Model
Lucid uses a demand-driven model for data computation. Each statement can be understood as an equation defining a network of processors and communication lines between them through which data flows. Each variable is an infinite stream of values and every function is a filter or a transformer. Iteration is simulated by 'current' values and 'fby' (read as 'followed by') operator allowing composition of streams.
Lucid is based on an algebra of histories, a history being an infinite sequence of data items. Operationally, a history can be thought of as a record of the changing values of a variable, history operations such as first and next can be understood in ways suggested by their names. Lucid was originally conceived as a disciplined, mathematically pure, single-assignment language, in which verification would be simplified. However, the dataflow interpretation has been an important influence on the direction in which Lucid has evolved.
Details
In Lucid (and other dataflow languages) an expression that contains a variable that has not yet been bound waits until the variable has been bound, before proceeding. An expression like x + y will wait until both x and y are bound before returning with the output of the expression. An important consequence of this is that explicit logic for updating related values is avoided, which results in substantial code reduction, compared to mainstream languages.
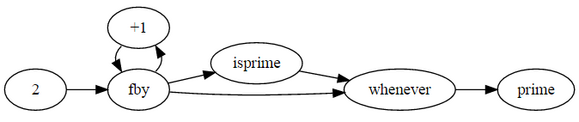
Each variable in Lucid is a stream of values. An expression n = 1 fby n + 1 defines a stream using the operator 'fby' (a mnemonic for "followed by"). fby defines what comes after the previous expression. (In this instance the stream produces 1,2,3,...). The values in a stream can be addressed by these operators (assuming x is the variable being used):
'first x' - fetches the first value in the stream x,
'x' - the current value of the stream,
'next x' - fetches the next value in the stream.
'asa' - an operator that does some thing 'as soon as' the condition given becomes true.
'x upon p' - upon is an operator that repeats the old value of the stream x, and updates to the new values only when the stream p makes a true value available. (It serves to slow down the stream x) i.e.: x upon p is the stream x with new values appearing upon the truth of p.
The computation is carried out by defining filters or transformation functions that act on these time-varying streams of data.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.