The prototype, Oberon, was followed by two boats originally ordered for the Royal Australian Navy, but transferred to the RN in 1931 because of the poor economic situation in Australia, and six modified boats ordered for the RN. Three modified boats were built for the Chilean Navy as the Capitan O'Brien-class submarines in 1929.

HMS Stygian was a S-class submarine of the British Royal Navy, and the only ship so far to bear the name. The boat is listed as being a member of the fourth group, although she had the external stern torpedo tube fitted as in the third group.

HMS Salmon was a second-batch S-class submarine built during the 1930s for the Royal Navy. Completed in 1935, the boat fought in the Second World War. Salmon is one of twelve boats named in the song "Twelve Little S-Boats".

The Rainbow-class submarine or R class was a quartet of patrol submarines built for the Royal Navy in the early 1930s.

HMS Taku was a British T class submarine built by Cammell Laird, Birkenhead. She was laid down on 18 November 1937 and was commissioned on 3 October 1940.

HMS Saga was a S-class submarine of the third batch built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She survived the war and was sold to Portugal.

HMS Scythian was a S-class submarine of the third batch built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She survived the war and was sold for scrap in 1960.

HMS Scorcher was an S-class submarine of the Royal Navy, and part of the third group built of that class. She was built by Cammell Laird and launched on 18 December 1944. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Scorcher. She was launched by Thomas Beacham, a Foreman Driller employed by Cammell Laird.
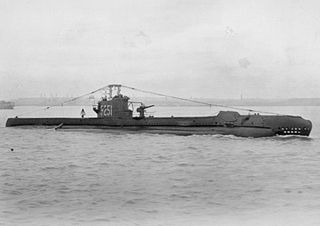
HMS Subtle was a S-class submarine of the third batch built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She survived the war and was scrapped in 1959.

HMS Sea Devil was a S-class submarine of the third batch built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She survived the war and was sold for scrap in 1966.

The second HMS Talisman (N78), and the first to enter service under the name, was a T-class submarine of the Royal Navy. She was laid down by Cammell Laird & Co Limited, Birkenhead and launched on 29 January 1940.

HMS Tetrarch (N77) was a T-class submarine of the Royal Navy. She was laid down by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow and launched in November 1939.

HMS Trusty (N45) was a T-class submarine of the Royal Navy. She was laid down by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow and launched in March 1941.

HMS Token was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P328 at Portsmouth Dockyard, and launched on 19 March 1943. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Token.

HMS Tudor was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P326 at Devonport Dockyard, and launched on 23 September 1942. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Tudor, after the Tudor period or Tudor dynasty.
The Archimede class were a group of four submarines built for the Regia Marina in the early 1930s. The boats fought in the Spanish Civil War and in World War II. In Spanish service, two boats were known as the General Mola class; these were taken out of service in 1959.
The Japanese submarine I-28 was one of 20 Type B cruiser submarines of the B1 sub-class built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1940s.

The Japanese submarine I-31 was one of 20 Type B cruiser submarines of the B1 sub-class built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1940s.
References
- Bishop, C., The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II, Metro Books, 1998, ISBN 1-58663-762-2
- Croix, P., The Encyclopedia of the World’s Warships p. 184, Chartwell Books, 1985, ISBN 0-89009-780-1
- Bagnasco, E. Submarines of World War Two, Naval Institute Press, 1978, ISBN 0-87021-962-6
- Friedman, N., U.S. Submarines Through 1945, Naval Institute Press, 1995, ISBN 1-55750-263-3
- Miller, D., Submarines of the World MBI Publishing, 2002, ISBN 0-7603-1345-8