Related Research Articles

The University of Madras is a public state university in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Established in 1857, it is one of the oldest and among the most prominent universities in India, incorporated by an act of the Legislative Council of India under the British government.

Egmore is a neighbourhood of Chennai, India. Situated on the northern banks of the Coovum River, Egmore is an important residential area as well as a commercial and transportation hub. The Egmore Railway Station was the main terminus of the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway and later, the metre gauge section of the Southern division of the Indian Railways. It continues to be an important railway junction. The Government Museum, Chennai is also situated in Egmore. Other important institutions based in Egmore include the Government Women and Children's Hospital, the Tamil Nadu State Archives and the Tamil Nadu Archaeology Department. The Wesley Church, Egmore is the oldest church of the region.

Saint Mary Church of Chennai, constructed in 1712 and reconstructed in 1772, is one of the oldest churches of the Indian subcontinent, located in Chennai. It is famous for its belfry of six. The Church, also called the Armenian Church of Virgin Mary, is located on the Armenian Street in the neighbourhood of George Town.
The Monitorial System, also known as Madras System or Lancasterian System, was an education method that took hold during the early 19th century, because of Spanish, French, and English colonial education that was imposed into the areas of expansion. This method was also known as "mutual instruction" or the "Bell–Lancaster method" after the British educators Andrew Bell and Joseph Lancaster who both independently developed it. The method was based on the abler pupils being used as 'helpers' to the teacher, passing on the information they had learned to other students.

Subbiah Muthiah,, was an Indian writer, journalist, cartographer, amateur historian and heritage activist known for his writings on the political and cultural history of Chennai city. He was the founder of the fortnightly newspaper Madras Musings and the principal organizer of the annual Madras Day celebrations. Muthiah was also the founder-President of the Madras Book Club.

Madras College, often referred to as Madras, is a Scottish comprehensive secondary school located in St Andrews, Fife. It educates over 1,400 pupils aged between 11 and 18 and was founded in 1833 by the Rev. Dr Andrew Bell.
Andrew Bell was a Scottish Episcopalian priest and educationalist who pioneered the Madras System of Education in schools and was the founder of Madras College, a secondary school in St Andrews.

Indian Institute of Technology Madras is a public technical university located in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is selected as one of the 8 public Institutes of Eminence of India. As one of the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), it is recognized as an Institute of National Importance. IIT Madras is ranked among the most prestigious academic institutions in India.

Kavitark Ram Shriram is an Indian-American billionaire businessman and philanthropist. He is a founding board member and one of the first investors in Google. He worked earlier in Amazon. Shriram came to Amazon.com in August 1998, when the company acquired Junglee, an online comparison shopping firm of which Shriram was president. Before Junglee and Amazon, Shriram was a member of the Netscape executive team, joining them in 1994, before they shipped products or posted revenue.

Bell Baxter High School is a non-denominational comprehensive school for 11 to 18-year-olds in Cupar, Fife, Scotland. Founded in 1889, it educates over 1,500 pupils mainly from the surrounding villages.
Chennai is home to many educational and research institutions. IIT Madras, located in South Chennai is considered as the premier centre of engineering education in India. Anna University and the University of Madras are the oldest state owned universities which are ranked among the best universities in India. The College of Engineering, Guindy and Madras Institute of Technology, which are the constituent college of Anna University along with Alagappa College of Technology are the pioneer institutes of engineering education in India. Some of the oldest medical colleges India, the Madras Medical College (1835) and Stanley Medical College (1938) are located in the city. Notable, liberal arts colleges in the city include Loyola College, Madras Christian College, Presidency College, Stella Maris College, Women's Christian College and Ethiraj College for Women.

St. George's Cathedral is a Church of South India cathedral in Chennai, India. The cathedral was built in 1815. St. George's occupies an important place in the history of Christianity in India, as the Church of South India was inaugurated here on 27 September 1947. It marked the breaking down of ecclesiastical barriers between Protestants of various traditions.
The National Society (Church of England and Church in Wales) for the Promotion of Education, often just referred to as the National Society, and since 2016 also as The Church of England Education Office (CEEO) is significant in the history of education in England and Wales. It promotes church schools and Christian education in line with the established church. Historically it was in strong competition with the nonconformist organization British and Foreign School Society. Both promoted the monitorial system, whereby a few paid teachers worked with senior students who in turn taught the junior students. The National Society was strongly supported by the Anglican clergy, Oxford and Cambridge universities, and the established church. The nonconformist Protestants were in strong opposition.
Handel Manuel was an Indian pianist, organist, conductor, composer and accompanist. He helped to make western classical music popular in Chennai, the capital of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu.
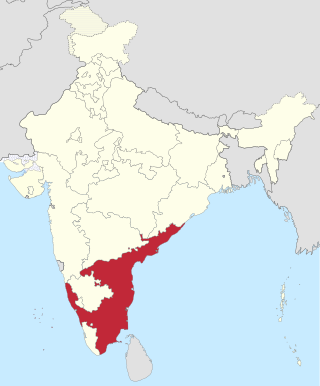
Madras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu, Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and central Kerala, Bellary, South Canara and Kollegal. Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema were separated to form Andhra State in 1953, while South Canara and Bellary districts along with the Kollegalam taluka of Coimbatore district were merged with Mysore State, and Malabar District with the State of Travancore-Cochin to form Kerala in 1956. Post State Reorganization in 1956, the remaining Madras State was renamed to Tamil Nadu on January 14, 1969.

Vepery is a suburb in the north of Chennai, India. Abutting the transportation hub of Park Town, the neighbourhood covers a rectangular area north of the Poonamallee High Road.
Events from the year 1833 in Scotland.
St. Andrew's Church, consecrated in 1866, is a Presbyterian church, located on Cubbon Road, Bangalore. Initially knows as St. Andrews's Kirk, it was a Church of Scotland church till 1959 when it became part of the Karnataka Central Diocese of the Church of South India. The church is named after Saint Andrew, the patron saint of Scotland. St Andrew's Church celebrated its 150 years anniversary on 20 November 2014.
The 1889 Birthday Honours were appointments by Queen Victoria to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by citizens of the British Empire. The appointments were made to celebrate the official birthday of The Queen, and were published in the London Gazette on 24 May 1889 and in The Times on 25 May 1889.
References
- ↑ Raman, Ragu (29 April 2009). "Madras School of Economics logs higher campus placements". indiatimes.com. times of india. Retrieved 4 June 2023.