Related Research Articles

Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean and has a mean transport estimated at 100–150 Sverdrups, or possibly even higher, making it the largest ocean current. The current is circumpolar due to the lack of any landmass connecting with Antarctica and this keeps warm ocean waters away from Antarctica, enabling that continent to maintain its huge ice sheet.

Downwelling is the downward movement of a fluid parcel and its properties within a larger fluid. It is closely related to upwelling, the upward movement of fluid.
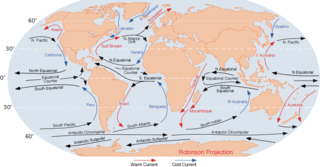
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean.
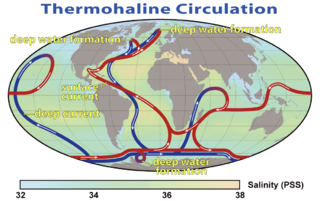
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective thermohaline derives from thermo- referring to temperature and -haline referring to salt content, factors which together determine the density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents travel polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling en route, and eventually sinking at high latitudes. This dense water then flows into the ocean basins. While the bulk of it upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters upwell in the North Pacific. Extensive mixing therefore takes place between the ocean basins, reducing differences between them and making the Earth's oceans a global system. The water in these circuits transport both energy and mass around the globe. As such, the state of the circulation has a large impact on the climate of the Earth.

The Agulhas Current is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the east coast of Africa from 27°S to 40°S. It is narrow, swift and strong. It is suggested that it is the largest western boundary current in the world ocean, with an estimated net transport of 70 sverdrups, as western boundary currents at comparable latitudes transport less — Brazil Current, Gulf Stream, Kuroshio.
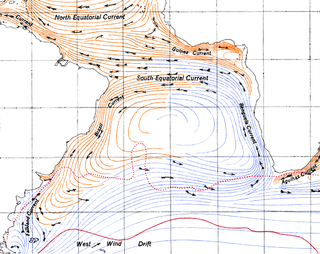
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela Front in the north, at around 16°S. The current is driven by the prevailing south easterly trade winds. Inshore of the Benguela Current proper, the south easterly winds drive coastal upwelling, forming the Benguela Upwelling System. The cold, nutrient rich waters that upwell from around 200–300 m (656–984 ft) depth in turn fuel high rates of phytoplankton growth, and sustain the productive Benguela ecosystem.

In oceanography, a gyre is any large system of circulating ocean surface currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the wind stress curl (torque).

John Alexander Church is an expert on sea level and its changes. He was co-convening lead author for the chapter on Sea Level in the IPCC Third Assessment Report. He was also a co-convening lead author for the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. He is a member of the Joint Scientific Committee of the WCRP. He was a project leader at CSIRO, until 2016. He is currently a professor with the University of New South Wales' Climate Change Research Centre.

The North Atlantic Gyre of the Atlantic Ocean is one of five great oceanic gyres. It is a circular ocean current, with offshoot eddies and sub-gyres, across the North Atlantic from the Intertropical Convergence Zone to the part south of Iceland, and from the east coasts of North America to the west coasts of Europe and Africa.

The Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) was the first of ESA's Living Planet Programme heavy satellites intended to map in unprecedented detail the Earth's gravity field. The spacecraft's primary instrumentation was a highly sensitive gravity gradiometer consisting of three pairs of accelerometers which measured gravitational gradients along three orthogonal axes.

The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is the main ocean current system in the Atlantic Ocean. It is a component of Earth's ocean circulation system and plays an important role in the climate system. The AMOC includes Atlantic currents at the surface and at great depths that are driven by changes in weather, temperature and salinity. Those currents comprise half of the global thermohaline circulation that includes the flow of major ocean currents, the other half being the Southern Ocean overturning circulation.
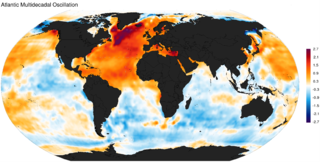
The Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), also known as Atlantic Multidecadal Variability (AMV), is the theorized variability of the sea surface temperature (SST) of the North Atlantic Ocean on the timescale of several decades.

