Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the atmosphere to the surface. As part of the larger Mars Exploration Program, Mars Global Surveyor performed atmospheric monitoring for sister orbiters during aerobraking, and helped Mars rovers and lander missions by identifying potential landing sites and relaying surface telemetry.
In planetary nomenclature, a fossa is a long, narrow depression (trough) on the surface of an extraterrestrial body, such as a planet or moon. The term, which means "ditch" or "trench" in Latin, is not a geological term as such but a descriptor term used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for topographic features whose geology or geomorphology is uncertain due to lack of data or knowledge of the exact processes that formed them. Fossae are believed to be the result of a number of geological processes, such as faulting or subsidence. Many fossae on Mars are probably graben.

The Memnonia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Memnonia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-16.

Terra Sirenum is a large region in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. It is centered at 39.7°S 150°W and covers 3900 km at its broadest extent. It covers latitudes 10 to 70 South and longitudes 110 to 180 W. Terra Sirenum is an upland area notable for massive cratering including the large Newton Crater. Terra Sirenum is in the Phaethontis quadrangle and the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis.

The Noachis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Noachis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-27.

The Diacria quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northwestern portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 180° to 240° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Diacria quadrangle is also referred to as MC-2. The Diacria quadrangle covers parts of Arcadia Planitia and Amazonis Planitia.

The Arcadia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 240° to 300° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Arcadia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-3.

The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 300° to 360° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-4.

The Elysium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Elysium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-15.

The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-17. Parts of Daedalia Planum, Sinai Planum, and Solis Planum are found in this quadrangle. Phoenicis Lacus is named after the phoenix which according to myth burns itself up every 500 years and then is reborn.

The Eridania quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Eridania quadrangle is also referred to as MC-29.
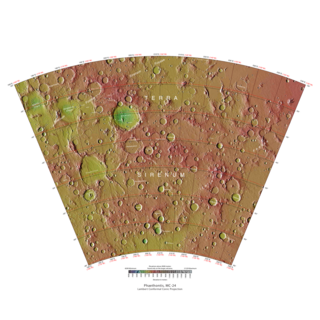
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24.

The Thaumasia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Thaumasia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-25 . The name comes from Thaumas, the god of the clouds and celestial apparitions.

The Argyre quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Argyre quadrangle is also referred to as MC-26. It contains Argyre Planitia and part of Noachis Terra.

The Mare Australe quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Mare Australe quadrangle is also referred to as MC-30. The quadrangle covers all the area of Mars south of 65°, including the South polar ice cap, and its surrounding area. The quadrangle's name derives from an older name for a feature that is now called Planum Australe, a large plain surrounding the polar cap. The Mars polar lander crash landed in this region.

Sirenum Fossae is a long trough in several quadrangles including Memnonia quadrangle and Phaethontis quadrangle of Mars, centered at 35.57° south latitude and 197.26° west longitude. Sirenum Fossae is 2,735 km long and was named after a classical albedo feature name. Troughs on Mars like this one are called Fossae. Sirenum Fossae is believed to have formed by movement along a pair of faults causing a center section to drop down. This kind of feature is called a graben.
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016.

Martian gullies are small, incised networks of narrow channels and their associated downslope sediment deposits, found on the planet of Mars. They are named for their resemblance to terrestrial gullies. First discovered on images from Mars Global Surveyor, they occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Usually, each gully has a dendritic alcove at its head, a fan-shaped apron at its base, and a single thread of incised channel linking the two, giving the whole gully an hourglass shape. They are estimated to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. A subclass of gullies is also found cut into the faces of sand dunes, that are themselves considered to be quite young. Linear dune gullies are now considered recurrent seasonal features.

The Mars Orbiter Camera and Mars Observer Camera (MOC) were scientific instruments on board the Mars Observer and Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. The camera was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) for NASA and the cost of the whole MOC scientific investigation project was about US$44 million, higher than anticipated in the budget.
The common surface features of Mars include dark slope streaks, dust devil tracks, sand dunes, Medusae Fossae Formation, fretted terrain, layers, gullies, glaciers, scalloped topography, chaos terrain, possible ancient rivers, pedestal craters, brain terrain, and ring mold craters.