
A single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) vehicle reaches orbit from the surface of a body using only propellants and fluids and without expending tanks, engines, or other major hardware. The term exclusively refers to reusable vehicles. To date, no Earth-launched SSTO launch vehicles have ever been flown; orbital launches from Earth have been performed by either fully or partially expendable multi-stage rockets.

A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word spaceport, and even more so cosmodrome, has traditionally been used for sites capable of launching spacecraft into orbit around Earth or on interplanetary trajectories. However, rocket launch sites for purely sub-orbital flights are sometimes called spaceports, as in recent years new and proposed sites for suborbital human flights have been frequently referred to or named "spaceports". Space stations and proposed future bases on the Moon are sometimes called spaceports, in particular if intended as a base for further journeys.

A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km. Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 1,000 and 1,500 km, such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. For certain purposes Sounding Rockets may be flown to altitudes as high as 3,000 kilometers to allow observing times of around 40 minutes to provide geophysical observations of the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere and mesosphere. Sounding rockets have been used for the examination of atmospheric nuclear tests by revealing the passage of the shock wave through the atmosphere. In more recent times Sounding Rockets have been used for other nuclear weapons research. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion, lifting 270–450-kg (600–1,000-pound) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 97 and 201 km.

Vostok was a family of rockets derived from the Soviet R-7 Semyorka ICBM and was designed for the human spaceflight programme. This family of rockets launched the first artificial satellite and the first crewed spacecraft (Vostok) in human history. It was a subset of the R-7 family of rockets.
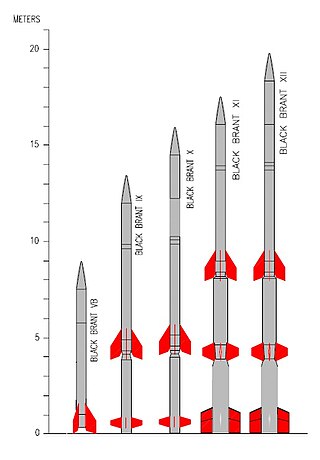
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.
Astrobee is the designation of series of American sounding rockets with one to three stages.

The Uchinoura Space Center is a space launch facility in the Japanese town of Kimotsuki, Kagoshima Prefecture. Before the establishment of the JAXA space agency in 2003, it was simply called the Kagoshima Space Center (鹿児島宇宙空間観測所) (KSC). All of Japan's scientific satellites were launched from Uchinoura prior to the M-V launch vehicles being decommissioned in 2006. It continues to be used for suborbital launches, stratospheric balloons and has also been used for the Epsilon orbital launch vehicle. Additionally, the center has antennas for communication with interplanetary space probes.

Ofeq, also spelled Offek or Ofek is the designation of a series of Israeli reconnaissance satellites first launched in 1988. Most Ofeq satellites have been carried on top of Shavit launch vehicles from Palmachim Airbase in Israel, on the Mediterranean coast. The low Earth orbit satellites complete one Earth orbit every 90 minutes.

TMK was the designation of a Soviet space exploration project to send a crewed flight to Mars and Venus without landing.

Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) is an Indian rocket launching site established on 21 November 1963. Operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), it is located in Thumba, Thiruvananthapuram, which is near the southwestern tip of mainland India, very close to Earth's magnetic equator. It is currently used by ISRO for launching sounding rockets.

The Saturn MLV was a proposed concept family of rockets, intended as a follow-on to the Saturn V. MLV stands for "Modified Launch Vehicle".
The Universal Rocket or UR family of missiles and carrier rockets is a Russian, previously Soviet rocket family. Intended to allow the same technology to be used in all Soviet rockets, the UR is produced by the Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center. Several variants were originally planned, of which only three flew, and only two of which entered service. In addition, the cancelled UR-500 ICBM formed the basis for the Proton carrier rocket.

The Altair was a solid-fuel rocket with a fiberglass casing, initially developed for use as the third stage of Vanguard rockets in 1959. It was manufactured by Allegany Ballistics Laboratory (ABL) as the X-248. It was also sometimes called the Burner 1.

The LR87 was an American liquid-propellant rocket engine used on the first stages of Titan intercontinental ballistic missiles and launch vehicles. Composed of twin motors with separate combustion chambers and turbopump machinery, it is considered a single unit and was never flown as a single combustion chamber engine or designed for this. The LR87 first flew in 1959.

Rohini is a series of sounding rockets developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for meteorological and atmospheric study. These sounding rockets are capable of carrying payloads of 2 to 200 kilograms between altitudes of 100 to 500 kilometres. The ISRO currently uses RH-200, RH-300,Mk-II, RH-560 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III rockets, which are launched from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Thumba and the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
The Star is a family of US solid-propellant rocket motors originally developed by Thiokol and used by many space propulsion and launch vehicle stages. They are used almost exclusively as an upper stage, often as an apogee kick motor. The number designations refer to the approximate diameter of the fuel casing in inches.

Progress M-43 was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in October 2000 to resupply the Mir space station.

Progress M-33 was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in November 1996 to resupply the Mir space station.













