
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. It is not necessarily proportional to luminance. This is a subjective attribute/property of an object being observed and one of the color appearance parameters of color appearance models. Brightness refers to an absolute term and should not be confused with Lightness.
Gamma correction, or often simply gamma, is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
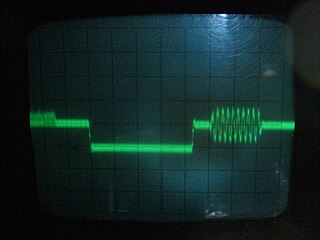
Colorburst is an analog video, composite video signal generated by a video-signal generator used to keep the chrominance subcarrier synchronized in a color television signal. By synchronizing an oscillator with the colorburst at the back porch (beginning) of each scan line, a television receiver is able to restore the suppressed carrier of the chrominance (color) signals, and in turn decode the color information. The most common use of colorburst is to genlock equipment together as a common reference with a vision mixer in a television studio using a multi-camera setup.

S-Video is a signaling standard for standard definition video, typically 480i or 576i. By separating the black-and-white and coloring signals, it achieves better image quality than composite video, but has lower color resolution than component video.
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.

High-dynamic-range imaging (HDRI) is a high dynamic range (HDR) technique used in imaging and photography to reproduce a greater dynamic range of luminosity than is possible with standard digital imaging or photographic techniques. The aim is to present a similar range of luminance to that experienced through the human visual system. The human eye, through adaptation of the iris and other methods, adjusts constantly to adapt to a broad range of luminance present in the environment. The brain continuously interprets this information so that a viewer can see in a wide range of light conditions.

The SMPTE color bars is a trademarked television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in North America. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to it as Engineering Guideline EG 1-1990. Its components are a known standard. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance information correctly. It was originally conceived by Norbert D. Larky and David D. Holmes of RCA Laboratories and first published in RCA Licensee Bulletin LB-819 on February 7, 1951. U.S. patent 2,742,525 Color Test Pattern Generator was awarded on April 17, 1956 to Norbert D. Larky and David D. Holmes. Previously categorized by SMPTE as ECR 1-1978, its development was awarded an Engineering Emmy in 2001-2002.
An extended version of SMPTE Color Bars signal, developed by the Japanese Association of Radio Industry and Businesses as ARIB STD-B28 and standardized as SMPTE RP 219:2002 was introduced to test HDTV signal with an aspect ratio of 16:9 that can be down converted to a SDTV color bar signal with an aspect ratio of either 4:3 or 16:9. The Color Bar signal is generated with unconventionally slow rise and fall time value to facilitate video level control and monitor color adjustments of HDTV and SDTV equipment. Digital test images generated following the SMPTE RP 219:2002 specifications and adapted to perfectly fit 114 standard and non-standard resolutions for both 16bpp and 8bpp, are freely available in the COLOR dataset of the TESTIMAGES archive.
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale or greyscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an amount of light, that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest.

Dot crawl is the popular name for a visual defect of color analog video standards when signals are transmitted as composite video, as in terrestrial broadcast television. It consists of animated checkerboard patterns which appear along horizontal color transitions. It results from intermodulation or crosstalk between chrominance and luminance components of the signal, which are imperfectly multiplexed in the frequency domain.
Video Encoded Invisible Light (VEIL) is a technology for encoding low-bandwidth digital data bitstream in video signal, developed by VEIL Interactive Technologies. VEIL is compatible with multiple formats of video signals, including PAL, SECAM, and NTSC. The technology is based on a steganographically encoded data stream in the luminance of the videosignal.

Contrast is the difference in luminance or colour that makes an object distinguishable. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the color and brightness of the object and other objects within the same field of view. The human visual system is more sensitive to contrast than absolute luminance; we can perceive the world similarly regardless of the huge changes in illumination over the day or from place to place. The maximum contrast of an image is the contrast ratio or dynamic range.
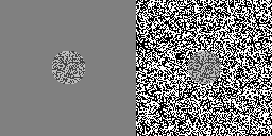
The Chubb illusion is an optical illusion or error in visual perception in which the apparent contrast of an object varies substantially to most viewers depending on its relative contrast to the field on which it is displayed. These visual illusions are of particular interest to researchers because they may provide valuable insights in regard to the workings of human visual systems.

In colorimetry and color theory, lightness, also known as value or tone, is a representation of variation in the perception of a color or color space's brightness. It is one of the color appearance parameters of any color appearance model.

A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with physical device profiling, it allows for reproducible representations of color, in both analog and digital representations. A color space may be arbitrary, with particular colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches and corresponding assigned color names or numbers such as with the Pantone collection, or structured mathematically as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB. A "color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers ; however, a color model with no associated mapping function to an absolute color space is a more or less arbitrary color system with no connection to any globally understood system of color interpretation. Adding a specific mapping function between a color model and a reference color space establishes within the reference color space a definite "footprint", known as a gamut, and for a given color model this defines a color space. For example, Adobe RGB and sRGB are two different absolute color spaces, both based on the RGB color model. When defining a color space, the usual reference standard is the CIELAB or CIEXYZ color spaces, which were specifically designed to encompass all colors the average human can see.
In television broadcasting, VIT signals are a group of test signals inserted in the composite video signal. These signals are used to weight the transmission characteristics of the system between the test generator and the output of the demodulator, where the system includes the microwave links, or TVROs as well as the TV transmitters and the transposers. There are both ATSC and EBU standards for VIT.
HCL (Hue-Chroma-Luminance) is a color space model designed to accord with human perception of color. HCL has been adopted by information visualization practitioners to present data without the bias implicit in using varying saturation.

ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, defines various aspects of high dynamic range (HDR) video such as display resolution, frame rate, chroma subsampling, bit depth, color space, and optical transfer function. It was posted on the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) website on July 4, 2016. Rec. 2100 expands on several aspects of Rec. 2020.










