
Pediatrics is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers patients until age 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, and some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word pediatrics and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from two Greek words: παῖς and ἰατρός. Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties.

Parenting or child rearing promotes and supports the physical, emotional, social, and intellectual development of a child from infancy to adulthood. Parenting refers to the intricacies of raising a child and not exclusively for a biological relationship.
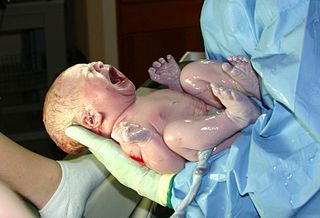
An infant is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term baby, meaning the very young offspring of human beings. The term may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants.
In psychology, temperament broadly refers to consistent individual differences in behavior that are biologically based and are relatively independent of learning, system of values and attitudes.
University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC) is the health sciences campus of the University of Mississippi and is located in Jackson, Mississippi, United States. UMMC, also referred to as the Medical Center, is the state's only academic medical center.

Thomas Berry Brazelton was an American pediatrician, author, and the developer of the Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS). Brazelton hosted the cable television program What Every Baby Knows, and wrote a syndicated newspaper column. He wrote more than two hundred scholarly papers and twenty-four books.

Attachment parenting (AP) is a parenting philosophy that proposes methods aiming to promote the attachment of parent and infant not only by maximal parental empathy and responsiveness but also by continuous bodily closeness and touch. The term attachment parenting was coined by the American pediatrician William Sears. There is no conclusive body of research that shows Sears' approach to be superior to "mainstream parenting".

Co-sleeping is a practice in which babies and young children sleep close to one or both parents, as opposed to in a separate room. Co-sleeping individuals sleep in sensory proximity to one another, where the individual senses the presence of others. This sensory proximity can either be triggered by touch, smell, taste, or noise. Therefore, the individuals can be a few centimeters away or on the other side of the room and still have an effect on the other. It is standard practice in many parts of the world, and is practiced by a significant minority in countries where cribs are also used.
William Penton Sears, also referred to as Dr. Bill, is an American pediatrician and the author or co-author of parenting books. Sears is a celebrity doctor, and has been a guest on various television talk shows. Sears is a proponent of the attachment parenting philosophy, and is most well known for authoring The Baby Book, which popularized that style of parenting.

A pacifier is a rubber, plastic, or silicone nipple substitute given to an infant to suckle upon between feedings to quiet its distress by satisfying the need to suck when it does not need to eat. Pacifiers normally have three parts, an elongated teat, a mouth shield, and a handle. The mouth shield is large enough to prevent the child from attempting to take the pacifier into its mouth, and so forecloses the danger that the child will swallow then choke on it.

On Becoming Baby Wise: Giving Your Infant the Gift of Nighttime Sleep is a Christianity-based infant management book written by Gary Ezzo and pediatrician Robert Bucknam in 1993. Baby Wise presents an infant care program which the authors say will cause babies to sleep through the night beginning between seven and nine weeks of age. It emphasizes parental control of the infant's sleep, play and feeding schedule rather than allowing the baby to decide when to eat, play and sleep.

Attachment in children is "a biological instinct in which proximity to an attachment figure is sought when the child senses or perceives threat or discomfort. Attachment behaviour anticipates a response by the attachment figure which will remove threat or discomfort". Attachment also describes the function of availability, which is the degree to which the authoritative figure is responsive to the child's needs and shares communication with them. Childhood attachment can define characteristics that will shape the child's sense of self, their forms of emotion-regulation, and how they carry out relationships with others. Attachment is found in all mammals to some degree, especially primates.

The Orphan Train Movement was a supervised welfare program that transported children from crowded Eastern cities of the United States to foster homes located largely in rural areas of the Midwest. The orphan trains operated between 1854 and 1929, relocating about 250,000 children. The co-founders of the Orphan Train movement claimed that these children were orphaned, abandoned, abused, or homeless, but this was not always true. They were mostly the children of new immigrants and the children of the poor and destitute families living in these cities. Criticisms include ineffective screening of caretakers, insufficient follow-ups on placements, and that many children were used as strictly slave farm labor.

Maternal deprivation is a scientific term summarising the early work of psychiatrist and psychoanalyst John Bowlby on the effects of separating infants and young children from their mother although the effect of loss of the mother on the developing child had been considered earlier by Freud and other theorists. Bowlby's work on delinquent and affectionless children and the effects of hospital and institutional care led to his being commissioned to write the World Health Organization's report on the mental health of homeless children in post-war Europe whilst he was head of the Department for Children and Parents at the Tavistock Clinic in London after World War II. The result was the monograph Maternal Care and Mental Health published in 1951, which sets out the maternal deprivation hypothesis.

Mt. Washington Pediatric Hospital is a United States 102-bed non-profit children's hospital set in the scenic neighborhood of Mt. Washington in Baltimore, Maryland, that provides long-term care for children with complex health problems. MWPH is jointly owned by Johns Hopkins Medical System and University of Maryland Medical System. Funded by patient revenue and private charitable donations, Mt. Washington Pediatric Hospital is a comprehensive sub-acute care facility for children from birth to young adult; MWPH provides transitional and support care for a variety of conditions, including premature birth, serious and chronic illness, traumatic injury, ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, childhood obesity, diabetes, feeding problems, among others. Mt. Washington Pediatric Hospital also has a unit at Prince George's Hospital Center in Cheverly, Maryland. MWPH accreditations include Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities and The Joint Commission.
Infant sleep training refers to a number of different regimens parents employ to adjust their child's sleep behaviors.

Lendon Howard Smith was an American Ob/Gyn, pediatrician, author, and television personality. He was notable for his advice on parenting and advocating children's health and eating issues. He was known to fans as "The Children's Doctor" for his expertise on the issues and an outspoken proponent of the use of vitamins for children.
Separation anxiety disorder (SAD) is an anxiety disorder in which an individual experiences excessive anxiety regarding separation from home and/or from people to whom the individual has a strong emotional attachment. Separation anxiety is a natural part of the developmental process. It is most common in infants and little children, typically between the ages of six to seven months to three years, although it may pathologically manifest itself in older children, adolescents and adults. Unlike SAD, normal separation anxiety indicates healthy advancements in a child's cognitive maturation and should not be considered a developing behavioral problem.
Newborn care and safety are the activities and precautions recommended for new parents or caregivers. It is also an educational goal of many hospitals and birthing centers when it's time to bring their infant home.

Frank Spooner Churchill was an American paediatrician who took a special interest in infant feeding. A graduate of Harvard University, as a paediatrician Churchill took a particular interest in public health, early child health and in breastfeeding. Much of his research centered around the untoward effects of lack of breast milk or inadequate modified milk.












