
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals that are transmitted via cables and other communication channels to another telephone which reproduces the sound to the receiving user. The term is derived from Greek: τῆλε and φωνή, together meaning distant voice. A common short form of the term is phone, which came into use early in the telephone's history.

The 5ESS Switching System is a Class 5 telephone electronic switching system developed by Western Electric for the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) and the Bell System in the United States. It came into service in 1982 and the last unit was produced in 2003.
Digital subscriber line is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), the most commonly installed DSL technology, for Internet access.

In telecommunications, a network interface device is a device that serves as the demarcation point between the carrier's local loop and the customer's premises wiring. Outdoor telephone NIDs also provide the subscriber with access to the station wiring and serve as a convenient test point for verification of loop integrity and of the subscriber's inside wiring.

A blue box is an electronic device that produces tones used to generate the in-band signaling tones formerly used within the North American long-distance telephone network to send line status and called number information over voice circuits. This allowed an illicit user, referred to as a "phreaker", to place long-distance calls, without using the network's user facilities, that would be billed to another number or dismissed entirely as an incomplete call. A number of similar "color boxes" were also created to control other aspects of the phone network.

In telephony, the demarcation point is the point at which the public switched telephone network ends and connects with the customer's on-premises wiring. It is the dividing line which determines who is responsible for installation and maintenance of wiring and equipment—customer/subscriber, or telephone company/provider. The demarcation point varies between countries and has changed over time.
In computer networks, a network element is a manageable logical entity uniting one or more physical devices. This allows distributed devices to be managed in a unified way using one management system.

A telephone line or telephone circuit is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or other signaling medium connecting the user's telephone apparatus to the telecommunications network, and usually also implies a single telephone number for billing purposes reserved for that user. Telephone lines are used to deliver landline telephone service and digital subscriber line (DSL) phone cable service to the premises. Telephone overhead lines are connected to the public switched telephone network. The voltage at a subscriber's network interface is typically 48 V between the ring and tip wires, with tip near ground and ring at –48 V.
A built-in self-test (BIST) or built-in test (BIT) is a mechanism that permits a machine to test itself. Engineers design BISTs to meet requirements such as:

Multibus is a computer bus standard used in industrial systems. It was developed by Intel Corporation and was adopted as the IEEE 796 bus.

A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is a device used to connect a computer or router to a telephone line which provides the digital subscriber line (DSL) service for connection to the Internet, which is often called DSL broadband. The modem connects to a single computer or router, through an Ethernet port, USB port, or is installed in a computer PCI slot.
A party line is a local loop telephone circuit that is shared by multiple telephone service subscribers.
The Number One Crossbar Switching System (1XB), was the primary technology for urban telephone exchanges served by the Bell System in the mid-20th century. Its switch fabric used the electromechanical crossbar switch to implement the topology of the panel switching system of the 1920s. The first No. 1 Crossbar was installed in the PResident-2 central office at Troy Avenue in Brooklyn, New York which became operational in February 1938.
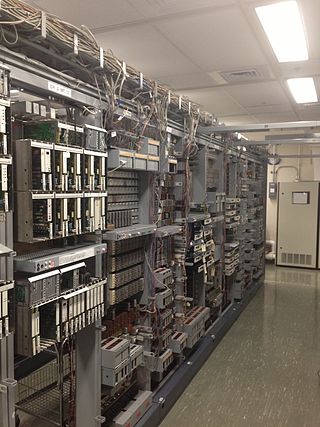
The Number One Electronic Switching System (1ESS) was the first large-scale stored program control (SPC) telephone exchange or electronic switching system in the Bell System. It was manufactured by Western Electric and first placed into service in Succasunna, New Jersey, in May 1965. The switching fabric was composed of a reed relay matrix controlled by wire spring relays which in turn were controlled by a central processing unit (CPU).
The Service Evaluation System (SES) was an operations support system developed by Bell Laboratories and used by telephone companies beginning in the late 1960s. Many local, long distance, and operator circuit-switching systems provided special dedicated circuits to the SES to monitor the quality of customer connections during the call setup process. Calls were selected at random by switching systems and one-way voice connections were established to the SES monitoring center.

A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital systems to establish telephone calls between subscribers.

Telex is a telecommunication service that provides text-based message exchange over the circuits of the public switched telephone network or by private lines. The technology operates on switched station-to-station basis with teleprinter devices at the receiving and sending locations. Telex was a major method of sending written messages electronically between businesses in the post–World War II period. Its usage went into decline as the fax machine grew in popularity in the 1980s.
Execulink Telecom Inc. is a Canadian telecommunications company headquartered in Woodstock, Ontario. Execulink Telecom was founded in 1904 as The Burgessville Telephone Company. After a number of mergers and renamings, Execulink is now one of the largest telecommunications providers in Ontario. Execulink provides telecommunications services including data, internet, television, mobility and advanced voice features. These services are now available to all levels of industry, including 50,000 business, enterprise, government, and residential customers.
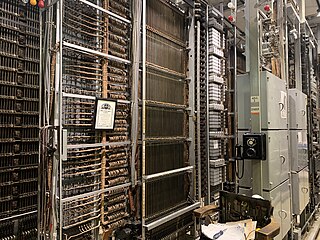
The Panel Machine Switching System is a type of automatic telephone exchange for urban service that was used in the Bell System in the United States for seven decades. The first semi-mechanical types of this design were installed in 1915 in Newark, New Jersey, and the last were retired in the same city in 1983.











