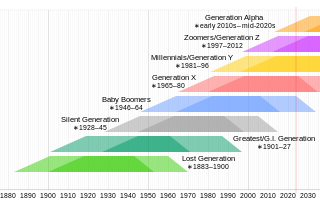
The Lost Generation is the demographic cohort that reached early adulthood during World War I, and preceded the Greatest Generation. The social generation is generally defined as people born from 1883 to 1900, coming of age in either the 1900s or the 1910s. The term is also particularly used to refer to a group of American expatriate writers living in Paris during the 1920s. Gertrude Stein is credited with coining the term, and it was subsequently popularised by Ernest Hemingway, who used it in the epigraph for his 1926 novel The Sun Also Rises: "You are all a lost generation." "Lost" in this context refers to the "disoriented, wandering, directionless" spirit of many of the war's survivors in the early postwar period.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1914.

John Archibald Wheeler was an American theoretical physicist. He was largely responsible for reviving interest in general relativity in the United States after World War II. Wheeler also worked with Niels Bohr to explain the basic principles of nuclear fission. Together with Gregory Breit, Wheeler developed the concept of the Breit–Wheeler process. He is best known for popularizing the term "black hole" for objects with gravitational collapse already predicted during the early 20th century, for inventing the terms "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit", and for hypothesizing the "one-electron universe". Stephen Hawking called Wheeler the "hero of the black hole story".

The American Historical Association (AHA) is the oldest professional association of historians in the United States and the largest such organization in the world. Founded in 1884, AHA works to protect academic freedom, develop professional standards, and support scholarship and innovative teaching. It publishes The American Historical Review four times annually, which features scholarly history-related articles and book reviews.

Gerald Ford's tenure as the 38th president of the United States began on August 9, 1974, upon the resignation of president Richard Nixon, and ended on January 20, 1977. Ford, a Republican from Michigan, had been appointed vice president since December 6, 1973, following the resignation of Spiro Agnew from that office. Ford was the only person to serve as president without being elected to either the presidency or the vice presidency. His presidency ended following his narrow defeat in the 1976 presidential election to Democrat Jimmy Carter, after a period of 895 days in office.

Robert Menzies McAlmon was an American writer, poet, and publisher. In the 1920s, he founded in Paris the publishing house, Contact Editions, where he published writers such as Ernest Hemingway, Gertrude Stein, James Joyce and Ezra Pound.
The Dial was an American magazine published intermittently from 1840 to 1929. In its first form, from 1840 to 1844, it served as the chief publication of the Transcendentalists. From the 1880s to 1919 it was revived as a political review and literary criticism magazine. From 1920 to 1929 it was an influential outlet for modernist literature in English. In January 2023, The Dial was revived once again as a magazine of international writing and reporting.

Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He previously served as the leader of the Republican Party in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1965 to 1973, and as the 40th vice president under President Richard Nixon from 1973 to 1974. Ford succeeded to the presidency when Nixon resigned in 1974, but was defeated for election to a full term in 1976. Ford is the only person to serve as president and vice president without being elected to either office.

Rufus R. Dawes was a military officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He used the middle initial "R" but had no middle name. He was noted for his service in the famed Iron Brigade, particularly during the Battle of Gettysburg. He was a post-war businessman, Congressman, and author, and the father of four nationally known sons, one of whom, Charles G. Dawes, won the Nobel Peace Prize and served as Vice President of the United States, and of two daughters. He was himself a great-grandson of William Dawes, who alerted colonial minutemen of the approach of the British Army prior to the Battles of Lexington and Concord at the outset of the American Revolution, and a maternal great-grandson of the Rev. Manasseh Cutler, who was instrumental in adoption of the Northwest ordinance of 1787, led the formation of the Ohio Company of Associates, and became "Father of Ohio University".

Thomas Ewing Jr. was an attorney, the first chief justice of Kansas and leading free state advocate, Union Army general during the American Civil War, and two-term United States Congressman from Ohio, 1877–1881. He narrowly lost the 1879 campaign for Ohio Governor.

Arthur Ford was an American psychic, spiritualist medium, clairaudient, and founder of the Spiritual Frontiers Fellowship (1955). He gained national attention when he claimed to have contacted the dead son of Bishop James Pike in 1967 on network TV. In 1928 Ford claimed to have contacted the deceased spirits of Houdini's mother and later in 1929 Harry Houdini himself.

William Terry was a nineteenth-century politician, lawyer, teacher, slaveowner, and Confederate soldier from Virginia. The last commander of the famed Stonewall Brigade during the American Civil War also twice won election to the U.S. House of Representatives after the conflict.
The bibliography of the American Civil War comprises books that deal in large part with the American Civil War. There are over 60,000 books on the war, with more appearing each month. Authors James Lincoln Collier and Christopher Collier stated in 2012, "No event in American history has been so thoroughly studied, not merely by historians, but by tens of thousands of other Americans who have made the war their hobby. Perhaps a hundred thousand books have been published about the Civil War."
American literary regionalism, often used interchangeably with the term "local color", is a style or genre of writing in the United States that gained popularity in the mid-to-late 19th century and early 20th century. In this style of writing, which includes both poetry and prose, the setting is particularly important and writers often emphasize specific features, such as dialect, customs, history and landscape, of a particular region, often one that is "rural and/or provincial". Regionalism is influenced by both 19th-century realism and Romanticism, adhering to a fidelity of description in the narrative but also infusing the tale with exotic or unfamiliar customs, objects, and people.
The bibliography of Thomas Jefferson refers to published works about Thomas Jefferson, the primary author of the Declaration of Independence and the third president of the United States. Biographical and political accounts for Jefferson now span across three centuries.

This is a bibliography of U.S. congressional memoirs by former and current U.S. representatives. The United States House of Representatives is one of the two houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.
The American Civil War bibliography comprises books that deal in large part with the American Civil War. There are over 60,000 books on the war, with more appearing each month. There is no complete bibliography to the war; the largest guide to books is over 40 years old and lists over 6,000 titles.
This bibliography of John F. Kennedy is a list of published works about John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States.









