
The Lordship of Baarsdorp is a (former) Dutch Lordship situated in the province of Zeeland, in the Netherlands.

The Lordship of Baarsdorp is a (former) Dutch Lordship situated in the province of Zeeland, in the Netherlands.
The lordship of Baarsdorp, is a Dutch landed estate. Until 1795 a Dutch lordship (Heerlijkheid) was the Dutch version of manorialism, nowadays it's an estate in land with a set of remaining manorial rights. [1]
The lordship of Baarsdorp was founded between 1206 and 1270, the first lords were Lord Petrus de Barsdorpe and his brother, Lord Dankert de Barsdorpe. The de Barsdorpe brothers were members of the Dutch noble family van Borssele, who named themselves after the lordship. [2] The brothers built a castle and a church, which gave the lordship and village of Baarsdorp a more prestigious aura. [3] The lordship of Baarsdorp remained in this family for the next 200 years, until in the fifteenth century the noble family van de Waerde became the owners. From then on the lordships of Baarsdorp and Sinoutskerke were owned by the same persons but never formally merged. [4] A hundred years later the castle was demolished after it was left empty for two decades. In 1846 the lordship of Baarsdorp was owned by 7 people. [5]
Up until today the manorial rights are still being exerted by the van Huykelom van de Pas family, who are the current owners of the lordship.Baarsdorp is one of the very few remaining lordships in the Netherlands with existingrights attached to it. Among those rights are fishing rights, sheep drifting and rights to plant trees etc. on the sides of the roads. M.J. van Huykelom van de Pas also uses the title "Lady of Baarsdorp". [6]
The coat of arms of the lordship of Baarsdorp is mentioned in 1696 in Mattheus Smallegange's “Cronyk van Zeeland” (Chronicle of Zeeland). According to Smallegange, the coat of arms of the lordship of Baarsdorp initially were the coat of arms of a branch of the van Borssele family, and adopted by the lordship after this family died out. [7] Similar coat of arms were later also used by the municipality of Sinoutskerke and Baarsdorp, with permission of the Dutch High Council of Nobility. [8]

Veere is a municipality with a population of 22,000 and a town with a population of 1,500 in the southwestern Netherlands, in the region of Walcheren in the province of Zeeland.

The Hook and Cod wars comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over the title of count of Holland, but some have argued that the underlying reason was because of the power struggle of the bourgeois in the cities against the ruling nobility.

Tuyll is the name of a noble Dutch family, with familial and historical links to England, whose full name is Van Tuyll van Serooskerken. Several knights, members of various courts, literary figures, generals, ambassadors, statesmen and explorers carried the family name.

Ellewoutsdijk is a village in the Dutch province of Zeeland. It is a part of the municipality of Borsele, and lies about 18 km east of Vlissingen.
Sinoutskerke en Baarsdorp is a former municipality in the Dutch province of Zeeland. It existed until 1816, when it was merged with 's-Heer Abtskerke. As its name implies, the municipality It covered two hamlets, Sinoutskerke and Baarsdorp, located west and northwest of 's-Heer Abtskerke.

A heerlijkheid was a landed estate that served as the lowest administrative and judicial unit in rural areas in the Dutch-speaking Low Countries before 1800. It originated as a unit of lordship under the feudal system during the Middle Ages. The English equivalents are manor, seigniory and lordship. The German equivalent is Herrschaft. The heerlijkheid system was the Dutch version of manorialism that prevailed in the Low Countries and was the precursor to the modern municipality system in the Netherlands and Flemish Belgium.

De Graeff is an old Dutch patrician and noble family,

The Free or high Lordship (Fief) of Purmerend and Purmerland and after 1618 Purmerland and Ilpendam was a type of local jurisdiction with many rights.
John of Beaumont was a younger brother of count William III of Holland. He was the lord of Beaumont and count of Soissons by virtue of his marriage.

Count John IV of Nassau-Siegen, German: Johann IV. Graf von Nassau-Siegen, official titles: Graf zu Nassau, Vianden und Diez, Herr zu Breda, was since 1442 Count of Nassau-Siegen, of Vianden and of half Diez, and Lord of Breda and of de Lek. He descended from the Ottonian Line of the House of Nassau.

Wilhem (II) van Citters was a Dutch politician, who served as grand pensionary of Zeeland from 1760 to 1766.

Jhr. Jacob van den Eynde III also known as Jacques van den Eynde, and better known as Jacobus Eyndius, was a Dutch poet, scientist, historian, and captain. His best known work is the Chronici Zelandiae. His motto was Marte prudens pace clemens.

Mattheus Smallegange was a Dutch historian, lawyer, genealogist and translator.

The New Chronicles of Zeeland is a reference work published in 1700 by the historian Mattheus Smallegange.

The Battle of Veere was a small naval battle that took place in late May 1351 during the Hook and Cod wars.
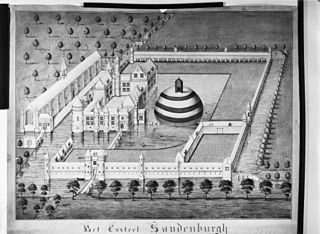
Zandenburg was a famous castle just south of Veere. Nothing remains of it, except some foundations below ground level.

The Burcht of Voorne is a ruinous motte-and-bailey castle in Oostvoorne, Netherlands. It was home to the Lords of Voorne, burgraves of Zeeland.

Sint-Maartensdijk Castle was a castle with a rich history. Except for a part of the moats nothing remains of it.

Ter Hooge Castle is an 18th-century manor in Middelburg. It includes parts of a medieval castle.
Jona Willem te Water (1740–1822) was a professor at Leiden University. He was a man of influence in the Dutch Reformed Church, in many learned societies, in academic theology, and in Dutch historiography.