
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago 80 km (50 mi) south of Italy, 284 km (176 mi) east of Tunisia, and 333 km (207 mi) north of Libya. The two official languages are Maltese and English. The country's capital is Valletta, which is the smallest capital city in the EU by both area and population. With a population of about 542,000 over an area of 316 km2 (122 sq mi), Malta is the world's tenth-smallest country by area and the ninth most densely populated. Various sources consider the country to consist of a single urban region, for which it is often described as a city-state.

Valletta is the capital city of Malta and one of its 68 council areas. Located between the Grand Harbour to the east and Marsamxett Harbour to the west, its population as of 2021 was 5,157. As Malta’s capital city, it is a commercial centre for shopping, bars, dining, and café life. It is also the southernmost capital of Europe, and at just 0.61 square kilometres (0.24 sq mi), it is the European Union's smallest capital city.

Malta is an island in Southern Europe. It is the largest and most populous of the three major islands that constitute the Maltese Archipelago.The island is situated in the Mediterranean Sea directly south of Italy and north of Libya. It lies south-east of the smaller islands of Gozo and Comino.The island is 27 kilometres (17 mi) long and 14.5 kilometres (9 mi) wide, with a total area of 246 square kilometres (95 sq mi). The capital is Valletta, while the largest locality is Rabat. The island is made up of many small towns, which together form one larger urban zone with a population of 409,259. The landscape is characterised by low hills with terraced fields.

Lampedusa is the largest island of the Italian Pelagie Islands in the Mediterranean Sea.

Birgu, also known by its title Città Vittoriosa, is an old fortified city on the south side of the Grand Harbour in the South Eastern Region of Malta. The city occupies a promontory of land with Fort Saint Angelo at its head and the city of Cospicua at its base. Birgu is ideally situated for safe anchorage, and over time it has developed a very long history with maritime, mercantile and military activities.

Fort Saint Elmo is a star fort in Valletta, Malta. It stands on the seaward shore of the Sciberras Peninsula that divides Marsamxett Harbour from Grand Harbour, and commands the entrances to both harbours along with Fort Tigné and Fort Ricasoli. It is best known for its role in the Great Siege of Malta in 1565.
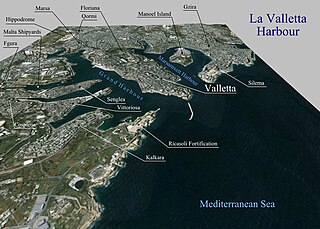
The Grand Harbour, also known as the Port of Valletta, is a natural harbour on the island of Malta. It has been substantially modified over the years with extensive docks, wharves, and fortifications.

Ċirkewwa is a harbour and zone situated at the northernmost point of Malta, part of the locality of Mellieħa.

Marsamxett Harbour, historically also referred to as Marsamuscetto, is a natural harbour on the island of Malta. It is located to the north of the larger Grand Harbour. The harbour is generally more dedicated to leisure use than the Grand Harbour.

The dgħajsa tal-pass is a traditional water taxi from Malta. It is often simply referred to as the dgħajsa, but this word refers to any type of boat in the Maltese language. The boat developed in the 17th century, and was extensively used to ferry passengers in the Grand Harbour and Marsamxett Harbour between the 18th and 20th centuries. Their use declined in the late 20th century, and today only a few dgħajjes remain in operation, ferrying tourists around the harbours. Variants of the boats are still used extensively in rowing regattas held twice a year.

The George Cross was awarded to the island of Malta by King George VI during the Siege of Malta undertaken by Italy and Germany in the early part of World War II. In a letter to the island's Governor, Lieutenant-General Sir William Dobbie, King George wrote, "so as to bear witness to the heroism and devotion of its people". The island was a British colony from 1813 to 1964. The George Cross was incorporated into the flag of Malta beginning in 1943 and remains on the current design of the flag.

The French occupation of Malta lasted from 1798 to 1800. It was established when the Order of Saint John surrendered to Napoleon Bonaparte following the French landing in June 1798. In Malta, the French established a constitutional tradition in Maltese history, granted free education for all, and theoretically established freedom of the press, although only the pro-French newspaper Journal de Malte was actually published during the occupation.

Hospitaller Malta, known in Maltese history as the Knights' Period, was a de facto state which existed between 1530 and 1798 when the Mediterranean islands of Malta and Gozo were ruled by the Order of St. John of Jerusalem. It was formally a vassal state of the Kingdom of Sicily, and it came into being when Emperor Charles V granted the islands as well as the city of Tripoli in modern Libya to the Order, following the latter's loss of Rhodes in 1522. Hospitaller Tripoli was lost to the Ottoman Empire in 1551, but an Ottoman attempt to take Malta in 1565 failed.

The Wignacourt Aqueduct is a 17th-century aqueduct in Malta, which was built by the Order of Saint John to carry water from springs in Dingli and Rabat to the newly built capital city Valletta. The aqueduct carried water through underground pipes and over arched viaducts across depressions in the ground.

The fortifications of Malta consist of a number of walled cities, citadels, forts, towers, batteries, redoubts, entrenchments and pillboxes. The fortifications were built over hundreds of years, from around 1450 BC to the mid-20th century, and they are a result of the Maltese islands' strategic position and natural harbours, which have made them very desirable for various powers.

The fortifications of Valletta are a series of defensive walls and other fortifications which surround Valletta, the capital city of Malta. The first fortification to be built was Fort Saint Elmo in 1552, but the fortifications of the city proper began to be built in 1566 when it was founded by Grand Master Jean de Valette. Modifications were made throughout the following centuries, with the last major addition being Fort Lascaris which was completed in 1856. Most of the fortifications remain largely intact today.

The National Congress Battalions, also known as the Truppe di Campagna, was an irregular military set up in Malta just after the Maltese rebellion against French rule in September 1798. It existed for two years before being disbanded on 11 September 1800.

The Manderaggio is a neighbourhood in Valletta, Malta. It is located behind the Manderaggio Curtain of the fortifications of Valletta, on the side of Marsamxett Harbour.

Victoria Gate is a city gate in Valletta, Malta. It was built by the British in 1885, and was named after Queen Victoria. The gate is the main entrance into the city from the Grand Harbour area, which was once the busiest part of the city. The gate is located between Marina Curtain and St. Barbara Bastion, on the site of the 16th-century Del Monte Gate.

The St Elmo Bridge is a single-span arched truss steel footbridge leading from the foreshore of Fort Saint Elmo in Valletta, Malta, to the breakwater at the entrance of the Grand Harbour. It was constructed in 2011–12 to designs of the Spanish architects Arenas & Asociados. The bridge stands on the site of an earlier bridge which had been built in 1906 and destroyed during World War II in 1941. The original bridge had a design similar to the present one, but it had two spans instead of one.




