Boundary currents are ocean currents with dynamics determined by the presence of a coastline, and fall into two distinct categories: western boundary currents and eastern boundary currents.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing world ocean.
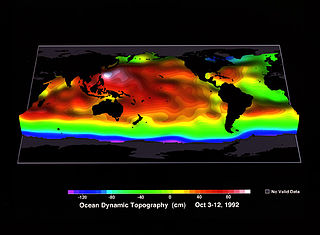
Ocean surface topography or sea surface topography, also called ocean dynamic topography, are highs and lows on the ocean surface, similar to the hills and valleys of Earth's land surface depicted on a topographic map. These variations are expressed in terms of average sea surface height (SSH) relative to Earth's geoid. The main purpose of measuring ocean surface topography is to understand the large-scale ocean circulation.
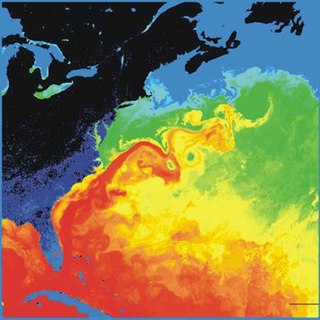
The Gulf Stream is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States, then veers east near 36°N latitude and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northward-accelerating current off the east coast of North America. Around 40°0′N30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.

The Agulhas Return Current (ARC) is an ocean current in the South Indian Ocean. The ARC contributes to the water exchange between oceans by forming a link between the South Atlantic Current and the South Indian Ocean Current. It can reach velocities of up to 4 knots and is therefore popular among participants in trans-oceanic sailing races.

Axel Timmermann is a German climate physicist and oceanographer with an interest in climate dynamics, human migration, dynamical systems' analysis, ice-sheet modeling and sea level. He served a co-author of the IPCC Third Assessment Report and a lead author of IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. His research has been cited over 18,000 times and has an h-index of 70 and i10-index of 161. In 2017, he became a Distinguished Professor at Pusan National University and the founding Director of the Institute for Basic Science Center for Climate Physics. In December 2018, the Center began to utilize a 1.43-petaflop Cray XC50 supercomputer, named Aleph, for climate physics research.
Delia Wanda Oppo is an American scientist who works on paleoceanography where she focuses on past variations in water circulation and the subsequent impact on Earth's climate system. She was elected a fellow of the American Geophysical Union in 2014.
The Agulhas Leakage is an inflow of anomalously warm and saline water from the Indian Ocean into the South Atlantic due to the limited latitudinal extent of the African continent compared to the southern extension of the subtropical super gyre in the Indian Ocean. The process occurs during the retroflection of the Agulhas Current via shedding of anticyclonic Agulhas Rings, cyclonic eddies and direct inflow. The leakage contributes to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) by supplying its upper limb, which has direct climate implications.
References
- ↑ "PL24C-2676 - The Mann Eddy: formation and interaction with the North Atlantic Current". Ocean Sciences Meeting 2020 - 16-21 February 2020 in San Diego, Calif. American Geophysical Union. 18 February 2020. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- ↑ Volkov, Denis. (2005). Interannual Variability of the Altimetry-Derived Eddy Field and Surface Circulation in the Extratropical North Atlantic Ocean in 1993–2001. Journal of Physical Oceanography. 35. 405-426. 10.1175/JPO2683.1.
- ↑ Bingham, R J; et al. (2010). "Using GOCE to estimate the mean North Atlantic circulation (Invited)". Abstract presented at 2010 Fall Meeting, AGU, San Francisco, Calif., 13-17 Dec. American Geophysical Union. Retrieved 2010-12-22.
- ↑ Jonathan Amos, Science correspondent, BBC News (21 Dec 2010). "Goce gravity mission traces ocean circulation". BBC News website, Science & Environment. BBC News. Retrieved 21 Dec 2010.