Related Research Articles

Wu Sangui, courtesy name Changbai (長白) or Changbo (長伯), 1612 – 2 October 1678, was a Chinese military leader who played an instrumental role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the establishment of the Qing dynasty in its place.

The Later Jin invasion of Joseon occurred in early 1627 when the Later Jin prince Amin lead an invasion of Korea's Joseon kingdom. The war ended after three months with the Later Jin establishing itself as sovereign tributary overlord over Joseon. However Joseon continued its relationship with the Ming dynasty and showed defiance in solidifying its tributary relationship with the Jurchens. It was followed by the Qing invasion of Joseon in 1636.

The Chongzhen Emperor, personal name Zhu Youjian, was the 17th and last Emperor of the Ming dynasty as well as the last ethnic Han to rule over a unified China proper. He reigned from 1627 to 1644. "Chongzhen," the era name of his reign, means "honorable and auspicious".

Yuan Chong huan, courtesy name Yuansu or Ziru, was a politician, military general and writer who served under the Ming dynasty. Widely regarded as a patriot in Chinese culture, he is best known for defending Liaoning from Jurchen invaders during the Later Jin invasion of the Ming. As a general, Yuan Chong huan excelled as a cannoneer and sought to incorporate European cannon designs into the Ming arsenal.
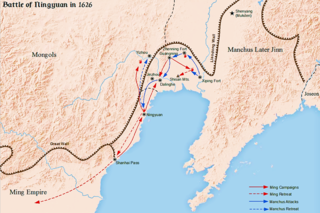
The Battle of Ningyuan was a battle between the Ming dynasty and the Later Jin dynasty in 1626. The Later Jin had been waging war on the Ming for several years, and their leader Nurhaci had deemed Ningyuan to be a suitable target for his attack, in part due to advice from a Ming defector, Li Yongfang. Later Jin failed to take the city and Nurhaci was wounded in the assault, dying eight months later. The Ming emerged victorious, marking a temporary resurgence of the Ming army after an eight-year-long series of defeats.

Hong Chengchou (1593–1665), courtesy name Yanyan and art name Hengjiu, was a Chinese official who served under the Ming and Qing dynasties. He was born in present-day Liangshan Village, Yingdu Town, Nan'an County, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, China. After obtaining the position of a jinshi in the imperial examination in 1616 during the reign of the Wanli Emperor, he joined the civil service of the Ming Empire and served as an official in Shaanxi. During the reign of the Chongzhen Emperor, he was promoted to Minister of War and Viceroy of Suliao. In 1642, he surrendered and defected to the Manchu-led Qing Empire after his defeat at the Battle of Songjin. He became one of the Qing Empire's leading Han Chinese scholar-politicians. While he was in office, he encouraged the Manchu rulers to adopt Han Chinese culture and provided advice to the Qing government on how to consolidate its control over the former territories of the fallen Ming Empire. Apart from Dorgon and Fan Wencheng (范文程), Hong Chengchou was regarded as one of the most influential politicians in the early Qing dynasty. However, he was also villainised by the Han Chinese for his defection to the Qing Empire and for his suppression of the Southern Ming dynasty.
The Battle of Song-Jin was fought in 1641 and 1642 at Songshan and Jinzhou, hence the name "Song-Jin". Hong Chengchou's 100,000 elite troops, sent to break the siege of Jinzhou, were crushed by the Eight banner armies of the Qing Dynasty at Songshan. Hong Chengchou and a small number of the remaining troops were besieged at Songshan and defeated a few months later. The Jinzhou garrison and the general Zu Dashou surrendered to the Qing army shortly after the defeat of Ming armies at Songshan.
Zu Dashou, courtesy name Fuyu (腹宇), was a Chinese military general who served on the northern border of the Ming dynasty during the Transition from Ming to Qing. He fought against the Qing dynasty in several major engagements before ultimately surrendering to them in 1642. An alleged descendant of the Eastern Jin dynasty general Zu Ti, he was the maternal uncle of the Ming general Wu Sangui, who surrendered Shanhai Pass to Qing forces and defected to the Qing side. Zu's tomb was acquired by the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto, Canada, and is considered one of the "iconic objects" of the museum.
Mao Wenlong, courtesy name Zhennan, was a Chinese military general of the Ming dynasty. He is best known for commanding Ming forces in the naval battles against forces of the Manchu Qing dynasty in the Yellow Sea during the Qing conquest of the Ming. He was also known for excelling in artillery warfare and for successfully incorporating Western-style tactics into the Chinese military.

Hongyipao was the Chinese name for European-style muzzle-loading culverins introduced to China and Korea from the Portuguese colony of Macau and by the Hendrick Hamel expedition to Joseon in the early 17th century.

