| Perifollicular fibroma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Perifollicular fibroma | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Perifollicular fibroma is a cutaneous condition, a benign tumor usually skin colored, most often affecting the face and upper trunk. [1] :674 [2]
| Perifollicular fibroma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Perifollicular fibroma | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Perifollicular fibroma is a cutaneous condition, a benign tumor usually skin colored, most often affecting the face and upper trunk. [1] :674 [2]

Scrofuloderma is a skin condition caused by tuberculous involvement of the skin by direct extension, usually from underlying tuberculous lymphadenitis.
Tuberculosis cutis orificialis is a form of cutaneous tuberculosis that occurs at the mucocutaneous borders of the nose, mouth, anus, urinary meatus, and vagina, and on the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue.
Papulonecrotic tuberculid is usually an asymptomatic, chronic skin disorder, presenting in successive crops, skin lesions symmetrically distributed on the extensor extremities.
Aquarium granuloma is a skin condition caused by Mycobacterium marinum, characterized by a skin lesion that presents roughly three weeks after exposure.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.
Cutaneous actinomycosis is a chronic disease that affects the deep subcutaneous tissue of the skin. Caused by an anaerobic, Gram-positive, filamentous type of bacteria in the genus Actinomyces, invasion of the soft tissue leads to the formation of abnormal channels leading to the skin surface that discharge pale yellow sulfur granules.
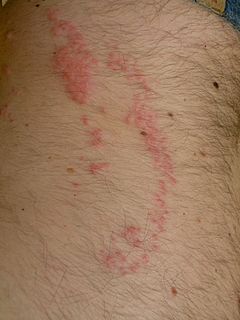
Jellyfish dermatitis is a cutaneous condition caused by stings from a jellyfish.
Melanoacanthoma is a common, benign, darkly pigmented cutaneous condition characterized by a skin lesion with a dull or lackluster surface.
Giant condyloma acuminatum is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by an aggressive, wart-like growth that is a verrucous carcinoma. It is attributed to human papillomavirus.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:
Mucosal melanoma is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by a melanoma of the mucous membranes.
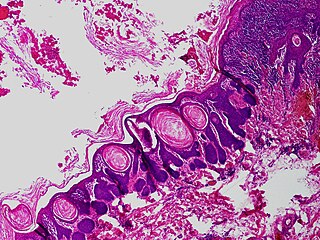
Trichofolliculoma is a cutaneous condition characterized by a benign, highly structured tumor of the pilosebaceous unit.

Trichoblastomas are a cutaneous condition characterized by benign neoplasms of follicular germinative cells. Trichoblastic fibroma is a designation used to characterize small nodular trichoblastomas with conspicuous fibrocytic stroma, sometimes constituting over 50% of the lesion.
A trichodiscoma is a cutaneous condition, a benign tumor usually skin colored, most often affecting the face and upper trunk.

A trichoadenoma is a cutaneous condition characterized by a solitary, rapidly growing skin lesion ranging from 3 to 15mm in diameter.

Isthmicoma are a cutaneous condition characterized by flat, keratotic papules of the head and neck, skin lesions that are usually solitary.

Proliferating trichilemmal cysts are a cutaneous condition characterized by proliferations of squamous cells forming scroll-like structures.
Median raphe cysts are a cutaneous condition of the penis due to developmental defects near the glans.
Sarcoidosis involves the skin in about 25% of patients. The most common lesions are erythema nodosum, plaques, maculopapular eruptions, subcutaneous nodules, and lupus pernio. Treatment is not required, since the lesions usually resolve spontaneously in two to four weeks. Although it may be disfiguring, cutaneous sarcoidosis rarely causes major problems.
| This Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, cysts article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |