
A reserve currency is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international transactions, international investments and all aspects of the global economy. It is often considered a hard currency or safe-haven currency.

The 1997 Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid, and worries of a meltdown quickly subsided.
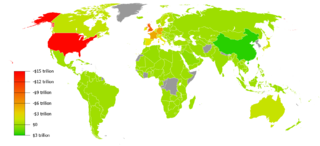
In international economics, the balance of payments of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. In other words, it is economic transactions between countries during a period of time. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.
In macroeconomics and international finance, a country's current account records the value of exports and imports of both goods and services and international transfers of capital. It is one of the two components of the balance of payments, the other being the capital account. Current account measures the nation's earnings and spendings abroad and it consists of the balance of trade, net primary income or factor income and net unilateral transfers, that have taken place over a given period of time. The current account balance is one of two major measures of a country's foreign trade. A current account surplus indicates that the value of a country's net foreign assets grew over the period in question, and a current account deficit indicates that it shrank. Both government and private payments are included in the calculation. It is called the current account because goods and services are generally consumed in the current period.

The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, and Australia and other countries, a total of 44 countries after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretton Woods system was the first example of a fully negotiated monetary order intended to govern monetary relations among independent states. The Bretton Woods system required countries to guarantee convertibility of their currencies into U.S. dollars to within 1% of fixed parity rates, with the dollar convertible to gold bullion for foreign governments and central banks at US$35 per troy ounce of fine gold. It also envisioned greater cooperation among countries in order to prevent future competitive devaluations, and thus established the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to monitor exchange rates and lend reserve currencies to nations with balance of payments deficits.
Petrocurrency is a word used with three distinct meanings, often confused:
- Dollars paid to oil-producing nations —a term invented in the 1970s meaning trading surpluses of oil-producing nations.
- Currencies of oil-producing nations which tend to rise in value against other currencies when the price of oil rises.
- Pricing of oil in US dollars: currencies used as a unit of account to price oil in the international market.

Nouriel Roubini is a Turkish-born Iranian-American economic consultant, economist, speaker and writer. He is a Professor Emeritus since 2021 at the Stern School of Business of New York University.
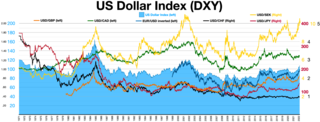
Strong dollar policy is United States economic policy based on the assumption that a "strong" exchange rate of the United States dollar is in the interests of the United States. In 1971, Treasury Secretary John Connally famously remarked how the US dollar was "our currency, but your problem," referring to how the US dollar was managed primarily for the US' interests despite it being the currency primarily used in global trade and global finance. A strong dollar is recognized to have many benefits but also potential downsides. Domestically in the US, the policy keeps inflation low, encourages foreign investment, and maintains the currency's role in the global financial system. Globally, a strong dollar is thought to be harmful for the rest of the world. In financial markets, the strength of the dollar is measured in the "DXY Index", an index which measures the exchange rate of the dollar relative to other major currencies.
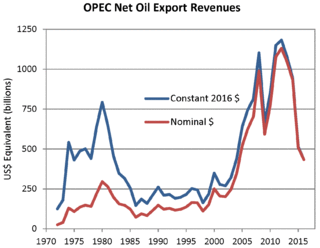
Petrodollar recycling is the international spending or investment of a country's revenues from petroleum exports ("petrodollars"). It generally refers to the phenomenon of major petroleum-exporting states, mainly the OPEC members plus Russia and Norway, earning more money from the export of crude oil than they could efficiently invest in their own economies. The resulting global interdependencies and financial flows, from oil producers back to oil consumers, can reach a scale of hundreds of billions of U.S. dollars per year – including a wide range of transactions in a variety of currencies, some pegged to the U.S. dollar and some not. These flows are heavily influenced by government-level decisions regarding international investment and aid, with important consequences for both global finance and petroleum politics. The phenomenon is most pronounced during periods when the price of oil is historically high.

