A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, H2), and the formation of H II regions. This is in contrast to other areas of the interstellar medium that contain predominantly ionized gas.

An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds of light years, and density from a few to about a million particles per cubic centimetre. The Orion Nebula, now known to be an H II region, was observed in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc by telescope, the first such object discovered.

The Galactic Center is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately 8 kiloparsecs (26,000 ly) away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula.

The Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy (Sgr dSph), also known as the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy, is an elliptical loop-shaped satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It contains four globular clusters in its main body, with the brightest of them – NGC 6715 (M54) – being known well before the discovery of the galaxy itself in 1994. Sgr dSph is roughly 10,000 light-years in diameter, and is currently about 70,000 light-years from Earth, travelling in a polar orbit at a distance of about 50,000 light-years from the core of the Milky Way. In its looping, spiraling path, it has passed through the plane of the Milky Way several times in the past. In 2018 the Gaia project of the European Space Agency showed that Sgr dSph had caused perturbations in a set of stars near the Milky Way's core, causing unexpected rippling movements of the stars triggered when it moved past the Milky Way between 300 and 900 million years ago.
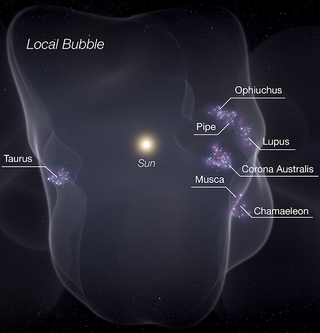
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud, the neighbouring G-Cloud, the Ursa Major moving group and the Hyades. It is estimated to be at least 1000 light years in size, and is defined by its neutral-hydrogen density of about 0.05 atoms/cm3, or approximately one tenth of the average for the ISM in the Milky Way (0.5 atoms/cm3), and one sixth that of the Local Interstellar Cloud (0.3 atoms/cm3).

The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is 3,500 light-years across and approximately 10,000 light-years in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion Bridge, and formerly, the Local Spur and Orion Spur.

Messier 29 or M29, also known as NGC 6913, is a quite small, bright open cluster of stars just south of the central bright star Gamma Cygni of a northerly zone of the sky, Cygnus. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, and can be seen from Earth by using binoculars.

NGC 891 is an edge-on unbarred spiral galaxy about 30 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 6, 1784. The galaxy is a member of the NGC 1023 group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster. It has an H II nucleus.

IC 2118 is an extremely faint reflection nebula believed to be an ancient supernova remnant or gas cloud illuminated by nearby supergiant star Rigel in the constellation of Orion. The nebula lies in the Eridanus Constellation, about 900 light-years from Earth. The nature of the dust particles, reflecting blue light better than red, is a factor in giving the Witch Head its blue color. Radio observations show substantial carbon monoxide emission throughout parts of IC 2118, an indicator of the presence of molecular clouds and star formation in the nebula. In fact candidates for pre-main sequence stars and some classic T-Tauri stars have been found deep within the nebula.

In astronomy, extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumpler. However, its effects had been noted in 1847 by Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and its effect on the colors of stars had been observed by a number of individuals who did not connect it with the general presence of galactic dust. For stars that lie near the plane of the Milky Way and are within a few thousand parsecs of the Earth, extinction in the visual band of frequencies is roughly 1.8 magnitudes per kiloparsec.

The Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), also known as the Local Fluff, is an interstellar cloud roughly 30 light-years (9.2 pc) across, through which the Solar System is moving. This feature overlaps a region around the Sun referred to as the solar neighborhood. It is unknown whether the Sun is embedded in the Local Interstellar Cloud, or is in the region where the Local Interstellar Cloud is interacting with the neighboring G-Cloud. Like the G-Cloud and others, the LIC is part of the Very Local Interstellar Medium which begins where the heliosphere and interplanetary medium end, the furthest that probes have traveled.

Geminga is a gamma ray and x-ray pulsar source thought to be a neutron star approximately 250 parsecs from the Sun in the constellation Gemini.

In astronomy a superbubble or supershell is a cavity which is hundreds of light years across and is populated with hot (106 K) gas atoms, less dense than the surrounding interstellar medium, blown against that medium and carved out by multiple supernovae and stellar winds. The winds, passage and gravity of newly born stars strip superbubbles of any other dust or gas. The Solar System lies near the center of an old superbubble, known as the Local Bubble, whose boundaries can be traced by a sudden rise in dust extinction of exterior stars at distances greater than a few hundred light years.

The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικὸς κύκλος, meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Doust Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies.

The Gould Belt is a local ring of stars in the Milky Way, tilted away from the galactic plane by about 16–20 degrees, first reported by John Herschel and Benjamin Gould in the 19th century. It contains many O- and B-type stars, and many of the nearest star-forming regions of the local Orion Arm, to which the Sun belongs. The relative proximity of these star-forming regions spurred the Gould Belt Survey project to determine what caused them.
The anticenter shell or anticenter superbubble is a region near the anticenter of the Milky Way Galaxy that emits 21 cm radiation. It is located at 06h 27m +15°, or l = 197°, b = +2° in galactic coordinates, near the border of the constellations Gemini and Orion. It is a supershell within our galaxy that is spherical in shape and features jets of gas.

In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space.
Phi2 Lupi, Latinized from φ2 Lupi, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Lupus. With an apparent magnitude of 4.535, it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 6.28 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 520 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.052±0.013 due to interstellar dust. It is a member of the Upper Centaurus–Lupus subgroup of the Scorpius–Centaurus association.

The Radcliffe wave is the nearest coherent gaseous structure in the Milky Way, dotted with a related high concentration of interconnected stellar nurseries. It stretches about 8,800 light years. This structure runs with the trajectory of the Milky Way arms, and lies at its closest at around 400 light-years and at its farthest about 5,000 light-years from the Sun, always within the Local Arm itself, spanning about 40% of its length and on average 20% of its width. Its discovery was announced in January 2020 and its proximity surprised astronomers.