
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material, a sash set in a frame in the opening; the sash and frame are also referred to as a window. Many glazed windows may be opened, to allow ventilation, or closed, to exclude inclement weather. Windows may have a latch or similar mechanism to lock the window shut or to hold it open by various amounts.
A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface in contact with a thermal mass of air. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space.

In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices.

Daylighting is the practice of placing windows, skylights, other openings, and reflective surfaces so that sunlight can provide effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy use. Energy savings can be achieved from the reduced use of artificial (electric) lighting or from passive solar heating. Artificial lighting energy use can be reduced by simply installing fewer electric lights where daylight is present or by automatically dimming/switching off electric lights in response to the presence of daylight – a process known as daylight harvesting.

Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. Daylighting is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings. Proper lighting can enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants.

The Walt Disney Concert Hall at 111 South Grand Avenue in downtown Los Angeles, California, is the fourth hall of the Los Angeles Music Center and was designed by Frank Gehry. It was opened on October 24, 2003. Bounded by Hope Street, Grand Avenue, and 1st and 2nd Streets, it seats 2,265 people and serves, among other purposes, as the home of the Los Angeles Philharmonic orchestra and the Los Angeles Master Chorale. The hall is a compromise between a vineyard-style seating configuration, like the Berliner Philharmonie by Hans Scharoun, and a classical shoebox design like the Vienna Musikverein or the Boston Symphony Hall.

Smart glass, also known as switchable glass, dynamic glass, and smart-tinting glass, is a type of glass that can change its reflective properties to prevent sunlight and heat from entering a building and to also provide privacy. Smart glass for building aims to provide more energy-efficient buildings by reducing the amount of solar heat that passes through glass windows.

Architectural lighting design is a field of work or study that is concerned with the design of lighting systems within the built environment, both interior and exterior. It can include manipulation and design of both daylight and electric light or both, to serve human needs.

Sustainable architecture is architecture that seeks to minimize the negative environmental impact of buildings through improved efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, development space and the ecosystem at large. Sustainable architecture uses a conscious approach to energy and ecological conservation in the design of the built environment.

A sunroom, also frequently called a solarium, is a room that permits abundant daylight and views of the landscape while sheltering from adverse weather. Sunroom and solarium have the same denotation: solarium is Latin for "place of sun[light]". Solaria of various forms have been erected throughout European history. Currently, the sunroom or solarium is popular in Europe, Canada, the United States, Australia, and New Zealand. Sunrooms may feature passive solar building design to heat and illuminate them.

The Eastgate Centre is a shopping centre and office block in central Harare, Zimbabwe, designed by Mick Pearce. Designed to be ventilated and cooled by entirely natural means, it was probably the first building in the world to use natural cooling to this level of sophistication. It opened in 1996 on Robert Mugabe Avenue and Second Street, and provides 5,600 m² of retail space, 26,000 m² of office space and parking for 450 cars.

A Zero-Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero-Energy (NZE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site or in other definitions by renewable energy sources offsite, using technology such as heat pumps, high efficiency windows and insulation, and solar panels.
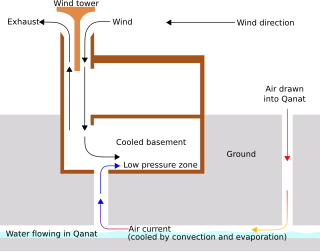
Passive cooling is a building design approach that focuses on heat gain control and heat dissipation in a building in order to improve the indoor thermal comfort with low or no energy consumption. This approach works either by preventing heat from entering the interior or by removing heat from the building.

Anidolic lighting systems use anidolic optical components to light rooms. Light redirected by these systems does not converge to a focal point or form an image, hence the name.

Solar air heating is a solar thermal technology in which the energy from the sun, insolation, is captured by an absorbing medium and used to heat air. Solar air heating is a renewable energy heating technology used to heat or condition air for buildings or process heat applications. It is typically the most cost-effective out of all the solar technologies, especially in commercial and industrial applications, and it addresses the largest usage of building energy in heating climates, which is space heating and industrial process heating.
The USC School of Architecture is the architecture school at the University of Southern California. Located in Los Angeles, California, it is one of the university's twenty-two professional schools, offering both undergraduate and graduate degrees in the fields of architecture, building science, landscape architecture and heritage conservation.

A skylight is a light-permitting structure or window, usually made of transparent or translucent glass, that forms all or part of the roof space of a building for daylighting and ventilation purposes.
Kenneth L. Haggard is an American architect, educator, and solar pioneer who has designed more than 300 buildings and seen more than 200 built. He is a licensed architect in California and Florida. He and his partner Polly Cooper were awarded the American Solar Energy Society Passive Solar Pioneer Award in 1996. They have been leaders in both passive solar architecture and the rediscovery of straw bale building.

In building engineering, a climate-adaptive building shell (CABS) is a facade or roof that interacts with the variability of its environment in a dynamic way. Conventional structures have static building envelopes and therefore cannot act in response to changing weather conditions and occupant requirements. Well-designed CABS have two main functions: they contribute to energy-saving for heating, cooling, ventilation, and lighting, and they induce a positive impact on the indoor environmental quality of buildings.

Ralph Lewis Knowles is an American professor emeritus of architecture and a leading theorist of solar access design. He created the concept of the "solar envelope" and championed solar access planning. The solar envelope has influenced many city design and planning documents. He is a fellow of the American Solar Energy Society and an ACSA Distinguished Professor. He received the prestigious AIA Medal for research in 1974.

