The Affaire in the Swing Age, also known as The Dynasty or Love Against Kingship, is a 2003 Chinese television series based on the novel Jiangshan Fengyu Qing by Zhu Sujin, who was also the screenwriter for the series. The series depicts the events in the transition of the Ming dynasty to the Qing dynasty in China, focusing on the lives of historical figures such as Li Zicheng, Wu Sangui, Chen Yuanyuan, the Chongzhen Emperor and Huangtaiji.
Geng Zhongming was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Feudatories who rebelled against Qing rule in the 1670s.

The Ming Great Wall, built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644), forms the most visible parts of the Great Wall of China today. A comprehensive archaeological survey, using advanced technologies, has concluded that the Ming walls measure 8,850 km (5,500 mi) from Jiayu Pass in the west to the sea in Shanhai Pass, then looping over to terminate in Manchuria at the Hushan Great Wall. This is made up of 6,259 km (3,889 mi) sections of actual wall, 359 km (223 mi) of trenches and 2,232 km (1,387 mi) of natural defensive barriers such as hills and rivers.
The Battle of Dalinghe was a battle between the Later Jin dynasty and the Ming dynasty that took place between September and November 1631. Later Jin forces besieged and captured the fortified northern Ming city of Dalinghe in Liaoning. Using a combined force of Jurchen and Mongol cavalry, along with recently captured Ming artillery units, the Later Jin khan Hong Taiji surrounded Dalinghe and defeated a series of Ming reinforcement forces in the field. The Ming defenders under general Zu Dashou surrendered the city after taking heavy losses and running out of food. Several of the Ming officers captured in the battle would go on to play important roles in the ongoing transition from Ming to Qing. The battle was the first major test for the Chinese firearms specialists incorporated into the Later Jin military. Whereas the Later Jin had previously relied primarily on their own Eight Banners cavalry in military campaigns, after the siege of Dalinghe the Chinese infantry would play a larger role in the fighting. Unlike Nurhaci's failed siege at the Battle of Ningyuan several years prior, the siege of Dalinghe was a success that would soon be replicated in Songshan and Jinzhou, paving the way for the establishment of the Qing dynasty and the ultimate defeat of the Ming.
Kong Youde was a Chinese adventurer and Ming dynasty military officer who served under the warlord Mao Wenlong until Mao's death in 1629. Subsequently he worked for Sun Yuanhua, governor of Shandong, along with fellow Mao subordinate Geng Zhongming. When ordered by Sun to reinforce Zu Dashou at the Battle of Dalinghe in 1631, Kong and Geng mutinied, pillaging the countryside, sacking Dengzhou, and subsequently defecting to the Manchu—soon to declare themselves China's Qing Dynasty—in 1633. They were joined in 1634 by another former officer under Mao, Shang Kexi. Together, the three were known as the "Three Miners from Shandong" and participated in many campaigns under the Qing dynasty, hastening the demise of the Ming.

The Later Jin (1616–1636) was a dynastic khanate in Manchuria ruled by the Jurchen Aisin Gioro leaders Nurhaci and Hong Taiji. Established in 1616 by the Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain Nurhaci upon his reunification of the Jurchen tribes, its name was derived from the former Jurchen-led Jin dynasty which had ruled northern China in the 12th and 13th centuries before falling to the Mongol Empire. In 1635, the lingering Northern Yuan under Ejei Khan formally submitted to the Later Jin. The following year, Hong Taiji officially renamed the realm to "Great Qing", thus marking the start of the Qing dynasty. The Qing subsequently overran Li Zicheng's Shun dynasty and various Southern Ming claimants and loyalists, going on to rule an empire comprising China proper, Tibet, Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, and Taiwan until the 1911 Xinhai Revolution established the Republic of China.

The Battle of Guanging was a military conflict between the Later Jin dynasty and the Ming dynasty in 1622. It occurred at and around the Ming's northern city of Guangning, which fell to the Later Jin in 1622.

The Battle of Ning-Jin was a military conflict between the Later Jin and Ming dynasty. In the spring of 1627, the Later Jin khan Hong Taiji invaded Ming territory in Liaoning under the pretext of illegal construction on Later Jin lands.
The Jisi Incident (己巳之變) was a military conflict between the Later Jin and Ming dynasty, named because it happened in 1629, a jisi year according to the Chinese sexagenary cycle. In the winter of 1629 Hong Taiji bypassed Ming's northeastern defenses by breaching the Great Wall of China west of the Shanhai Pass and reached the outskirts of Beijing before being repelled by reinforcements from Shanhai Pass. The Later Jin secured large amounts of war material by looting the region around Beijing. This was the first time the Jurchens had broken through the Great Wall into China proper since they rose up against Ming China.