
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American engineer, futurist, and inventor. He is known for his contributions to the design of the modern alternating current (AC) electricity supply system.

Graphology is the analysis of handwriting in an attempt to determine the writer's personality traits. Its methods and conclusions are not supported by scientific evidence, and as such it is considered to be a pseudoscience.

Wardenclyffe Tower (1901–1917), also known as the Tesla Tower, was an early experimental wireless transmission station designed and built by Nikola Tesla on Long Island in 1901–1902, located in the village of Shoreham, New York. Tesla intended to transmit messages, telephony, and even facsimile images across the Atlantic Ocean to England and to ships at sea based on his theories of using the Earth to conduct the signals. His decision to increase the scale of the facility and implement his ideas of wireless power transfer to better compete with Guglielmo Marconi's radio-based telegraph system was met with refusal to fund the changes by the project's primary backer, financier J. P. Morgan. Additional investment could not be found, and the project was abandoned in 1906, never to become operational.

Graz University of Technology is a public research university located in Styria, Austria. It was founded in 1811 by Archduke John of Austria and is the oldest science and technology research and educational institute in Austria. It currently comprises seven faculties and is a public university. It offers 19 bachelor's and 36 master's study programmes across all technology and natural sciences disciplines. Doctoral training is organised in 14 English-speaking doctoral schools. The university has more than 17,000 students, and around 1,900 students graduate every year. The Graz University of Technology and the University of Graz co-operate in teaching and research of natural sciences.

The Tesla Experimental Station was a laboratory in Colorado Springs, Colorado, USA built in 1899 by inventor Nikola Tesla and for his study of the use of high-voltage, high-frequency electricity in wireless power transmission. Tesla used it for only one year, until 1900, and it was torn down in 1904 to pay his outstanding debts.
Tesla Electric Light and Manufacturing Company was an electric lighting company in Rahway, New Jersey that operated from December 1884 through 1886.
Evan I. Schwartz is an American author who writes about history, innovation, tech, music, and media.

Robert Saudek was a Czech-born graphologist, diplomat, and writer of novels, stories, poems and plays. He had considerable influence on the content and standing of graphology worldwide. He also published numerous articles in many languages in periodicals as diverse as The Listener, Zeitschrift für Menschenkenntnis and the Journal of Social Psychology. He also founded the professional graphology society in the Netherlands. He also started two academic periodicals: one in Dutch and the other in English. Many graphologists worldwide today use Saudek’s work without knowing the origin.

The book Wizard, the Life and Times of Nikola Tesla is a biography of Nikola Tesla by Marc J. Seifer published in 1996.

The Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla is a book compiled and edited by Thomas Commerford Martin detailing the work of Nikola Tesla through 1893. The book is a comprehensive compilation of Tesla's early work with many illustrations.

Prodigal Genius: The Life of Nikola Tesla (ISBN 0914732331) is a 1944 book by John Joseph O'Neill detailing the life of Nikola Tesla. The book was also released in an Armed Services Edition for American overseas soldiers as book 684. The first printing was November, 1944.

Tesla's electro-mechanical oscillator is a steam-powered electric generator patented by Nikola Tesla in 1893. Later in life, Tesla claimed one version of the oscillator caused an earthquake in New York City in 1898, gaining it the colloquial title "Tesla's earthquake machine".
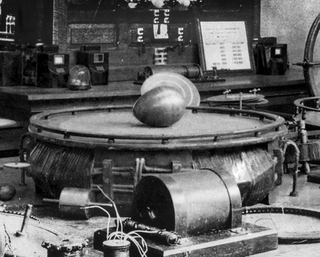
Tesla's Egg of Columbus was a device exhibited in the Westinghouse Electric display at the 1893 Chicago World's Columbian Exposition to explain the rotating magnetic field that drove the new alternating current induction motors designed by inventor Nikola Tesla by using that magnetic field to spin a copper egg on end.
Teleforce is a proposed defensive weapon by Nikola Tesla that accelerated pellets or slugs of material to a high velocity inside a vacuum chamber via electrostatic repulsion and then fired them out of aimed nozzles at intended targets. Tesla claimed to have conceived of it after studying the Van de Graaff generator. Tesla described the weapon as being able to be used against ground-based infantry or for anti-aircraft purposes.

The World Wireless System was a turn of the 20th century proposed telecommunications and electrical power delivery system designed by inventor Nikola Tesla based on his theories of using Earth and its atmosphere as electrical conductors. He claimed this system would allow for "the transmission of electric energy without wires" on a global scale as well as point-to-point wireless telecommunications and broadcasting. He made public statements citing two related methods to accomplish this from the mid-1890s on. By the end of 1900 he had convinced banker J. P. Morgan to finance construction of a wireless station based on his ideas intended to transmit messages across the Atlantic to England and to ships at sea. His decision to change the design to include wireless power transmission to better compete with Guglielmo Marconi's new radio based telegraph system was met with Morgan's refusal to fund the changes. The project was abandoned in 1906, never to become operational.

Martin Sekulić (1833–1905) was a mathematics and physics teacher from Karlovac, one of the few high-school professors who were members of the Croatian community of physicists at the time.
Benjamin Franklin Miessner was an American radio engineer and inventor. He is most known for his electronic organ, electronic piano, and other musical instruments. He was the inventor of the Cat's whisker detector.
Kenneth Malcolm Swezey (1904-1972) was an American journalist. He was a science writer living and working in New York City.












