Related Research Articles

A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, supercomputers have existed which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.

The Cray-1 was a supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research. Announced in 1975, the first Cray-1 system was installed at Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1976. Eventually, eighty Cray-1s were sold, making it one of the most successful supercomputers in history. It is perhaps best known for its unique shape, a relatively small C-shaped cabinet with a ring of benches around the outside covering the power supplies and the cooling system.
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world.

The ETA10 is a vector supercomputer designed, manufactured, and marketed by ETA Systems, a spin-off division of Control Data Corporation (CDC). The ETA10 was an evolution of the CDC Cyber 205, which can trace its origins back to the CDC STAR-100, one of the first vector supercomputers to be developed.

The CDC 7600 was designed by Seymour Cray to be the successor to the CDC 6600, extending Control Data's dominance of the supercomputer field into the 1970s. The 7600 ran at 36.4 MHz and had a 65 Kword primary memory using magnetic core and variable-size secondary memory. It was generally about ten times as fast as the CDC 6600 and could deliver about 10 MFLOPS on hand-compiled code, with a peak of 36 MFLOPS. In addition, in benchmark tests in early 1970 it was shown to be slightly faster than its IBM rival, the IBM System/360, Model 195. When the system was released in 1967, it sold for around $5 million in base configurations, and considerably more as options and features were added.

The CDC STAR-100 is a vector supercomputer that was designed, manufactured, and marketed by Control Data Corporation (CDC). It was one of the first machines to use a vector processor to improve performance on appropriate scientific applications. It was also the first supercomputer to use integrated circuits and the first to be equipped with one million words of computer memory.

The Cray-3 was a vector supercomputer, Seymour Cray's designated successor to the Cray-2. The system was one of the first major applications of gallium arsenide (GaAs) semiconductors in computing, using hundreds of custom built ICs packed into a 1 cubic foot (0.028 m3) CPU. The design goal was performance around 16 GFLOPS, about 12 times that of the Cray-2.
The Cray Time Sharing System, also known in the Cray user community as CTSS, was developed as an operating system for the Cray-1 or Cray X-MP line of supercomputers in 1978. CTSS was developed by the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory in conjunction with the Lawrence Livermore Laboratory. CTSS was popular with Cray sites in the United States Department of Energy (DOE), but was used by several other Cray sites, such as the San Diego Supercomputing Center.

Scalable POWERparallel (SP) is a series of supercomputers from IBM. SP systems were part of the IBM RISC System/6000 (RS/6000) family, and were also called the RS/6000 SP. The first model, the SP1, was introduced in February 1993, and new models were introduced throughout the 1990s until the RS/6000 was succeeded by eServer pSeries in October 2000. The SP is a distributed memory system, consisting of multiple RS/6000-based nodes interconnected by an IBM-proprietary switch called the High Performance Switch (HPS). The nodes are clustered using software called PSSP, which is mainly written in Perl.
The Network Livermore Timesharing System is an operating system that was actively developed at Lawrence Livermore Laboratory from 1979 until about 1988, though it continued to run production applications until 1995. An earlier system, the Livermore Time Sharing System had been developed over a decade earlier.

The National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), is a high-performance computing (supercomputer) National User Facility operated by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory for the United States Department of Energy Office of Science. As the mission computing center for the Office of Science, NERSC houses high performance computing and data systems used by 9,000 scientists at national laboratories and universities around the country. Research at NERSC is focused on fundamental and applied research in energy efficiency, storage, and generation; Earth systems science, and understanding of fundamental forces of nature and the universe. The largest research areas are in High Energy Physics, Materials Science, Chemical Sciences, Climate and Environmental Sciences, Nuclear Physics, and Fusion Energy research. NERSC's newest and largest supercomputer is Perlmutter, which debuted in 2021 ranked 5th on the TOP500 list of world's fastest supercomputers.

The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non-distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coincides with the International Supercomputing Conference in June, and the second is presented at the ACM/IEEE Supercomputing Conference in November. The project aims to provide a reliable basis for tracking and detecting trends in high-performance computing and bases rankings on HPL benchmarks, a portable implementation of the high-performance LINPACK benchmark written in Fortran for distributed-memory computers.
LTSS can mean:
Harry Lewis Nelson was an American mathematician and computer programmer. He was a member of the team that won the World Computer Chess Championship in 1983 and 1986, and was a co-discoverer of the 27th Mersenne prime in 1979. He also served as editor of the Journal of Recreational Mathematics for five years. Most of his professional career was spent at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory where he worked with some of the earliest supercomputers. He was particularly noted as one of the world's foremost experts in writing optimized assembly language routines for the Cray-1 and Cray X-MP computers. Nelson had a lifelong interest in puzzles of all types, and founded the MiniMax Game Company, a small venture that helps puzzle inventors to develop and market their products.

The history of supercomputing goes back to the 1960s when a series of computers at Control Data Corporation (CDC) were designed by Seymour Cray to use innovative designs and parallelism to achieve superior computational peak performance. The CDC 6600, released in 1964, is generally considered the first supercomputer. However, some earlier computers were considered supercomputers for their day such as the 1954 IBM NORC in the 1950s, and in the early 1960s, the UNIVAC LARC (1960), the IBM 7030 Stretch (1962), and the Manchester Atlas (1962), all of which were of comparable power.
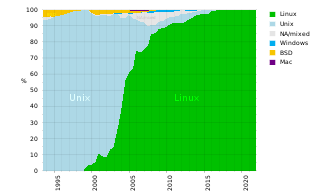
A supercomputer operating system is an operating system intended for supercomputers. Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, as fundamental changes have occurred in supercomputer architecture. While early operating systems were custom tailored to each supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been moving away from in-house operating systems and toward some form of Linux, with it running all the supercomputers on the TOP500 list in November 2017. In 2021, top 10 computers run for instance Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or some variant of it or other Linux distribution e.g. Ubuntu.

Appro was a developer of supercomputing supporting High Performance Computing (HPC) markets focused on medium- to large-scale deployments. Appro was based in Milpitas, California with a computing center in Houston, Texas, and a manufacturing and support subsidiary in South Korea and Japan.
In the high-performance computing environment, burst buffer is a fast intermediate storage layer positioned between the front-end computing processes and the back-end storage systems. It bridges the performance gap between the processing speed of the compute nodes and the Input/output (I/O) bandwidth of the storage systems. Burst buffers are often built from arrays of high-performance storage devices, such as NVRAM and SSD. It typically offers from one to two orders of magnitude higher I/O bandwidth than the back-end storage systems.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise El Capitan, is an upcoming exascale supercomputer, hosted at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, United States and projected to become operational in 2024. It is based on the Cray EX Shasta architecture. When deployed, El Capitan is projected to displace Frontier as the world's fastest supercomputer.
References
- ↑ "The NMFECC Cray Time-Sharing System" (PDF). NMFECC at LLNL. Retrieved 7 March 2023.
- ↑ N. Metropolis; D. H. Sharp; W. J. Worlton; K. R. Ames, eds. (1986). "Supercomputers and Magnetic Fusion Energy". Frontiers of supercomputing. University of California Press. p. 250. ISBN 0-520-05190-4.
- ↑ David E. Williams (2007). Virtualization with Xen. Elsevier. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-59749-167-9.