David J. Rothkopf is an American foreign policy, national security and political affairs analyst and commentator. He is the founder and CEO of TRG Media and The Rothkopf Group, a columnist for The Daily Beast and a former member of the USA Today Board of Contributors. He is the author of ten books including Running the World: The Inside Story of the National Security Council and the Architects of American Power, National Insecurity: American Leadership in an Age of Fear, and most recently, Traitor: A History of American Betrayal from Benedict Arnold to Donald Trump. He is also the podcast host of Deep State Radio. Rothkopf also serves as a registered foreign agent of the United Arab Emirates.
The Triffin dilemma is the conflict of economic interests that arises between short-term domestic and long-term international objectives for countries whose currencies serve as global reserve currencies. This dilemma was identified in the 1960s by Belgian-American economist Robert Triffin. He noted that a country whose currency is the global reserve currency, held by other nations as foreign exchange (FX) reserves to support international trade, must somehow supply the world with its currency in order to fulfill world demand for these FX reserves. This supply function is nominally accomplished by international trade, with the country holding reserve currency status being required to run an inevitable trade deficit. After going off of the gold standard in 1971 and setting up the petrodollar system later in the 1970s, the United States accepted the burden of such an ongoing trade deficit in 1985 with its permanent transformation from a creditor to a debtor nation. The U.S. goods trade deficit is currently on the order of one trillion dollars per year. Such a continuing drain to the United States in its balance of trade leads to ongoing tension between its national trade policies and its global monetary policy to maintain the U.S. dollar as the current global reserve currency. Alternatives to international trade that address this tension include direct transfer of dollars via foreign aid and swap lines.
Modern monetary theory or modern money theory (MMT) is a heterodox macroeconomic theory that describes currency as a public monopoly and unemployment as evidence that a currency monopolist is overly restricting the supply of the financial assets needed to pay taxes and satisfy savings desires. According to MMT, governments do not need to worry about accumulating debt since they can pay interest by printing money. MMT argues that the primary risk once the economy reaches full employment is inflation, which acts as the only constraint on spending. MMT also argues that inflation can be controlled by increasing taxes on everyone, to reduce the spending capacity of the private sector.

Michael Hudson is an American economist, Professor of Economics at the University of Missouri–Kansas City and a researcher at the Levy Economics Institute at Bard College, former Wall Street analyst, political consultant, commentator and journalist. He is a contributor to The Hudson Report, a weekly economic and financial news podcast produced by Left Out.

Currency intervention, also known as foreign exchange market intervention or currency manipulation, is a monetary policy operation. It occurs when a government or central bank buys or sells foreign currency in exchange for its own domestic currency, generally with the intention of influencing the exchange rate and trade policy.

Lawrence 'Larry' G. McDonald is an author and CNBC contributor, currently founder of 'The Bear Traps Report', an investment newsletter focused on Political and Systemic Risk with actionable trade ideas and Macro perspective. Former Head of U.S. Macro Strategy at Societe Generale and former vice-president of distress debt and convertible securities trading at Lehman Brothers.

Currency war, also known as competitive devaluations, is a condition in international affairs where countries seek to gain a trade advantage over other countries by causing the exchange rate of their currency to fall in relation to other currencies. As the exchange rate of a country's currency falls, exports become more competitive in other countries, and imports into the country become more and more expensive. Both effects benefit the domestic industry, and thus employment, which receives a boost in demand from both domestic and foreign markets. However, the price increases for import goods are unpopular as they harm citizens' purchasing power; and when all countries adopt a similar strategy, it can lead to a general decline in international trade, harming all countries.

James G. Rickards is an American lawyer, investment banker, media commentator, and author on matters of finance and precious metals. He is the author of Currency Wars: The Making of the Next Global Crisis (2011) and six other books. He currently lives in Connecticut.
Tarun Khanna is an Indian-born American academic, author, and an economic strategist. He is currently the Jorge Paulo Lemann professor at Harvard Business School; where he is a member of the strategy group, and the director of Harvard University’s South Asia initiative since 2010.
The Currency War of 2009–2011 was an episode of competitive devaluation which became prominent in the financial press in September 2010. It involved states competing with each other in order to achieve a relatively low valuation for their own currency, so as to assist their domestic industry. Due to the Great Recession, the export sectors of many emerging economies experienced declining orders and from 2009, several states began or increased their levels of currency intervention. According to many analysts the currency war had largely fizzled out by mid-2011 although the war rhetoric persisted into the following year. In 2013, there were concerns of an outbreak of another currency war, this time between Japan and the Euro-zone.
Yukon Huang is a Chinese-American economist. He is a senior fellow and research associate in the Asia Program at the Carnegie Endowment in Washington, D.C. His areas of research include China's economic and political development and its impact in Asia and globally.













