Vienna is the capital, most populous city, and one of nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. Its larger metropolitan area has a population of nearly 2.9 million, representing nearly one-third of the country's population. Vienna is the cultural, economic, and political center of the country, the fifth-largest city by population in the European Union, and the most-populous of the cities on the Danube river.

Leopoldstadt is the 2nd municipal district of Vienna in Austria. As of 1 January 2016, there are 103,233 inhabitants over 19.27 km2 (7 sq mi). It is situated in the heart of the city and, together with Brigittenau, forms a large island surrounded by the Danube Canal and, to the north, the Danube. It is named after Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor. Due to its relatively high percentage of Jewish inhabitants before the Holocaust, Leopoldstadt gained the nickname Mazzesinsel. This context was a significant aspect for the district twinning with the New York City borough Brooklyn in 2007.
Kugelmugel, officially the Republic of Kugelmugel, is a spherical art object located in Vienna, Austria.
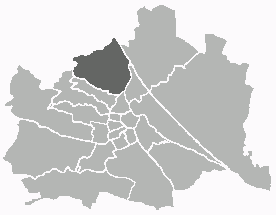
Döbling is the 19th district in the city of Vienna, Austria. It is located in the north of Vienna, north of the districts Alsergrund and Währing. Döbling has some heavily populated urban areas with many residential buildings, and borders the Vienna Woods. It includes some of the most expensive residential areas such as Grinzing, Sievering, and Neustift am Walde, and is home to many Heurigen taverns. There are some large Gemeindebauten, including Vienna's most famous, the Karl-Marx-Hof.
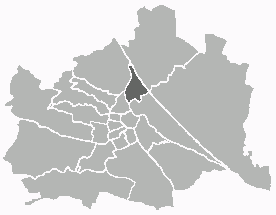
Brigittenau is the 20th district of Vienna. It is located north of the central districts, north of Leopoldstadt on the same island area between the Danube and the Danube Canal. Brigittenau is a heavily populated urban area with many residential buildings.

The Prater is a large public park in Leopoldstadt, Vienna, Austria. The Wurstelprater, an amusement park that is often simply called "Prater", lies in one corner of the Wiener Prater and includes the Wiener Riesenrad Ferris wheel.

Vindobona was a Roman military camp in the province of Pannonia, located on the site of the modern city of Vienna in Austria. The settlement area took on a new name in the 13th century, being changed to Berghof, or now simply known as Alter Berghof.

The Donaukanal is a former arm of the river Danube, now regulated as a water channel, within the city of Vienna, Austria. It is 17.3 kilometres (10.7 mi) long and, unlike the Danube itself, it borders Vienna's city centre, Innere Stadt, where the Wien River (Wienfluss) flows into it.

The Reichsbrücke is a major bridge in Vienna, linking Mexikoplatz in Leopoldstadt with the Donauinsel in Donaustadt across the Danube. The bridge is used by 50,000 vehicles per day and carries six lanes of traffic, U-Bahn tracks, two footpaths, two cyclepaths and two utility tunnels.

The Vienna Stadtbahn was a rail-based public transportation system operated under this name from 1898 until 1989. Today, the Vienna U-Bahn lines U4 and U6 and the Vienna S-Bahn run on its former lines.
Julius von Borsody was an Austrian film architect and one of the most employed set designers in the Austrian and German cinemas of the late silent and early sound film periods. His younger brother, Eduard von Borsody, was a film director in Austria and Germany. He is also the great-uncle of German actress Suzanne von Borsody.

The Augarten is a public park of 52.2 hectares situated in the Leopoldstadt, the second district of Vienna, Austria. It contains the city's oldest Baroque park.

For a long time, it was not necessary to build a Harbour in Vienna, because the existing natural landing points were sufficient for the level of trade on the Danube. It was only when steamships began to arrive in great numbers that a harbour offering safe berths became essential. Even then however, goods were for the most part loaded and unloaded at an unenclosed river harbour that was established at the end of the 19th century.

The Nussdorf weir and lock are works of hydraulic engineering located in the Viennese suburb of Nussdorf at the point where the Donaukanal leaves the Danube. Designed by Austrian architect Otto Wagner, The weir and lock were built following the adoption of a new law in July 1892, which also authorised the construction of the Vienna Stadtbahn and the transformation of the Donaukanal into a winter harbour.

The Vienna Museum is a group of museums in Vienna consisting of the museums of the history of the city. In addition to the main building in Karlsplatz, the group includes some locations, numerous specialised museums, musicians' residences and archaeological excavations.

The Stone Bridge in Regensburg, Germany, is a 12th-century bridge across the Danube linking the Old Town with Stadtamhof. For more than 800 years, until the 1930s, it was the city's only bridge across the river. It is a masterwork of medieval construction and an emblem of the city.

The Wien Nordwestbahnhof, abbreviated as Wien NWBH, is the site of a goods station in Brigittenau district of Vienna, Austria. Passenger transport ended in 1959. It served as the southern terminus of the Austrian Northwestern Railway. The northwestern terminus of the line was Prague Těšnov station till 1972. Freight transport is the process of termination. Starting in 2018, the site is being redeveloped into a residential district.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Vienna:

Konstantin Viktor Ernst Emil Karl Alexander Friedrich Prinz zu Hohenlohe-Schillingsfürst was a k.u.k. First Obersthofmeister and General of the Cavalry of Austria-Hungary.