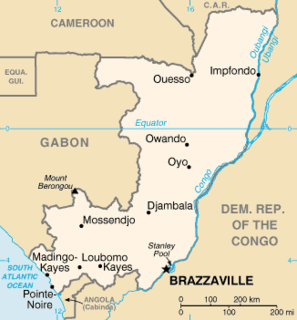
The Republic of the Congo is located in the western part of northern Africa. on the Equator, it is eby the Angola exclave of Cabinda to the south (231 km), the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north and west(1,229 km), the Central African Republic (487 km) and Cameroon (494 km) to the north and Gabon to the west (2,567 km). Congo has a 169 km long Atlantic coast with several important ports. The Republic of the Congo covers an area of 342,000 km², of which 341,500 km² is land while 500 km² is water. Congo claims 200 nautical miles (370 km) of territorial sea.

The Congo River, formerly known as the Zaire River during the dictatorship of Mobutu Sese Seko, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge volume, following only the Amazon. It is also the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths in excess of 220 m (720 ft). The Congo-Lualaba-Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,920 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,120 mi).

Matadi is the chief sea port of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the capital of the Kongo Central province, adjacent to the border with Angola. It has a population of 245,862 (2004). Matadi is situated on the left bank of the Congo River, 148 km (92 mi) from the mouth and 8 km (5.0 mi) below the last navigable point before the rapids that make the river impassable for a long stretch upriver. It was founded by Sir Henry Morton Stanley in 1879.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Kinshasa, Zaire, DR Congo, DRC, the DROC, or simply the Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It was formerly called Zaire (1971–1997). It is, by area, the largest country in sub-Saharan Africa, the second-largest in all of Africa, and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of over 101 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world, as well as the fourth-most-populous in Africa, and the 15th-most-populous country in the world. Since 2015, the Eastern DR Congo has been the scene of an ongoing military conflict in Kivu.

The Kasai River is a tributary of the Congo River, located in Central Africa. The river begins in central Angola and flows to the east until it reaches the border between Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), where it turns north and serves as the border until it flows into the DRC. From Ilebo, between the confluences with Lulua river and Sankuru river, the Kasai river turns to a westerly direction. The lower stretch of the river from the confluence with Fimi river, is known as the Kwa(h) River, before it joins the Congo at Kwamouth northeast of Kinshasa. The Kasai basin consists mainly of equatorial rainforest areas, which provide an agricultural land in a region noted for its infertile, sandy soil. It is a tributary of Congo river and diamonds are found in this river. Around 60% of diamonds in Belgium go from Kasai river for cutting and shaping.

The Second Congo War began in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in August 1998, little more than a year after the First Congo War, and involved some of the same issues. The war officially ended in July 2003, when the Transitional Government of the Democratic Republic of the Congo took power. Although a peace agreement was signed in 2002, violence has continued in many regions of the country, especially in the east. Hostilities have continued since the ongoing Lord's Resistance Army insurgency, and the Kivu and Ituri conflicts.

Kananga, formerly known as Luluabourg or Luluaburg, is the capital city of the Kasai-Central Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and was the capital of the former Kasaï-Occidental Province. In 2015 the city had an estimated population of 1,271,704

The Congolian rainforests are a broad belt of lowland tropical moist broadleaf forests which extend across the basin of the Congo River and its tributaries in Central Africa.

Rail transport in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is provided by the National Railway Company of the Congo, the ONATRA and the Office of the Uele Railways.
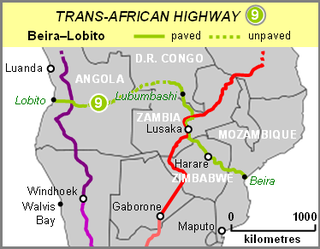
The Beira–Lobito Highway is Trans-African Highway 9 in the transcontinental road network being developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA), the African Development Bank (ADB), and the African Union. The route has a length of 3,523 km (2,189 mi) crossing Angola, the most southerly part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and central Mozambique.

Angola is located on the western Atlantic Coast of Central Africa between Namibia and the Republic of the Congo. It also is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia to the east. The country consists of a sparsely watered and somewhat sterile coastal plain extending inland for a distance varying from 50 to 160 km. Slightly inland and parallel to the coast is a belt of hills and mountains and behind those a large plateau. The total land size is 1,246,700 km2 (481,400 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 518,433 km2 (200,168 sq mi).

Noqui is a town and municipality in Zaire Province in Angola. It is on the Congo River, just across the border from the city of Matadi in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The municipality had a population of 23,880 in 2014.

The Cuango or Kwango is a transboundary river of Angola and Democratic Republic of Congo. It is the largest left bank tributary of the Kasai River in the Congo River basin. It flows through Malanje town in Angola. The Kwango River basin has large resources of diamonds in the Chitamba-Lulo Kimberlite Cluster in Lunda Norte Province, discovered in the main river channel and on flats and terraces in its flood plains.

Kwango is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kwango, Kwilu, and Mai-Ndombe provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Bandundu province. Kwango was formed from the Kwango district whose town of Kenge was elevated to capital city of the new province.
Prostitution in Angola is illegal and prevalent since the 1990s. Prostitution increased further at the end of the civil war in 2001. Prohibition is not consistently enforced. Many women engage in prostitution due to poverty. It was estimated in 2013 that there were about 33,00 sex workers in the country. Many Namibian women enter the country illegally, often via the border municipality of Curoca, and travel to towns such as Ondjiva, Lubango and Luanda to work as prostitutes.

Anthene lusones, the large red-spot ciliate blue, is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sudan, Uganda and Tanzania. The habitat consists of forests.

The Angola–Democratic Republic of the Congo border is 2,646 km in length and consists of two non-contiguous sections: a 225 km section along the border with Angola's province of Cabinda, running from the Atlantic Ocean to the tripoint with the Republic of Congo, and a much longer 2,421 km section running from the Atlantic to the tripoint with Zambia.
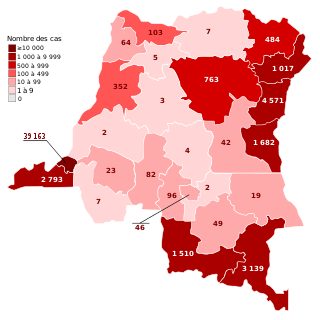
The COVID-19 pandemic in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 10 March 2020. The first few confirmed cases were all outside arrivals.

Bas-Congo was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various significant changes in extent. It roughly corresponds to the present province of Kongo Central.



















