
A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) is a shoulder-fired rocket weapon that launches rockets equipped with an explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, and are frequently used as anti-tank weapons. These warheads are affixed to a rocket motor which propels the RPG towards the target and they are stabilized in flight with fins. Some types of RPG are reloadable with new rocket-propelled grenades, while others are single-use. RPGs are generally loaded from the front.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor.

Anti-tank warfare originated during World War I from the desire to develop technology and tactics to destroy tanks. After the Allies deployed the first tanks in 1916, the German Empire introduced the first anti-tank weapons. The first developed anti-tank weapon was a scaled-up bolt-action rifle, the Mauser 1918 T-Gewehr, that fired a 13.2 mm cartridge with a solid bullet that could penetrate the thin armor used by tanks at that time and destroy the engine or ricochet inside, killing occupants. Because tanks represent an enemy's strong force projection on land, military strategists have incorporated anti-tank warfare into the doctrine of nearly every combat service since. The most predominant anti-tank weapons at the start of World War II in 1939 included the tank-mounted gun, anti-tank guns and anti-tank grenades used by the infantry, and ground-attack aircraft.

The Carl Gustaf 8.4 cm recoilless rifle is a Swedish-developed 84 mm (3.3 in) caliber shoulder-fired recoilless rifle, initially developed by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of the 1940s as a crew-served man-portable infantry support gun for close-range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battlefield illumination, smoke screening and marking fire, which has seen great export success around the globe and continues to be a popular multi-purpose support weapon in use by many nations. The Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless rifle is a lightweight, low-cost weapon that uses a wide range of ammunition, which makes it extremely flexible and suitable for a wide variety of roles.
The M60, officially the Machine Gun, Caliber 7.62 mm, M60, is a family of American general-purpose machine guns firing 7.62×51mm NATO cartridges from a disintegrating belt of M13 links. There are several types of ammunition approved for use in the M60, including ball, tracer, and armor-piercing rounds.

The M72 LAW is a portable one-shot 66 mm (2.6 in) unguided anti-tank weapon.

The M67 recoilless rifle is a 90 mm anti-tank recoilless rifle made in the United States and later in South Korea. It could also be employed in an anti-personnel role with the use of the M590 antipersonnel round. It was designed to be fired primarily from the ground using the bipod and monopod, but could also be fired from the shoulder using the folded bipod as a shoulder rest and the monopod as a front grip. The weapon was air-cooled and breech-loaded, and fired fixed ammunition. It is a direct fire weapon employing stadia lines to allow simple range finding, based on a typical tank target bridging the lines once in range.
The Panzerfaust 3 is a modern semi-disposable recoilless anti-tank weapon, which was developed between 1978 and 1985 and first entered service with the Bundeswehr in 1987. It was first ordered in 1973 to provide West German infantry with an effective weapon against contemporary Soviet armor, thereby replacing West Germany's aging PzF 44 Light Lanze launchers and the heavy Carl Gustaf 84 mm anti-tank recoilless rifle manufactured in Sweden.

The HJ-8 or Hongjian-8 is a second generation tube-launched, optically tracked, wire-guided anti-tank missile system which was originally deployed by the People's Liberation Army since the late 1980s.
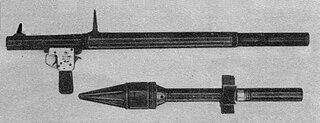
The RPG-2 is a man-portable, shoulder-fired anti-tank weapon that was designed in the Soviet Union. It was the first successful anti-tank weapon of its type, being a successor to the earlier and unsuccessful rocket-propelled grenade RPG-1.

The M40 recoilless rifle is a portable, crew-served 105 mm recoilless rifle made in the United States. Intended primarily as an anti-tank weapon, it could also be employed in an antipersonnel role with the use of an antipersonnel-tracer flechette round. The bore was commonly described as being 106 mm caliber but is in fact 105 mm; the 106 mm designation was intended to prevent confusion with incompatible 105 mm ammunition from the failed M27. The air-cooled, breech-loaded, single-shot rifle fired fixed ammunition and was used primarily from a wheeled ground mount or M92 ground mount. It was designed for direct firing only, and sighting equipment for this purpose was furnished with each weapon, including an affixed M8C .50 cal spotting rifle.

