A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national government.

New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions for local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils, and five are administered by unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities that also perform the functions of regional councils. The Chatham Islands Council is not a region but is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation.

There are 137 local government areas (LGAs) in Western Australia, which comprise 27 cities, 102 shires, and 8 towns that manage their own affairs to the extent permitted by the Local Government Act 1995. The Local Government Act 1995 also makes provision for regional local governments (referred to as "regional councils", established by two or more local governments for a particular purpose.

Perth and Kinross is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and a lieutenancy area. It is bordered by Highland and Aberdeenshire to the north, Angus, Dundee, and Fife to the east, Clackmannanshire to the south, and Stirling and Argyll and Bute to the west.

Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. There are 67 territorial authorities: 13 city councils, 53 district councils and the Chatham Islands Council. District councils serve a combination of rural and urban communities, while city councils administer the larger urban areas. Five territorial authorities also perform the functions of a regional council and thus are unitary authorities. The Chatham Islands Council is a sui generis territorial authority that is similar to a unitary authority.
An alderman is a member of a municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law with similar officials existing in the Netherlands (wethouder) and Belgium (schepen). The term may be titular, denoting a high-ranking member of a borough or county council, a council member chosen by the elected members themselves rather than by popular vote, or a council member elected by voters.
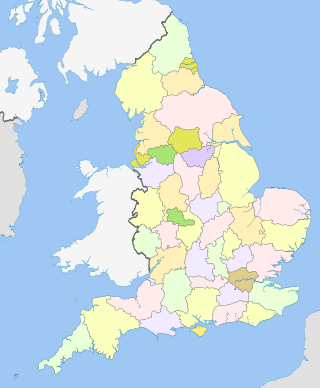
The counties of England are a type of subdivision of England. Counties have been used as administrative areas in England since Anglo-Saxon times. There are three definitions of county in England: the 48 ceremonial counties used for the purposes of lieutenancy; the 84 metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties for local government; and the 39 historic counties which were used for administration until 1974.

Ceremonial counties, formally known as counties for the purposes of the lieutenancies, are areas of England to which lord-lieutenants are appointed. They are one of the two main legal definitions of the counties of England in modern usage, the other being the counties for the purposes of local government legislation. A lord-lieutenant is the monarch's representative in an area. Shrieval counties have the same boundaries and serve a similar purpose, being the areas to which high sheriffs are appointed. High sheriffs are the monarch's judicial representative in an area.
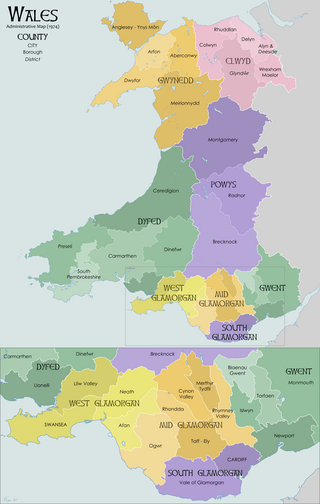
The districts of Wales were a form of local government in Wales used between 1974 and 1996. There were thirty-seven districts, and they were the second tier of local government introduced by the Local Government Act 1972, being subdivisions of the eight counties introduced at the same time. This system of two-tier local government was abolished in 1996 and replaced with the current system of unitary principal areas.
A non-metropolitan county, or colloquially, shire county, is a subdivision of England used for local government.

The Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) lists places deemed to be of cultural heritage significance to the State of Victoria, Australia. It has statutory weight under the Heritage Act 2017. The Minister for Planning is the responsible Minister. Heritage Victoria was established as the State Government listing and permit authority in 1995, replacing the original authority, the Historic Buildings Preservation Council, established in 1974. Listing on the Victorian Heritage Register is separate from listing by a local Council or Shire, known as a Heritage Overlay. Heritage Victoria is currently part of the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning of the Government of Victoria, Australia. Heritage Victoria reports to the Heritage Council who approve recommendations to the Register and hear appeals when a registration is disputed. The council also hears appeals by an owner to a permit issued by Heritage Victoria. As of 2021, there are over 2,400 places and objects listed on the VHR.

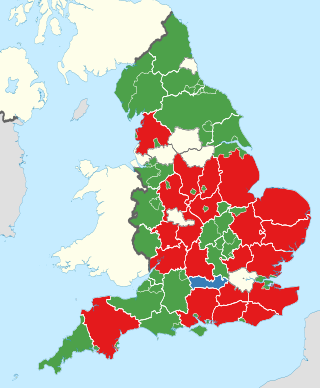
The 1995 United Kingdom local elections took place on Thursday 6 April 1995 in Scotland, and Thursday 4 May 1995 in England and Wales. The Conservative Party lost over 2,000 councillors in the election, while the Labour Party won 48% of the vote, a record high for the party in local elections.

The unitary authorities of England are a type of local authority responsible for all local government services in an area. They combine the functions of a non-metropolitan county council and a non-metropolitan district council, which elsewhere in England provide two tiers of local government.
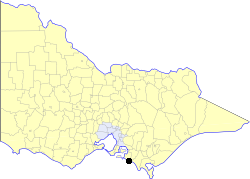
The Borough of Wonthaggi was a local government area about 120 kilometres (75 mi) south-southeast of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia. The borough covered an area of 56.99 square kilometres (22.0 sq mi), and existed from 1911 until 1994. Unlike many local government areas, it was constituted under its own Act of Parliament, rather than the Local Government Act.

Local elections were held in Scotland on 6 April 1995, as part of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994. The elections were held for the 29 new mainland unitary authorities created under the act, which replaced the nine former regions established in 1975. The three island areas were retained from the previous system. These areas did not take part in the 1995 election, having held local elections on 5 May 1994.
Independent politicians contest elections without the support of a political party. They have played a continuous role in the politics of the Republic of Ireland since its independence in 1922.











