

The Margraviate of Baden-Hachberg was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire, in the upper Rhine valley, which existed from 1212 to 1415.


The Margraviate of Baden-Hachberg was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire, in the upper Rhine valley, which existed from 1212 to 1415.
The Margraviate came into being around 1212 by splitting off from the Margraviate of Baden. Henry I, Margrave of Baden-Hachberg and his brother Herman V, Margrave of Baden-Baden shared the inheritance of their father Herman IV, Margrave of Baden, who had died in 1190. The center of the Margraviate was the stronghold on the Hochburg (Hachberg) near Emmendingen. In the course of the 13th century, the Hachberg line was able to assert itself against the competition from the Counts of Freiburg in the area between the Black Forest and the Rhine (Breisgau). The Margraviate of Baden-Hachberg existed as an independent territory until 1415, when Otto II von Hachberg sold his property to Bernard I, Margrave of Baden-Baden.
The Margraviate of Baden-Hachberg was briefly recreated between 1584 and 1590, when it was separated from Margraviate of Baden-Durlach and ruled by the Margrave's second son James III, Margrave of Baden-Hachberg until his death in 1590, after which it was reunited with Baden-Durlach.

The Hochburg is a castle ruin situated between the city of Emmendingen and the village of Sexau in the region of Baden, located in the southwest of Germany. It was presumably built in the 11th century and was originally known as castle Hachberg. The line of nobles known as the Margraves of Baden-Hachberg most likely derive their name from this castle and before it was razed by the French it was the second largest fortification in Baden.

The Margraviate of Baden was a historical territory of the Holy Roman Empire. Spread along the right banks of the Upper Rhine in south-western Germany, it was named a margraviate in 1112 and existed until 1535, when it was split into the two margraviates of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden. The two parts were reunited in 1771 under Margrave Charles Frederick, even if the three parts of the state maintained their distinct seats to the Reichstag. The restored Margraviate of Baden was elevated to the status of electorate in 1803. In 1806, the Electorate of Baden, receiving territorial additions, became the Grand Duchy of Baden. The rulers of Baden, known as the House of Baden, were a line of the Swabian House of Zähringen.

Bernard I of Baden was Margrave of the Margraviate of Baden from 1391 to 1431.

Charles II, Margrave of Baden-Durlach, nicknamed Charles with the bag, governed the Margravate of Baden-Durlach from 1552 to 1577. On 1 June 1556 Charles issued a new Church Order, which made Lutheranism the official religion in Baden-Durlach.

George Frederick of Baden-Durlach was Margrave of Baden-Durlach from 1604 until his abdication in 1622. He also ruled Baden-Baden.
The Margraviate of Landsberg was a march of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 13th to the 14th century under the rule of the Wettin dynasty. It was named after Landsberg Castle in present-day Saxony-Anhalt.

The March of Verona and Aquileia was a vast march of the Holy Roman Empire in the northeastern Italian region during the Middle Ages, centered on the cities of Verona and Aquileia. Seized by King Otto I of Germany in 952, it was held by the Dukes of Bavaria; from 976 in personal union with the Duchy of Carinthia. The margravial regime ended with the advent of the Lombard League in 1167.

The Margraviate of Baden-Durlach was an early modern territory of the Holy Roman Empire, in the upper Rhine valley, which existed from 1535 to 1771. It was formed when the Margraviate of Baden was split between the sons of Margrave Christopher I and was named for its capital, Durlach. The other half of the territory became the Margraviate of Baden-Baden, located between the two halves of Baden-Durlach. Baden-Durlach became Lutheran during the Protestant Reformation, unlike Baden-Baden, which remained Catholic. Baden-Durlach occupied Baden-Baden from 1594 to 1622, but was driven out after being defeated at the Battle of Wimpfen, during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). The territory was ravaged during the Nine Years' War (1688–1697). Following the extinction of the Baden-Baden line in 1771, the Baden-Durlach inherited their territories and reunited the Margraviate of Baden. The reunified territory was caught up in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, emerging in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Baden.

Margrave Philip I of Baden took over the administration of his father's possessions Baden (Baden-Baden), Durlach, Pforzheim and Altensteig and parts of Eberstein, Lahr and Mahlberg in 1515 and ruled as governor until he inherited the territories in 1527. From 1524 till 1527, he also acted as an imperial governor in the second Imperial Government.
His official title was Margrave of Baden-Sponheim.
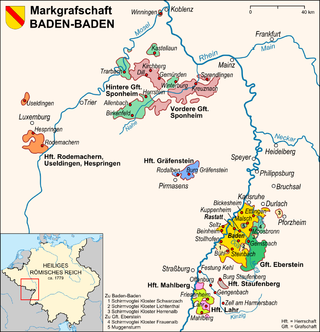
The Margraviate of Baden-Baden was an early modern southwest German territory within the Holy Roman Empire. It was created in 1535 along with the Margraviate of Baden-Durlach as a result of the division of the Margraviate of Baden. Its territory consisted of a core area on the middle stretch of the Upper Rhine around the capital city of Baden, as well as lordships on the Moselle and Nahe.
Countess Palatine Anna of Veldenz was Margravine of Baden-Durlach by marriage to Charles II, Margrave of Baden-Durlach, and co-regent of the Margraviate of Baden-Durlach during the minority of her son Ernest Frederick from 1577 to 1584.

Ernest Frederick of Baden-Durlach ruled the northern part of the Margraviate of Baden-Durlach. He came to power when he came of age in 1584. He founded the first Gymnasium Illustre in the margraviate. Ernst Friedrich, who had a strict Lutheran upbringing, started a reconciliation between Lutheranism and Calvinism with the publication of the Staffort Book in 1599 His occupation of Upper Baden caused serious conflicts – even with the Emperor – the consequences of which damaged Lower Baden and ultimately also led to losses of territory.

Margrave James III of Baden-Hachberg was margrave of Baden-Hachberg from 1584 to 1590 and resided at Emmendingen. He converted, in 1590, from Lutheranism to the Roman Catholic confession, causing some political turmoil.

Margrave Rudolf III of Hachberg-Sausenberg (1343–1428) was the son of Margrave Rudolf II of Hachberg-Sausenberg and Catherine of Thierstein. He inherited Hachberg-Sausenberg when his father died in 1352. As he was a minor at the time, his uncle Otto I acted as regent. When Rudolf II came of age, he and Otto I ruled jointly, until Otto's death in 1384. Rudolf III is considered the most important of the Margraves of Hachberg-Sausenberg.

Margrave Rudolf I of Hachberg-Sausenberg (d.1313) was the son of Margrave Henry II of Hachberg and Anne of Üsenberg. He married in 1298 or 1299 to Agnes, the heiress of Otto of Rötteln. In 1306 he founded the side-line Hachberg-Sausenberg at Sausenburg Castle, a castle which the Margraves of Hachberg had built in 1240 on top of Mount Sausenberg. His elder brother Henry III continued the main Baden-Hachberg line at Hochburg castle in Emmendingen.