The B-10 recoilless rifle is a Soviet 82 mm smoothbore recoilless gun. It could be carried on the rear of a BTR-50 armoured personnel carrier. It was a development of the earlier SPG-82, and entered Soviet service during 1954. It was phased out of service in the Soviet Army in the 1960s and replaced by the SPG-9, remaining in service with parachute units at least until the 1980s. Although now obsolete it was used by many countries during the Cold War.
Tank development both evolved considerably from World War II and played a key role during the Cold War (1945–1990). The period pitted the nations of the Eastern Bloc and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) against each other.

The M20 recoilless rifle is a U.S. 75 mm caliber recoilless rifle T21E12 that was used during the last months of the Second World War and extensively during the Korean War. It could be fired from an M1917A1 .30 caliber machine gun tripod, or from a vehicle mount, typically a Jeep. Its shaped charge warhead, also known as HEAT, was capable of penetrating 100 mm of armor. Although the weapon proved ineffective against the T-34 tank and most other tanks during the Korean War, it was used primarily as a close infantry support weapon to engage all types of targets including infantry and lightly armored vehicles. The M20 proved useful against pillboxes and other types of field fortifications.
The SPG-82 was a Soviet wheeled antitank rocket launcher that entered service after the end of World War II. It was replaced in Soviet service by the B-10 recoilless rifle from 1954 but remained in service with some armies, notably in the Middle East until the 1970s. The SPG-82 was also carried by BRIMOB in 1963. It has been replaced by B-10 recoilless rifle.

The PAW 600 was a lightweight anti-tank gun that used the high-low pressure system to fire hollow charge warheads. In 1945, it was used operationally by the Wehrmacht in small numbers. Only about 260 were produced before the war's end.

The RPG-75 is a portable, disposable, single-shot anti-tank weapon, developed in the 1970s in Czechoslovakia. It fires a 68 mm grenade with an effective range of 300 meters and maximum range of 1000 meters. It resembles the American M72 LAW rocket launcher. This recoilless rifle is recommended to be used against light tanks and armoured tracked vehicles.

The M18 recoilless rifle is a 57 mm shoulder-fired, anti-tank recoilless rifle that was used by the U.S. Army in World War II and the Korean War. Recoilless rifles are capable of firing artillery-type shells at reduced velocities comparable to those of standard cannon, but with greater accuracy than anti-tank weapons that used unguided rockets, and almost entirely without recoil. The M18 was a breech-loaded, single-shot, man-portable, crew-served weapon. It could be used in both anti-tank and anti-personnel roles. The weapon could be both shoulder fired or fired from a prone position. The T3 front grip doubled as an adjustable monopod and the two-piece padded T3 shoulder cradle could swing down and to the rear as a bipod for the gunner. The most stable firing position was from the tripod developed for the water-cooled Browning M1917 machine gun.

The Model 1968 recoilless gun is a 105-mm antitank weapon developed and employed by Argentina. The weapon has been in active service since 1968 and 150 were still operational with Argentine forces as of 2000. A similar weapon is the Argentine 105-mm Model 1974 FMK-1 recoilless gun.

The AT4 is a Swedish 84 mm (3.31 in) unguided, man-portable, disposable, shoulder-fired recoilless anti-tank weapon manufactured by Saab Bofors Dynamics. The AT4 is not a rocket launcher strictly speaking, because the explosive warhead is not propelled by a rocket motor. Rather, it is a smooth-bore recoilless gun. Saab has had considerable sales success with the AT4, making it one of the most common light anti-tank weapons in the world. The M136 AT4 is a variant used by the United States Army.

















