Related Research Articles

A leiomyoma, also known as fibroids, is a benign smooth muscle tumor that very rarely becomes cancer (0.1%). They can occur in any organ, but the most common forms occur in the uterus, small bowel, and the esophagus. Polycythemia may occur due to increased erythropoietin production as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome.

Surface epithelial-stromal tumors are a class of ovarian neoplasms that may be benign or malignant. Neoplasms in this group are thought to be derived from the ovarian surface epithelium or from ectopic endometrial or Fallopian tube (tubal) tissue. Tumors of this type are also called ovarian adenocarcinoma. This group of tumors accounts for 90% to 95% of all cases of ovarian cancer. Serum CA-125 is often elevated but is only 50% accurate so it is not a useful tumor marker to assess the progress of treatment.

A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that lacks the ability to either invade neighboring tissue or metastasize. When removed, benign tumors usually do not grow back, whereas malignant tumors sometimes do. Unlike most benign tumors elsewhere in the body, benign brain tumors can be life-threatening. Benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate than malignant tumors and the tumor cells are usually more differentiated. They are typically surrounded by an outer surface or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.
Cementoblastoma, or benign cementoblastoma, is a relatively rare benign neoplasm of the cementum of the teeth. It is derived from ectomesenchyme of odontogenic origin. Less than 0.69–8% of all tumors of the teeth.there is no paresthesia.

Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells and/or organs, and/or the abnormal histology or anatomical structure presumably resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathologic senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not neoplastic. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus span across a spectrum of histopathologic variations.

A hamartoma is a mostly benign, local malformation of cells that resembles a neoplasm of local tissue but is usually due to an overgrowth of multiple aberrant cells, with a basis in a systemic genetic condition, rather than a growth descended from a single mutated cell (monoclonality), as would typically define a benign neoplasm/tumor. Despite this, many hamartomas are found to have clonal chromosomal aberrations that are acquired through somatic mutations, and on this basis the term hamartoma is sometimes considered synonymous with neoplasm. Hamartomas are by definition benign, slow-growing or self-limiting, though the underlying condition may still predispose the individual towards malignancies.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.

A Hürthle cell is a cell in the thyroid that is often associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis as well as benign and malignant tumors. This version is a relatively rare form of differentiated thyroid cancer, accounting for only 3-10% of all differentiated thyroid cancers. Oncocytes in the thyroid are often called Hürthle cells. Although the terms oncocyte, oxyphilic cell, and Hürthle cell are used interchangeably, Hürthle cell is used only to indicate cells of thyroid follicular origin.

In pathology, grading is a measure of the cell appearance in tumors and other neoplasms. Some pathology grading systems apply only to malignant neoplasms (cancer); others apply also to benign neoplasms. The neoplastic grading is a measure of cell anaplasia in the sampled tumor and is based on the resemblance of the tumor to the tissue of origin. Grading in cancer is distinguished from staging, which is a measure of the extent to which the cancer has spread.

The Gleason grading system is used to help evaluate the prognosis of men with prostate cancer using samples from a prostate biopsy. Together with other parameters, it is incorporated into a strategy of prostate cancer staging which predicts prognosis and helps guide therapy. A Gleason score is given to prostate cancer based upon its microscopic appearance. Cancers with a higher Gleason score are more aggressive and have a worse prognosis. Pathological scores range from 2 to 10, with higher numbers indicating greater risks and higher mortality.

Salivary gland tumours or neoplasms are tumours that form in the tissues of salivary glands. The salivary glands are classified as major or minor. The major salivary glands consist of the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. The minor salivary glands consist of 800-1000 small mucus-secreting glands located throughout the lining of the oral cavity.
Neoplasms of the nailbed may often present with paronychia, ingrown nail, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, nail-plate dystrophy, longitudinal erythronychia, bleeding, and discolorations. There are various benign and malignant neoplasms that may occur in or overlying the nail matrix and in the nailbed, and symptoms may include pain, itching, and throbbing.

Warty dyskeratoma, also known as an Isolated dyskeratosis follicularis, is a benign epidermal proliferation with distinctive histologic findings that may mimic invasive squamous cell carcinoma and commonly manifests as an umbilicated lesion with a keratotic plug, WD have some histopathologic similarities to viral warts but it's not caused by HPV and the majority of these lesions display overall histopathologic features consistent with a follicular adnexal neoplasm. usually limited to the head, neck, scalp or face and vulva. Lesions are generally solitary and sporadic and may be associated with a follicular unit. Oral involvement, particularly the hard palate, and genital involvement have been reported. it can also be thought of as one of the manifestations of focal acantholytic dyskeratosis, an epidermal reaction pattern that can be seen in several disorders, including Darier's disease and Grover's disease. But the main Difference between Darier disease and Warty dyskeratoma, is that Darier disease inherited dermatosis consisting of multiple keratotic papules on the face, trunk, and extremities, while WD occurs as an isolated, noninherited, single keratotic nodule mainly confined to the head and neck as mentioned earlier.
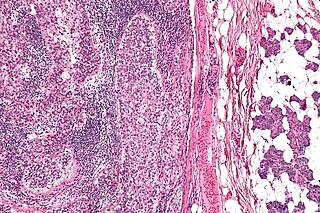
Sebaceous carcinoma, also known as sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGc), sebaceous cell carcinoma, and meibomian gland carcinoma is an uncommon malignant cutaneous tumor. Most are typically about 1.4 cm at presentation. SGc originates from sebaceous glands in the skin and, therefore, may originate anywhere in the body where these glands are found. SGc can be divided into 2 types: periocular and extraocular. The periocular region is rich in sebaceous glands making it a common site of origin. The cause of these lesions in the vast majority of cases is unknown. Occasional cases may be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome. SGc accounts for approximately 0.7% of all skin cancers, and the incidence of SGc is highest in Caucasian, Asian, and Indian populations. Due to the rarity of this tumor and variability in clinical and histological presentation, SGc is often misdiagnosed as an inflammatory condition or a more common neoplasm. SGc is commonly treated with wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery, and the relative survival rates at 5 and 10 years are 92.72 and 86.98%, respectively.

Mucinous cystadenoma is a benign cystic tumor lined by a mucinous epithelium. It is a type of cystic adenoma (cystadenoma).

Pilomatricoma, is a benign skin tumor derived from the hair matrix. These neoplasms are relatively uncommon and typically occur on the scalp, face, and upper extremities. Clinically, pilomatricomas present as a subcutaneous nodule or cyst with unremarkable overlying epidermis that can range in size from 0.5-3.0 cm, but the largest reported case was 24 cm.

Trichilemmoma is a benign cutaneous neoplasm that shows differentiation toward cells of the outer root sheath. The lesion is often seen in the face and neck region. Multifocal occurrence is associated with Cowden syndrome, in which hamartomatous intestinal polyposis is seen in conjunction with multiple tricholemmoma lesions.
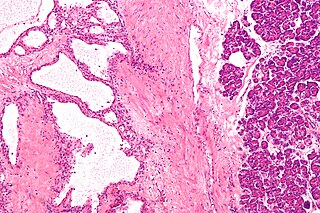
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma is a benign tumour of pancreas. It is usually found in the tail of the pancreas, and may be associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome.
References
- ↑ Steffen C (August 1993). "Mantleoma. A benign neoplasm with mantle differentiation". The American Journal of Dermatopathology. 15 (4): 306–10. doi:10.1097/00000372-199308000-00002. PMID 8214387.
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
| This Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, cysts article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |