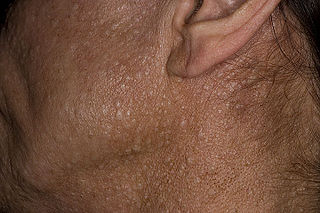
Rasmussen syndrome is a condition characterized by multiple trichoepitheliomas.
Chondrodysplasia punctata is a clinically and genetically diverse group of rare diseases, first described by Erich Conradi (1882–1968), that share the features of stippled epiphyses and skeletal changes.

Kindler syndrome is a rare congenital disease of the skin caused by a mutation in the KIND1 gene.
Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa is a distinctive skin condition of generalized hyperkeratosis and polycyclic and serpiginous erythematous plaques with a characteristic, migratory, double-edged scale at the margins, and is the typical cutaneous manifestation of Netherton's syndrome.

Trichoepithelioma is a neoplasm of the adnexa of the skin. Its appearance is similar to basal cell carcinoma.
Tooth and nail syndrome is a rare disorder, first described in 1965, characterized by nails that are thin, small, and friable, and which may show koilonychia at birth.
Epidermal nevus syndrome is a rare disease that was first described in 1968 and consists of extensive epidermal nevi with abnormalities of the central nervous system (CNS), skeleton, skin, cardiovascular system, genitourinary system and eyes. However, since the syndrome's first description, a broader concept for the "epidermal nevus" syndrome has been proposed, with at least six types being described:
Pigmented hairy epidermal nevus syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by a Becker nevus, ipsilateral hypoplasia of the breast, and skeletal defects such as scoliosis.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.
Graham-Little syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by lichen planus-like skin lesions.

A sebaceous adenoma, a type of adenoma, a cutaneous condition characterized by a slow-growing tumor usually presenting as a pink, flesh-coloured, or yellow papule or nodule.

Trichilemmoma is a benign cutaneous neoplasm that shows differentiation toward cells of the outer root sheath. The lesion is often seen in the face and neck region. Multifocal occurrence is associated with Cowden syndrome, in which hamartomatous intestinal polyposis is seen in conjunction with multiple tricholemmoma lesions.
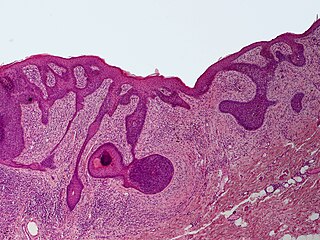
Perifollicular fibroma is a cutaneous condition, a benign tumor usually skin colored, most often affecting the face and upper trunk.
Brooke–Fordyce syndrome is a condition characterized by multiple trichoepitheliomas.