
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated.
Defined in the narrowest sense, glycobiology is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, and biology of saccharides that are widely distributed in nature. Sugars or saccharides are essential components of all living things and aspects of the various roles they play in biology are researched in various medical, biochemical and biotechnological fields.
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology, glycosylation usually refers to an enzyme-catalysed reaction, whereas glycation may refer to a non-enzymatic reaction.
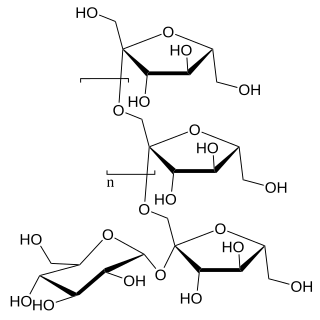
An oligosaccharide is a saccharide polymer containing a small number of monosaccharides. Oligosaccharides can have many functions including cell recognition and cell adhesion.

The United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority is a UK government research organisation responsible for the development of fusion energy. It is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ).
Pharming, a portmanteau of farming and pharmaceutical, refers to the use of genetic engineering to insert genes that code for useful pharmaceuticals into host animals or plants that would otherwise not express those genes, thus creating a genetically modified organism (GMO). Pharming is also known as molecular farming, molecular pharming, or biopharming.

Biocon Limited is an Indian biopharmaceutical company based in Bengaluru, India. It was founded by Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw in 1978. The company manufactures generic active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that are sold in approximately 120 countries, including the United States and Europe. It also manufactures novel biologics as well as biosimilar insulins and antibodies, which are sold in India as branded formulations. Biocon's biosimilar products are also sold in both bulk and formulation forms in several emerging markets.
A biopharmaceutical, also known as a biological medical product, or biologic, is any pharmaceutical drug product manufactured in, extracted from, or semisynthesized from biological sources. Different from totally synthesized pharmaceuticals, they include vaccines, whole blood, blood components, allergenics, somatic cells, gene therapies, tissues, recombinant therapeutic protein, and living medicines used in cell therapy. Biologics can be composed of sugars, proteins, nucleic acids, or complex combinations of these substances, or may be living cells or tissues. They are isolated from living sources—human, animal, plant, fungal, or microbial. They can be used in both human and animal medicine.
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate portion of a glycoconjugate, such as a glycoprotein, glycolipid, or a proteoglycan, even if the carbohydrate is only an oligosaccharide. Glycans usually consist solely of O-glycosidic linkages of monosaccharides. For example, cellulose is a glycan composed of β-1,4-linked D-glucose, and chitin is a glycan composed of β-1,4-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Glycans can be homo- or heteropolymers of monosaccharide residues, and can be linear or branched.
Biomarker discovery is a medical term describing the process by which biomarkers are discovered. Many commonly used blood tests in medicine are biomarkers. There is interest in biomarker discovery on the part of the pharmaceutical industry; blood-test or other biomarkers could serve as intermediate markers of disease in clinical trials, and as possible drug targets.
The pharmaceutical industry in India was valued at an estimated US$42 billion in 2021 and is estimated to reach $130 billion by 2030. India is the world's largest provider of generic medicines by volume, with a 20% share of total global pharmaceutical exports. It is also the largest vaccine supplier in the world by volume, accounting for more than 60% of all vaccines manufactured in the world. Indian pharmaceutical products are exported to various regulated markets including the US, UK, European Union and Canada.

Chi-Huey Wong is a Taiwanese-American biochemist. He is currently the Scripps Family Chair Professor at the Scripps Research Institute. He is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences, as awarded the 2014 Wolf Prize in Chemistry and 2015 RSC Robert Robinson Award. Wong is also the holder of more than 100 patents and publisher of 700 more scholarly academic research papers under his name.
Anne Dell is an Australian biochemist specialising in the study of glycomics and the carbohydrate structures that modify proteins. Anne's work could be used to figure out how pathogens such as HIV are able to evade termination by the immune system which could be applied toward understanding how this occurs in fetuses. Her research has also led to the development of higher sensitivity mass spectroscopy techniques which have allowed for the better studying of the structure of carbohydrates. Anne also established GlycoTRIC at Imperial College London, a research center that allows for glycobiology to be better understood in biomedical applications. She is currently Professor of Carbohydrate Biochemistry and Head of the Department of Life Sciences at Imperial College London. Dell's other contributions to the study of Glycobiology are the additions she has made to the textbook "Essentials of Glycobiology" Dell was appointed Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) in the 2009 Birthday Honours.
China has seen double-digit growth in its biotechnology industry and has gone from being one of the slowest to one of the fastest nations in the adoption of new biotechnologies. The biotech sector is seen in China and internationally as a core area of national scientific and economic development. The main national biotech body in the country is the China National Center for Biotechnology Development. The CNCBD is an organization established on November 3, 1983, under the Ministry of Science and Technology with the approval of the State Council. CNCBD is the sole national center to coordinate and implement the national S&T program in Biotechnology and Health.
Glycopeptides are peptides that contain carbohydrate moieties (glycans) covalently attached to the side chains of the amino acid residues that constitute the peptide.
N-linked glycosylation is the attachment of an oligosaccharide, a carbohydrate consisting of several sugar molecules, sometimes also referred to as glycan, to a nitrogen atom, in a process called N-glycosylation, studied in biochemistry. The resulting protein is called an N-linked glycan, or simply an N-glycan.
Reading Scientific Services Ltd. (RSSL) is a British company providing scientific analysis, consultancy, product development and training to the global food, drink, healthcare, pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical and consumer goods sectors. It has been inspected by regulatory authorities including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and the United Kingdom Accreditation Service.
Synageva BioPharma Corp. was a publicly listed biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Lexington, Massachusetts dedicated to discovering, developing and delivering medicines for patients with rare diseases and high unmet medical needs. The company had manufacturing and laboratory locations in Lexington and Holden, Massachusetts, Bogart and Athens Georgia, as well as offices in a variety of locations around the world.
Translational glycobiology or applied glycobiology is the branch of glycobiology and glycochemistry that focuses on developing new pharmaceuticals through glycomics and glycoengineering. Although research in this field presents many difficulties, translational glycobiology presents applications with therapeutic glycoconjugates, with treating various bone diseases, and developing therapeutic cancer vaccines and other targeted therapies. Some mechanisms of action include using the glycan for drug targeting, engineering protein glycosylation for better efficacy, and glycans as drugs themselves.

Sphere Fluidics is a Cambridge(UK)-based Life Sciences R&D company that specializes in biopharmaceutical discovery and development, cell therapy engineering, bioproduction and synthetic biology, analysis and isolation. The company is reported to own 25 patented products that include instruments, biochips, and specialist chemicals.






