
From 20 to 23 September 1993, during the Sukhumi massacre, separatists in Sukhumi, Abkhazia blocked Georgian troops' overland supply routes as part of the war in Abkhazia. In response, the Georgian government used Sukhumi Babushara Airport to ferry supplies to troops stationed in Sukhumi. Abkhaz forces attacked the airport in an attempt to further block the supply routes.
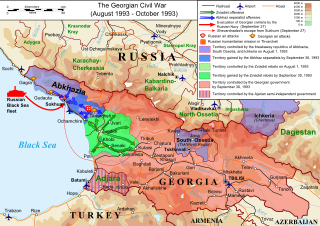
The Georgian Civil War lasted from 1991 to 1993 in the South Caucasian country of Georgia. It consisted of inter-ethnic and international conflicts in the regions of South Ossetia and Abkhazia, as well as the violent military coup d'état against the first democratically-elected President of Georgia, Zviad Gamsakhurdia, and his subsequent uprising in an attempt to regain power.

Politics in Abkhazia is dominated by its conflict with Georgia. Abkhazia became de facto independent from Georgia after the 1992–1993 war, but its de jure independence has only been recognised by a few other countries. Abkhazia is a presidential representative democratic republic with a multi-party system, wherein the President is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government of the Republic of Abkhazia. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the People's Assembly of Abkhazia.

Zhiuli Shartava was a Georgian politician and the Head of the Council of Ministers of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia who was killed by Abkhaz militants during the ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia in 1993.

Irakli Alasania is a Georgian politician, soldier and former diplomat who served as the Minister of Defense of Georgia from 2012 to 2014. He was Georgia's Ambassador to the United Nations from September 11, 2006, until December 4, 2008. His previous assignments include Chairman of the Government of Abkhazia(-in-exile) and the President of Georgia's aide in the Georgian-Abkhaz talks. Soon after his resignation, Alasania withdrew into opposition to the Mikheil Saakashvili administration, setting up the Our Georgia – Free Democrats party in July 2009. In 2012 Alasania was appointed Minister of Defense, a position he held until 2014.

The ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia, also known in Georgia as the genocide of Georgians in Abkhazia, refers to the ethnic cleansing, massacres, and forced mass expulsion of thousands of ethnic Georgians living in Abkhazia during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict of 1992–1993 and 1998 at the hands of Abkhaz separatists and their allies. Armenians, Greeks, Russians, and opposing Abkhazians were also killed. In 2007, 267,345 Georgian civilians were registered as internally displaced persons (IDPs). The ethnic cleansing and massacres of Georgians have been officially recognized by Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) conventions in 1994, 1996, and again in 1997 during the Budapest, Lisbon, and Istanbul summits, which condemned the "perpetrators of war crimes committed during the conflict." On May 15, 2008, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a resolution A/RES/62/249, which "Emphasizes the importance of preserving the property rights of refugees and internally displaced persons from Abkhazia, Georgia, including victims of reported "ethnic cleansing," and calls upon all the Member States to deter persons under their jurisdiction from obtaining property within the territory of Abkhazia, Georgia in violation of the rights of returnees." The UN Security Council passed a series of resolutions in which it appealed for a cease-fire.

Guram Gabiskiria was a Mayor of Sukhumi who was murdered by Abkhaz separatists during the ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia in 1993.
The Sukhumi massacre took place on September 27, 1993, during and after the fall of Sukhumi into separatist hands in the course of the War in Abkhazia. It was perpetrated against Georgian civilians of Sukhumi, mainly by militia forces of Abkhaz separatists and North Caucasian allies. It became part of a violent ethnic cleansing campaign carried out by the separatists.
The Government of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia is an administration recognized by Georgia as the legal and only government of Abkhazia. Abkhazia has been de facto independent of Georgia – though with very little international recognition – since the early 1990s. Ruslan Abashidze, elected in May 2019, is the current head of the government-in-exile.

This article refers to the history of Abkhazia from its pre-historic settlement by the lower-paleolithic hunter-gatherers to the post-1992-1993 war situation.
The War in Abkhazia was fought between Georgian government forces for the most part and Abkhaz separatist forces, Russian government armed forces and North Caucasian militants between 1992 and 1993. Ethnic Georgians who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population largely supported the Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists received support from thousands of North Caucasus and Cossack militants and from the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.

The Kamani Massacre took place on July 9, 1993, during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict. It was perpetrated against Georgian inhabitants of Kamani, mainly by militia forces of Abkhaz separatists, and their North Caucasian and Russian allies. It became a part of the bloody campaign carried out by the separatists, which was known as the ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia
2008 Georgian drone shootdowns refers to several incidents in March, April and May 2008, when Georgia's pro-Russian breakaway region of Abkhazia claimed to have shot down unmanned Georgian reconnaissance aircraft. Georgia initially denied that any of these downings took place, but made the allegations public following the April 20 shootdown carried out by a fighter jet belonging to the Russian Air Force. Involvement of the Russian military was denied by the Abkhaz separatists and Russia, with both falsely claiming that the separatists alone had accomplished the task. However, Russian military involvement was later confirmed by a UNOMIG fact finding mission which represented its results on May 26. On June 1, in a note sent to the Russian delegation at the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), Georgia recognised that two other downings of its drones had taken place in the past.

Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which views the region as an autonomous republic. It lies on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, south of the Greater Caucasus mountains in northwestern Georgia. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.
The German involvement in Abkhazia dates back to the 1870s, when Russian Tsar Alexander II decided to settle German villagers in Abkhazia to "civilize" the newly conquered Caucasian peoples. The German Empire was briefly involved in a military intervention in 1918. More recently, Germany has been involved in diplomatic and peacekeeping efforts to resolve the dispute between the so-called Republic of Abkhazia and Georgia, Germany's strategic ally.
Giorgi (Gia) Karkarashvili is a Georgian politician and retired major general who served as Georgia's Minister of Defense from May 1993 to March 1994. A former Soviet army captain, he was a high-profile military commander during the civil war and wars against the secessionists in Abkhazia and South Ossetia in the 1990s. A gunshot wound received in the 1995 attack in Moscow left him severely disabled. He was member of the Parliament of Georgia from 1999 to 2004. He is currently member of the Our Georgia – Free Democrats party led by Irakli Alasania.
The War in Abkhazia from 1992 to 1993 was waged chiefly between Georgian government forces on one side, Russian military forces on other side supporting separatist forces demanding independence of Abkhazia from Georgia. http://www.historyorb.com/russia/georgia.php Ethnic Georgians, who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population, largely supported Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists were supported by thousands of the North Caucasus and Cossack militants and by the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.

The Kamani Monastery is located at the village of Kamani in Abkhazia/Georgia, north of Sukhumi. The monastery building is a 1980s construction on the foundations of a medieval church.
Mamia I Gurieli, of the House of Gurieli, was Prince of Guria from 1512 until his death in 1534. Succeeding on the death of his father Giorgi I Gurieli, Mamia became involved in the conflict between the two eastern Georgian kingdoms of Kartli and Kakheti in 1520; by force of arms, he compelled David X of Kartli to agree on peace with Levan of Kakheti, his son-in-law. Mamia Gurieli's 1533 campaign, jointly with his namesake Prince of Mingrelia, against the homebase of Circassian pirates ended in a fiasco, with Mamia being captured and ransomed later that year.

Alexander (Sasha) Berulava was a Georgian journalist, writer, and human rights activist, founder of the Georgian Television of Abkhazia, who was murdered by Abkhaz separatists during the ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia in 1993 together with other members of the Government of Abkhazia.













