
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word cave can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called exogene caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called endogene caves.
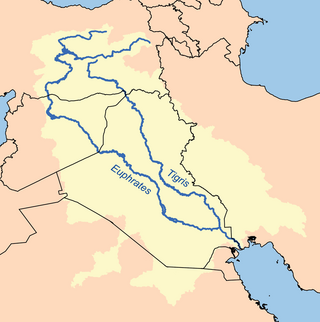
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia which discharges into the Persian Gulf. Its principal rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates along with smaller tributaries.

The Kura is an east-flowing river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, it flows through Turkey to Georgia, then to Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and enters the Caspian Sea at Neftçala. The total length of the river is 1,515 kilometres (941 mi).

A Tabriz rug/carpet is a type in the general category of Persian carpets from the city of Tabriz, the capital city of East Azarbaijan Province in north west of Iran. It is one of the oldest rug weaving centers and makes a huge diversity of types of carpets. The range starts at Bazaar quality of 24 raj and on up to the incredibly fine 110 raj. Raj is the unit of knot density. It shows the rigidity of the rug which based on the number of strings used for the foundation of the rug. Strings materials are usually made of cotton or silk which is used for very fine rugs.

Stygofauna are any fauna that live in groundwater systems or aquifers, such as caves, fissures and vugs. Stygofauna and troglofauna are the two types of subterranean fauna. Both are associated with subterranean environments – stygofauna are associated with water, and troglofauna with caves and spaces above the water table. Stygofauna can live within freshwater aquifers and within the pore spaces of limestone, calcrete or laterite, whilst larger animals can be found in cave waters and wells. Stygofaunal animals, like troglofauna, are divided into three groups based on their life history - stygophiles, stygoxenes, and stygobites.
- Stygophiles inhabit both surface and subterranean aquatic environments, but are not necessarily restricted to either.
- Stygoxenes are like stygophiles, except they are defined as accidental or occasional presence in subterranean waters. Stygophiles and stygoxenes may live for part of their lives in caves, but don't complete their life cycle in them.
- Stygobites are obligate, or strictly subterranean, aquatic animals and complete their entire life in this environment.
Garra typhlops, also known as the Iran cave barb is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is endemic to caves in Iran. Like other cave-adapted fish, it is blind and lacks pigmentation.
Eidinemacheilus smithi, also known as the Zagroz blind loach, is a species of loach in the family Nemacheilidae. This cavefish is endemic to an aquifer in the Karun River drainage in the Zagros Mountains of Iran.
Typhlogarra widdowsoni or Garra widdowsoni, the Iraq blind barb or Haditha cave garra, is a species of cyprinid fish endemic to underground water systems near Haditha in Iraq. Although traditionally placed in its own genus Typhlogarra, this is not supported by genetic evidence, leading to its move to Garra. This cavefish is considered critically endangered because of water extraction, which has lowered the groundwater level. Once abundant, a survey in 2012 found that it now was very rare. Another species from the same place, Caecocypris basimi, may already be extinct. The only other known cavefish in Iraq is Eidinemacheilus proudlovei.
The Georgia blind salamander is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to the south-eastern United States where its natural habitats are inland karsts, caves and subterranean habitats. It is listed as "Endangered" by the IUCN and is threatened by habitat loss.

The Mexican blind brotula is a species of viviparous brotula endemic to Mexico, where it is found in sinkholes and caves. It is known as sak kay in Mayan and dama blanca ciega in Spanish. This cavefish grows to a standard length of 9.7 cm (3.8 in). It is the only known member of its genus.

The blind cave eel is a species of cavefish in the family Synbranchidae. It is the longest cavefish in Australia and one of the only three vertebrates in Australia that is restricted to underground waters, the other being the blind gudgeon and the Barrow cave gudgeon. It is blind, its body is eel-like and elongated, and it has a non-pigmented skin with colours ranging from white to pink.
The Mexican blindcat, in Spanish bagre de muzquiz, is a species of North American freshwater catfish. Until recently, it was believed to be endemic to Coahuila in the Rio Bravo drainage in northern Mexico; however, in 2016 the species was reported from the Amistad National Recreation Area, Texas, following earlier, unconfirmed sightings of blind, white catfish in the area. The captured specimens were brought to the San Antonio Zoo and Aquarium.

Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreatic fish and hypogean fish.
Water supply and sanitation in Iran has witnessed some important improvements, especially in terms of increased access to urban water supply, while important challenges remain, particularly concerning sanitation and service provision in rural areas. Institutionally, the Ministry of Energy is in charge of policy and provincial companies are in charge of service provision.

Ardabil rugs originate from Ardabil located in the province of Ardabil Province in northwestern Iran, 639 kilometers from Tehran. Ardabil has a long and illustrious history of Persian carpet weaving.

Polycheles typhlops is a species of blind, deep water decapod crustacean with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is "one of the dominant and most characteristic crustaceans in deep-sea communities of the Mediterranean Sea".

Hydrodynamic reception refers to the ability of some animals to sense water movements generated by biotic or abiotic sources. This form of mechanoreception is useful for orientation, hunting, predator avoidance, and schooling. Frequent encounters with conditions of low visibility can prevent vision from being a reliable information source for navigation and sensing objects or organisms in the environment. Sensing water movements is one resolution to this problem.

Rock art in Iran includes archaeological petroglyphs, or carving in rock; pictographs, or painting on rock; and rock reliefs. Large numbers of prehistoric rock art, more than 50,000, have been discovered in Iran.











