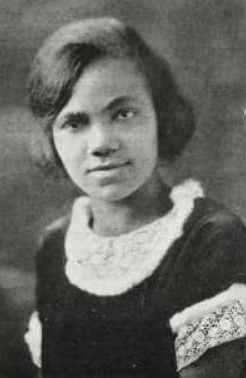Alban Maria Johannes Berg was an Austrian composer of the Second Viennese School. His compositional style combined Romantic lyricism with the twelve-tone technique. Although he left a relatively small oeuvre, he is remembered as one of the most important composers of the 20th century for his expressive style encompassing "entire worlds of emotion and structure".

Julia Carolyn Child was an American chef, author, and television personality. She is recognized for bringing French cuisine to the American public with her debut cookbook, Mastering the Art of French Cooking, and her subsequent television programs, the most notable of which was The French Chef, which premiered in 1963.

Leoš Janáček was a Czech composer, musical theorist, folklorist, publicist, and teacher. He was inspired by Moravian and other Slavic music, including Eastern European folk music, to create an original, modern musical style.

Howard Harold Hanson was an American composer, conductor, educator, music theorist, and champion of American classical music. As director for 40 years of the Eastman School of Music, he built a high-quality school and provided opportunities for commissioning and performing American music. In 1944, he won a Pulitzer Prize for his Symphony No. 4, and received numerous other awards including the George Foster Peabody Award for Outstanding Entertainment in Music in 1946.
Gisela Marie Augusta Richter was a British-American classical archaeologist and art historian. She was a prominent figure and an authority in her field.

Abigail May Alcott Nieriker was an American artist and the youngest sister of Louisa May Alcott. She was the basis for the character Amy in her sister's semi-autobiographical novel Little Women (1868). She was named after her mother, Abigail May, and first called Abba, then Abby, and finally May, which she asked to be called in November 1863 when in her twenties.

Alice Louise Waters is an American chef, restaurateur, and author. In 1971, she opened Chez Panisse, a restaurant in Berkeley, California, famous for its role in creating the farm-to-table movement and for pioneering California cuisine.

Mary Church Terrell was an American civil rights activist, journalist, teacher and one of the first African-American women to earn a college degree. She taught in the Latin Department at the M Street School —the first African American public high school in the nation—in Washington, DC. In 1895, she was the first African-American woman in the United States to be appointed to the school board of a major city, serving in the District of Columbia until 1906. Terrell was a charter member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (1909) and the Colored Women's League of Washington (1892). She helped found the National Association of Colored Women (1896) and served as its first national president, and she was a founding member of the National Association of College Women (1923).

Matilda Sissieretta Joyner Jones was an American soprano. She sometimes was called "The Black Patti" in reference to Italian opera singer Adelina Patti. Jones' repertoire included grand opera, light opera, and popular music. Trained at the Providence Academy of Music and the New England Conservatory of Music, Jones made her New York City debut in 1888 at Steinway Hall, and four years later she performed at the White House for President Benjamin Harrison. She sang for four consecutive presidents and the British royal family, and was met with international success. Besides the United States and the West Indies, Jones toured in South America, Australia, India, southern Africa, and Europe.

Faith Marie Domergue was an American film and television actress. Discovered at age 16 by media and aircraft mogul Howard Hughes, she was signed to a contract with Hughes's RKO Radio Pictures and cast as the lead in the studio's thriller Vendetta, which had a troubled four-year production before finally being released in 1950.

Elinor Mary Darwin was an Irish born illustrator, engraver and portrait painter. Her illustrations were included in several of her husband, Bernard Darwin's books for children.

Jessie Willcox Smith was an American illustrator during the Golden Age of American illustration. She was considered "one of the greatest pure illustrators". A contributor to books and magazines during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Smith illustrated stories and articles for clients such as Century, Collier's, Leslie's Weekly, Harper's, McClure's, Scribners, and the Ladies' Home Journal. She had an ongoing relationship with Good Housekeeping, which included a long-running Mother Goose series of illustrations and also the creation of all of the Good Housekeeping covers from December 1917 to 1933. Among the more than 60 books that Smith illustrated were Louisa May Alcott's Little Women and An Old-Fashioned Girl, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's Evangeline, and Robert Louis Stevenson's A Child's Garden of Verses.

Sue Bailey Thurman was an American author, lecturer, historian and civil rights activist. She was the first non-white student to earn a bachelor's degree in music from Oberlin College, Ohio. She briefly taught at the Hampton Institute in Virginia, before becoming involved in international work with the YWCA in 1930. During a six-month trip through Asia in the mid-1930s, Thurman became the first African-American woman to have an audience with Mahatma Gandhi. The meeting with Gandhi inspired Thurman and her husband, theologian Howard Thurman, to promote non-violent resistance as a means of creating social change, bringing it to the attention of a young preacher, Martin Luther King Jr. While she did not actively protest during the Civil Rights Movement, she served as spiritual counselors to many on the front lines, and helped establish the first interracial, non-denominational church in the United States.

Elizabeth Shippen Green was an American illustrator. She illustrated children's books and worked for publications such as The Ladies' Home Journal, The Saturday Evening Post and Harper's Magazine.

Nora Douglas Holt was an American critic, composer, singer and pianist who was the first African American to receive a master's degree in music in the United States. She composed more than 200 works of music and was associated with the leading figures of the Harlem Renaissance and the co-founder of the National Association of Negro Musicians. She died in 1974 in Los Angeles.
John de Vere, 14th Earl of Oxford was an English peer and landowner.
Ezra Schabas, was a Canadian musician, educator and author. He was active in Canada's musical life beginning in 1952, when he emigrated from Cleveland with his family. During his time in Canada, he was a leading musical educator, clarinetist, and administrator in Toronto's musical institutions. He wrote several books on Canadian and American musical history, and he was appointed to the Order of Ontario and made a Member of the Order of Canada.

Ernest Henri Alexandre Boulanger was a French composer of comic operas and a conductor. He was more known, however, for being a choral music composer, choral group director, voice teacher, and vocal contest jury member.

Harriet Gibbs Marshall was an American pianist, writer, and educator of music. She is best known for opening the Washington Conservatory of Music and School of Expression in 1903 in Washington, D.C.
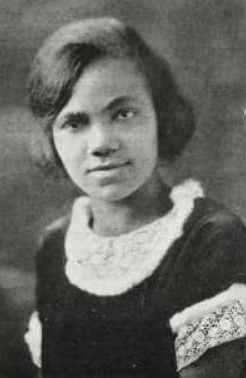
Joanna Raynor Houston, later Joanna Houston Ransom, was an American English instructor, college administrator, assistant dean of women at Howard University, third Grand Basileus of Zeta Phi Beta, and a member of the National Pan-Hellenic Council of Presidents.