
The Schengen Agreement is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the ten member states of the then European Economic Community. It proposed measures intended to gradually abolish border checks at the signatories' common borders, including reduced-speed vehicle checks which allowed vehicles to cross borders without stopping, allowing residents in border areas freedom to cross borders away from fixed checkpoints, and the harmonisation of visa policies.

A border checkpoint is a location on an international border where travelers or goods are inspected and allowed passage through. Authorization often is required to enter a country through its borders. Access-controlled borders often have a limited number of checkpoints where they can be crossed without legal sanctions. Arrangements or treaties may be formed to allow or mandate less restrained crossings. Land border checkpoints can be contrasted with the customs and immigration facilities at seaports, international airports, and other ports of entry.

A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances and products. SDSs are a widely used type of fact sheet used to catalogue information on chemical species including chemical compounds and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. The older MSDS formats could vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements; however, the newer SDS format is internationally standardized.

The special territories of members of the European Economic Area (EEA) are the 32 special territories of EU member states and EFTA member states which, for historical, geographical, or political reasons, enjoy special status within or outside the European Union and the European Free Trade Association.
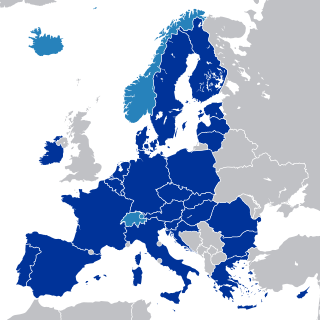
The European single market, also known as the European internal market or the European common market, is the single market comprising mainly the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). With certain exceptions, it also comprises Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods, capital, services, and people, known collectively as the "four freedoms". This is achieved through common rules and standards that all participating states are legally committed to follow.

Switzerland is not a member state of the European Union (EU). It is associated with the Union through a series of bilateral treaties in which Switzerland has adopted various provisions of European Union law in order to participate in the Union's single market, without joining as a member state. Among Switzerland's neighbouring countries, all but one are EU member states.

The visa policy of the Schengen Area is a component within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the European Union. It applies to the Schengen Area and to other EU member states except Ireland. The visa policy allows nationals of certain countries to enter the Schengen Area via air, land or sea without a visa for up to 90 days within any 180-day period. Nationals of certain other countries are required to have a visa to enter and, in some cases, transit through the Schengen area.

The Citizens' Rights Directive 2004/38/EC sets out the conditions for the exercise of the right of free movement for citizens of countries in the European Economic Area (EEA), which includes the member states of the European Union (EU) and the three European Free Trade Association (EFTA) members Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein. Switzerland, which is a member of EFTA but not of the EEA, is not bound by the Directive but rather has a separate multilateral sectoral agreement on free movement with the EU and its member states.

A Norwegian passport is the passport issued to nationals of Norway for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Norwegian citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Norwegian consular officials abroad.

Liechtenstein passports are issued to nationals of Liechtenstein for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Liechtenstein citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Liechtenstein consular officials abroad.

The European Union Customs Union (EUCU), formally known as the Community Customs Union, is a customs union which consists of all the member states of the European Union (EU), Monaco, and the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia. Some detached territories of EU states do not participate in the customs union, usually as a result of their geographic separation. In addition to the EUCU, the EU is in customs unions with Andorra, San Marino and Turkey, through separate bilateral agreements.
The European Union Visa Information System (VIS) is a database containing information, including biometrics, on visa applications by Third Country Nationals requiring a visa to enter the Schengen area.

The Albanian passport is a travel document issued by the Ministry of Interior to Albanian citizens to enable them to travel abroad. They are also used as proof of identity within the country, along with the Albanian ID card.

The Schengen Area encompasses 29 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders. As an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) policy of the European Union (EU), it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg.

The area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) of the European Union (EU) is a policy domain concerning home affairs and migration, justice as well as fundamental rights, developed to address the challenges posed to internal security by collateral effects of the free movement of people and goods in the absence of border controls or customs inspection throughout the Schengen Area, as well as to safeguard adherence to the common European values through ensuring that the fundamental rights of people are respected across the EU.

National identity cards are identity documents issued to citizens of most European Union and European Economic Area (EEA) member states, with the exception of Denmark and Ireland. As a new common identity card model harmonized the various formats in use from 2 August 2021, with older ID cards currently being phased out according to EU Regulation 2019/1157.
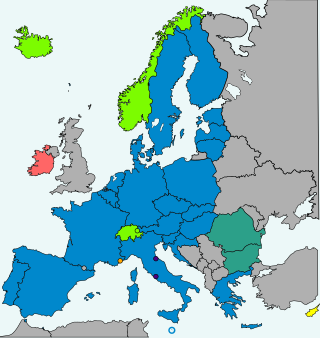
The Schengen acquis is a set of rules and legislation, integrated into European Union law, which regulate the abolition of border controls at the internal borders within the Schengen Area, as well as the strengthening of border controls at the external borders.

Passports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.
The migration and asylum policy of the European Union is within the area of freedom, security and justice, established to develop and harmonise principles and measures used by member countries of the European Union to regulate migration processes and to manage issues concerning asylum and refugee status in the European Union.














