Related Research Articles

The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World.

Constantinople was the capital of the Roman Empire, and later, the Eastern Roman Empire, the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Officially renamed Istanbul in 1930, the city is today the largest city and financial centre of the Republic of Turkey (1923–present). It remains the largest city in Europe.

Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. At room temperature and pressure, another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon, but diamond converts to it extremely slowly. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth.

Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of 446,300 km2 (172,300 sq mi) or 710,850 km2 (274,460 sq mi), with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a vibrant mix of Berber, Arab, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca.

The Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa.

The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.

The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BCE and 2,000 BCE, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BCE, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys into tools, supplanting stone in many uses.

The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread. Its sites spanned an area from northeast Afghanistan and much of Pakistan to western and northwestern India. The civilisation flourished both in the alluvial plain of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the Ghaggar-Hakra, a seasonal river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.

Early modern human (EMH) or anatomically modern human (AMH) are terms used to distinguish Homo sapiens that are anatomically consistent with the range of phenotypes seen in contemporary humans from extinct archaic human species. This distinction is useful especially for times and regions where anatomically modern and archaic humans co-existed, for example, in Paleolithic Europe. Among the oldest known remains of Homo sapiens are those found at the Omo-Kibish I archaeological site in south-western Ethiopia, dating to about 233,000 to 196,000 years ago, the Florisbad site in South Africa, dating to about 259,000 years ago, and the Jebel Irhoud site in Morocco, dated about 300,000 years ago.
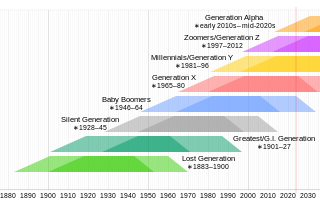
Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000s as ending birth years, with the generation typically being defined as people born from 1981 to 1996. Most millennials are the children of baby boomers and early Gen Xers; millennials are often the parents of Generation Alpha.

The atmosphere of Earth or air is the layer of gases retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention, and reducing temperature extremes between day and night.

The Sahara is a desert on the African continent. With an area of 9,200,000 square kilometres (3,600,000 sq mi), it is the largest hot desert in the world and the third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Arctic.

The Deccan Plateau is defined as the entire southern peninsula of India south of the Narmada River. It is a high triangular tableland, bounded on the west and east by the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, respectively, that meet at the plateau’s southern tip and to the north, by the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges.

The natural environment or natural world encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial. The term is most often applied to the Earth or some parts of Earth. This environment encompasses the interaction of all living species, climate, weather and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity. The concept of the natural environment can be distinguished as components:

The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in the 1920s and 1930s. It appears around 11,500–11,000 uncalibrated years before present (YBP) at the end of the last glacial period and is characterized by the manufacture of "Clovis points" and distinctive bone and ivory tools. Archaeologists' most precise determinations at present suggest this radiocarbon age is equal to roughly 13,200 to 12,900 calendar years ago.

The Upper Paleolithic is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago, according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture.

Culture of Uganda is made up of a diverse range of ethnic groups. Lake Kyoga forms the northern boundary for the Bantu-speaking people, who dominate much of East, Central, and Southern Africa. In Uganda, they include the Baganda and several other tribes

The domestication of the dog was the process which created the domestic dog. This included the dog's genetic divergence from the wolf, its domestication, and the emergence of the first dogs. Genetic studies show that all ancient and modern dogs share a common ancestry and descended from an ancient, now-extinct wolf population – or closely related wolf populations – which was distinct from the modern wolf lineage. The dog's similarity to the grey wolf is the result of substantial dog-into-wolf gene flow, with the modern grey wolf being the dog's nearest living relative. An extinct Late Pleistocene wolf may have been the ancestor of the dog.
Howiesons Poort is a lithic technology cultural period in the Middle Stone Age in Africa named after the Howieson's Poort Shelter archeological site near Grahamstown in South Africa. It seems to have lasted around 5,000 years between roughly 65,800 BP and 59,500 BP.

In paleoanthropology, the recent African origin of modern humans, also called the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA), recent single-origin hypothesis (RSOH), replacement hypothesis, or recent African origin model (RAO), is the dominant model of the geographic origin and early migration of anatomically modern humans. It follows the early expansions of hominins out of Africa, accomplished by Homo erectus and then Homo neanderthalensis.
References
- ↑ "Magosian". Oxford Reference. Retrieved 2021-05-15.