
Diatoms are a major group of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.

The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Ross who visited this area in 1841. To the west of the sea lies Ross Island and Victoria Land, to the east Roosevelt Island and Edward VII Peninsula in Marie Byrd Land, while the southernmost part is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf, and is about 200 miles (320 km) from the South Pole. Its boundaries and area have been defined by the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research as having an area of 637,000 square kilometres (246,000 sq mi).

James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 64 km in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound.
This is a list of extreme points in Antarctica.

Bacteriastrum is a genus of diatoms in family Chaetocerotaceae. There are more than 30 described species in genus Bacteriastrum, but many of these are not currently accepted, and new species are still added to the genus. The type species for the genus is Bacteriastrum furcatum Shadbolt.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic South Pole and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle, and is surrounded by the Southern Ocean. At 14,200,000 square kilometres, it is the fifth-largest continent and nearly twice the size of Australia. At 0.00008 people per square kilometre, it is by far the least densely populated continent. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice that averages 1.9 km in thickness, which extends to all but the northernmost reaches of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Craticula is a genus of diatom that lies on or in the top layers of sediments in the freshwater to brackish water environments it inhabits. In addition to frustule morphology the genus differs from closely related species by its sexual reproduction and movement in response to light.
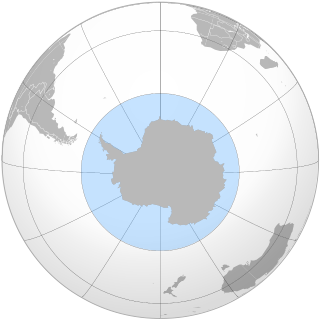
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean or the Austral Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem.
Antarctica is one of the most physically and chemically extreme terrestrial environments to be inhabited by lifeforms. The largest plants are mosses, and the largest animals that do not leave the continent are a few species of insects.
Homaxinella balfourensis is a species of sea sponge in the family Suberitidae. It is found in the seas around Antarctica and can grow in two forms, either branching out in one plane like a fan or forming an upright club-like structure.
Luticola desmetii is a species of non-marine diatom first found in lakes of James Ross Island.
Luticola evkae is a species of non-marine diatom first found in lakes of James Ross Island.
Luticola permuticopsis is a species of non-marine diatom first found in lakes of James Ross Island.
Luticola tomsui is a species of non-marine diatom first found in lakes of James Ross Island.

The Ross expedition was a voyage of scientific exploration of the Antarctic in 1839 to 1843, led by James Clark Ross, with two unusually strong warships, HMS Erebus and HMS Terror. It explored what is now called the Ross Sea and discovered the Ross Ice Shelf. On the expedition, Ross discovered the Transantarctic Mountains and the volcanoes Erebus and Terror, named after his ships. The young botanist Joseph Dalton Hooker made his name on the expedition.
Navicula australoshetlandica is an algae species in the genus Navicula, known from inland waters of the Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic regions.
Navicula dobrinatemniskovae is an algal species in the genus Navicula, known from inland waters of the Antarctic region. The species was named after Prof. Dsc Dobrina Temniskova from the University of Sofia
Navicula cremeri is an algae in the genus Navicula, known from inland waters of the Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic regions.

Cocconeis is a genus of diatoms. Members of the genus are elliptically shaped diatoms.
Cyclotella is a genus of diatoms often found in oligotrophic environments, both marine and fresh water. It is in the family Stephanodiscaceae and the order Thalassiosirales. The genus was first discovered in the mid 1800s and since then has become an umbrella genus for nearly 100 different species, the most well-studied and the best known being Cyclotella meneghiniana. Despite being among the most dominant genera in low-productivity environments, it is relatively understudied.







